Youth sports leagues occupy unique positions in community life, serving as gathering places where families connect, volunteer opportunities where adults contribute meaningfully, and developmental environments where children learn lessons extending far beyond athletic fields. Research consistently demonstrates that youth sports participation correlates with numerous positive outcomes including improved physical health and fitness habits, enhanced academic performance and school engagement, stronger social skills and peer relationships, increased self-confidence and resilience, and reduced behavioral problems and substance abuse risk.
However, these benefits materialize only when youth sports programs are organized thoughtfully with age-appropriate structures, volunteer leadership trained in effective coaching principles, balanced competitive and developmental philosophies, and inclusive cultures ensuring all participants feel valued regardless of athletic ability. Communities implementing best practices create leagues that retain participants across multiple seasons, develop not just athletic skills but character and life skills, engage families as partners rather than just spectators, and build reputations attracting new participants and volunteer support.
The landscape of youth sports has evolved significantly over recent decades. Where previous generations experienced primarily informal neighborhood pickup games, today’s youth increasingly participate in structured leagues with formal registration, scheduled practices and competitions, trained volunteer coaches, and organizational oversight. This evolution brings both opportunities and challenges—opportunities to provide higher-quality instruction and safety oversight, but challenges around cost barriers, over-competition, and parental pressure that can undermine developmental goals when leagues lose sight of youth-centered principles.

The Purpose and Benefits of Youth Sports Leagues
Understanding the fundamental purposes youth sports leagues serve helps organizations design programs aligned with developmental needs rather than merely replicating professional sports models inappropriate for children.
Physical Development and Lifelong Health Foundations
Youth sports leagues introduce children to structured physical activity during critical developmental windows when motor skills, coordination, and athletic foundations form. Well-designed programs teach fundamental movement patterns—running, jumping, throwing, catching—that support all athletic activities while reducing injury risk through proper technique development.
Building Athletic Foundations: Ages 5-10 represent optimal periods for developing basic motor skills and movement literacy. Youth leagues emphasizing skill development over competitive outcomes during these years create athletic foundations supporting future success across all sports. Children who master fundamental movements through varied youth sports experiences typically outperform early-specializers who focus narrowly on single sports before developing broad athletic bases.
Establishing Healthy Habits: Perhaps more importantly than immediate athletic development, youth sports leagues establish patterns and habits influencing health throughout entire lifespans. Children who participate regularly in organized sports develop positive associations with physical activity, understanding that movement can be enjoyable rather than merely obligatory. These early experiences significantly predict adult exercise habits and lifelong health outcomes.
Preventing Childhood Obesity: With childhood obesity rates tripling over recent decades, youth sports leagues provide crucial opportunities for regular vigorous physical activity. The structured nature of league participation—scheduled practices and games requiring attendance—creates accountability supporting consistent activity levels that unstructured free play often fails to provide in increasingly sedentary modern environments.
Social and Emotional Development
Youth sports create unique social contexts where children develop interpersonal skills, emotional regulation, and character traits difficult to cultivate through other childhood experiences.
Teamwork and Cooperation: Sports require children to coordinate with teammates toward shared goals, understanding that individual success depends on collective effort. They learn to trust teammates, communicate effectively, and subordinate personal desires when team needs require different contributions. These teamwork experiences provide practical contexts for developing collaboration skills that schools emphasize but often struggle to teach effectively.
Handling Success and Disappointment: Sports competitions create regular experiences with both victory and defeat in low-stakes environments where children can learn to manage emotions constructively. Winning gracefully without excessive boasting, losing with dignity rather than tantrums, and maintaining effort despite setbacks represent crucial emotional regulation skills that youth sports naturally teach when coaches emphasize appropriate responses.
Building Confidence Through Competence: As children develop skills and see tangible improvement through practice and coaching, they build self-efficacy—belief in their ability to accomplish goals through effort. Sports provide clear, immediate feedback about skill development, allowing children to recognize their own growth and understand that persistent practice produces measurable results.

Character Development and Life Skills
Beyond physical and social development, youth sports provide contexts for teaching character traits and life skills that influence success throughout entire lifespans.
Discipline and Work Ethic: Regular practices requiring attendance, drills demanding repetition, and competitive situations requiring preparation teach children that achievement requires consistent effort over time. They learn to do difficult things even when they don’t feel like it, delaying gratification for longer-term goals—executive function skills predicting academic and career success far better than raw intelligence.
Handling Authority and Following Rules: Sports require respecting coaches’ authority, following referees’ decisions even when disagreeing, and adhering to rule structures even when convenient to ignore them. These experiences help children understand appropriate responses to authority figures and rule structures they’ll encounter throughout life—in classrooms, workplaces, and society generally.
Goal-Setting and Improvement Focus: Effective coaches help athletes set specific, measurable improvement goals—reducing lap times, increasing free throw percentages, mastering specific skills. This goal-setting process teaches children how to identify targets, break large goals into manageable steps, track progress objectively, and adjust approaches when initial strategies prove ineffective—metacognitive skills supporting all forms of achievement.
Resilience and Perseverance: Sports naturally involve challenges, setbacks, and failures—missed shots, lost games, injuries, performance slumps. Learning to respond to adversity constructively rather than quitting when difficulties arise represents perhaps the most valuable lesson youth sports provide. Children who learn through sports that temporary setbacks don’t define them and that persistent effort overcomes obstacles carry this resilience throughout their lives.
Types of Youth Sports League Structures
Youth sports leagues operate under various organizational models, each offering distinct advantages and serving different community needs and developmental philosophies.
Recreational Leagues: Participation and Development Focus
Recreational leagues prioritize broad participation, skill development, and enjoyment over competitive outcomes. These programs typically ensure every participant receives substantial playing time regardless of ability, balance teams to maintain competitive parity, emphasize skill instruction and player development, minimize travel requirements focusing on local competition, and keep costs low to maximize accessibility.
Ideal For: Children ages 4-12 beginning sports participation, families seeking low-commitment introductory experiences, communities prioritizing inclusive access over elite development, and athletes participating in multiple sports across different seasons.
Organizational Characteristics: Recreational leagues typically operate through municipal parks and recreation departments, community centers or YMCA/YWCA organizations, school district community education programs, or volunteer-run neighborhood associations. Seasons generally last 6-10 weeks with one or two weekly practices and weekly games. Registration fees remain modest—typically $50-150 per season—to avoid excluding families based on cost.
Recognition Approaches: Recreational leagues typically emphasize participation recognition ensuring all athletes feel celebrated. End-of-season awards often include participation medals or ribbons for all players, fun team awards highlighting personality and effort, basic skill improvement acknowledgments, and sportsmanship recognition rather than purely competitive achievements. The goal is creating positive associations with sports participation rather than identifying winners and losers among young children.
Competitive Travel Leagues: Advanced Skill Development
Competitive travel leagues serve higher-skilled athletes seeking more intensive instruction, stronger competition, and potential pathways toward high school and college athletics. These programs typically require tryouts with selective team formation, significant family commitments including frequent travel for competitions, higher registration costs covering enhanced coaching and travel expenses, year-round or extended season schedules, and intensive training focusing on sport-specific skill development.
Ideal For: Athletes ages 10+ demonstrating strong interest and ability in specific sports, families willing to make significant time and financial commitments, children seeking preparation for high school varsity competition, and athletes pursuing potential college athletic opportunities.
Organizational Characteristics: Competitive leagues typically operate through private sports organizations, independent club programs, high school feeder systems, or sport-specific governing bodies. Seasons often extend 6-9 months with multiple weekly practices, weekend tournaments requiring regional travel, and substantial coaching from paid professionals or highly trained volunteers. Registration costs typically range $500-3,000+ annually depending on travel requirements and program quality.
Recognition Approaches: Competitive programs typically emphasize achievement-based recognition acknowledging statistical leaders, tournament performance, skill testing results, and competitive success. Many programs implement comprehensive digital recognition systems showcasing player achievements, team accomplishments, and program history—creating visible celebration that motivates continued excellence while building program identity.
House Leagues: Community-Based Competition
House leagues represent middle ground between purely recreational and competitive travel programs. Operating within single communities or organizations, these leagues create internal competition without extensive travel while offering more structured skill development than basic recreational programs.
Characteristics: Multiple teams form from registration pools within single organizations, regular season schedules with playoffs and championships, balanced teams ensuring competitive parity, more structured practices emphasizing skill development, and moderate registration costs between recreational and competitive programs.
Advantages: House leagues provide competitive experiences without travel burdens and costs, create natural social connections since participants typically attend same schools, enable flexible commitment levels accommodating varied family schedules, and build community identity through recognized local programs.
School-Affiliated Youth Programs
Some communities operate youth sports leagues through school district affiliations, creating natural feeder systems for middle and high school athletics while leveraging school facilities, coaching staff connections, and existing administrative infrastructure.
Benefits: School affiliation provides facility access reducing rental costs, creates clear progression pathways from youth through high school programs, enables coordination between youth coaches and high school staff ensuring consistent skill development, and builds school community identity from earliest ages.
Considerations: School affiliation sometimes creates perception of exclusivity favoring eventual varsity athletes, may involve conflicts between youth program needs and school priority scheduling, and requires careful policies preventing inappropriate early recruitment or inappropriate pressure on young athletes.
Organizational Best Practices for Youth Sports Leagues
Successful youth sports leagues share common organizational characteristics distinguishing thriving programs from struggling operations that fail to serve participants effectively.
Age-Appropriate Program Design
Developmental appropriateness represents the foundation of effective youth sports programming. Programs must align with children’s physical, cognitive, and emotional capabilities at different ages rather than simply scaling down adult sports models.
Ages 4-6: Introduction and Fundamental Skills
Programs for the youngest athletes should emphasize fun and fundamental movement over sport-specific skills or competitive outcomes. Appropriate activities include basic motor skill development through varied movement games, extremely short games or scrimmages (15-20 minutes maximum), minimal standing or waiting with constant activity, and simple rules focusing on basic concepts rather than complex regulations.
Structure should involve combined practice and games without separate skill sessions, small-sided games maximizing touches and participation, and mixed-gender teams with flexible positioning allowing all children to experience different roles. Recognition should emphasize participation and effort universally with no competitive awards distinguishing performance levels among such young children.
Ages 7-9: Skill Development and Beginning Competition
Middle elementary ages can handle increased structure while still prioritizing skill development over competitive outcomes. Appropriate programming includes dedicated practice time teaching sport-specific fundamentals, introduction of basic tactics and strategies, short games or matches with clear rules, and beginning competitive elements like standings or playoffs.
However, playing time should remain relatively equal ensuring all participants receive substantial game experience, score differentials shouldn’t be overemphasized, and recognition should balance competitive acknowledgment for top performers with comprehensive participation recognition ensuring all athletes feel valued.
Ages 10-12: Competitive Introduction with Development Focus
Late elementary and middle school athletes can handle more competitive structures while still requiring developmental focus over pure outcome emphasis. Appropriate elements include regular practices with structured skill instruction, competitive games and tournaments with standings and playoffs, some playing time differentiation based on performance, and introduction of specialized positions matching strengths.
Recognition can include performance-based awards while maintaining inclusive elements ensuring developing athletes continue feeling valued. Programs should emphasize improvement and development alongside competitive success, recognizing that physical development occurs at dramatically different rates requiring patience with late bloomers who may eventually surpass early-maturing athletes.
Ages 13+: Advanced Competition and Specialization
Adolescent athletes capable of higher-level thinking and having developed more consistent physical capabilities can handle structures more closely resembling older competitive models. Programs may involve intensive practices emphasizing advanced skills, competitive games with full rule application, playing time differentiation based on merit, and position specialization based on demonstrated strengths.
However, even competitive adolescent programs should avoid complete early specialization, maintain appropriate perspective about relative importance of athletics, and ensure recognition extends beyond just top performers to include character, improvement, and team contribution acknowledgment.

Volunteer Recruitment, Training, and Support
Youth sports leagues typically depend heavily on volunteer coaches and administrators. Program quality correlates directly with how effectively organizations recruit, train, and support these volunteers.
Effective Recruitment Approaches
Successful programs recruit volunteers through direct personal outreach to parents of registered athletes, clear communication about time commitments and expectations, emphasis on training and support provided to volunteers without prior experience, and recognition celebrating volunteer contributions to programs and communities.
Many parents assume coaching requires extensive sports expertise they lack. Programs should explicitly communicate that enthusiasm and willingness to learn matter more than prior coaching experience, training and resources will support volunteer development, and multiple roles exist beyond head coaching including assistant coaches, team parents, and administrative support.
Comprehensive Training Programs
All volunteers should receive training addressing sport-specific fundamentals and age-appropriate instruction methods, child development and age-appropriate expectations, positive coaching philosophies emphasizing development over winning, safety protocols including concussion awareness and injury prevention, appropriate behavior and communication with children, parents, and officials, and organizational policies and administrative requirements.
Organizations should provide ongoing support beyond initial training through experienced mentor coaches supporting new volunteers, ready access to organizational leadership for questions or concerns, regular coaching meetings sharing effective practices, and resources including practice plans, skill progression frameworks, and drill libraries.
Volunteer Recognition and Retention
Volunteers devoting significant time to youth sports deserve genuine recognition beyond perfunctory thank-yous. Effective appreciation includes public acknowledgment through newsletters, social media, and digital recognition displays, awards celebrating tenure and contribution levels, social events honoring volunteers and building community, and soliciting input ensuring volunteers feel valued partners rather than merely free labor.
Financial Sustainability and Accessibility
Youth sports leagues must balance financial sustainability with accessibility, ensuring programs remain affordable while generating revenue supporting quality operations.
Registration Fee Structures
Registration fees represent primary funding for most youth sports leagues. Fee structures should account for facility rental and equipment costs, referee and official expenses, insurance coverage, volunteer training and support materials, basic recognition and awards, and modest reserves for unexpected expenses or equipment replacement.
However, fees must remain accessible to diverse families. Tiered structures allowing families to choose service levels, scholarship programs ensuring cost doesn’t exclude participants, payment plans spreading costs across season length, and family discounts for multiple participating siblings help maintain accessibility while covering necessary expenses.
Supplemental Fundraising
Most leagues supplement registration fees through additional fundraising including booster club support from parent organizations, local business sponsorships funding teams or equipment, concession sales during competitions, special events like tournaments or camps, and merchandise sales including team apparel and equipment.
Effective fundraising communicates specific funding needs and how resources will be used, recognizes contributors publicly, diversifies revenue sources rather than over-relying on single approaches, and maintains transparency about financial operations building trust with families and community supporters.
Managing Costs to Maintain Accessibility
Beyond generating revenue, leagues should actively manage costs including negotiating facility access through school district partnerships or municipal agreements, purchasing equipment in bulk through league coordination rather than individual team procurement, sharing administrative costs across multiple programs within organizations, and eliminating unnecessary expenses that don’t directly benefit participant experiences.
Recognition Systems That Motivate and Inspire Young Athletes
Recognition represents one of the most powerful tools youth sports leagues possess for motivating continued participation, celebrating diverse contributions, and building positive program cultures.
Balancing Participation and Achievement Recognition
Youth sports recognition must balance celebrating excellence with ensuring all participants feel valued regardless of athletic ability or competitive outcomes.
Developmental Stage Considerations
For young children (ages 4-8), recognition should emphasize universal participation ensuring every child receives acknowledgment, fun awards highlighting personality and effort, basic skill development celebration without competitive comparison, and sportsmanship and character recognition modeling desired behaviors.
Middle elementary athletes (ages 9-12) benefit from combined recognition including some performance-based awards for competitive achievement, improvement awards celebrating development regardless of absolute ability, character and sportsmanship recognition, and creative awards ensuring all participants receive some form of celebration.
Older athletes (ages 13+) can handle predominantly achievement-based recognition while still benefiting from diverse award categories ensuring recognition extends beyond just top performers to include leadership and character acknowledgment, improvement and development recognition, role player and team contribution awards, and specialized recognition for different position groups or skill categories.

Creating Visible, Lasting Recognition
Traditional youth sports recognition—paper certificates tucked in folders, trophies collecting dust on shelves, or brief ceremony acknowledgments forgotten within weeks—provides limited ongoing motivational value. Modern recognition approaches extend visibility and impact far beyond single moments.
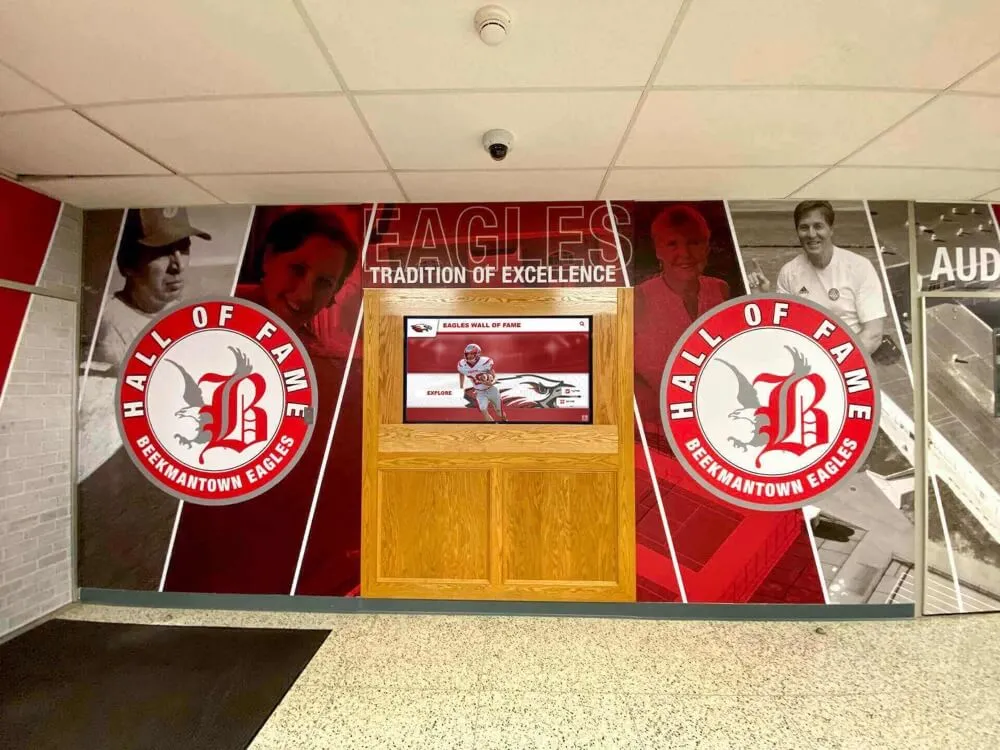
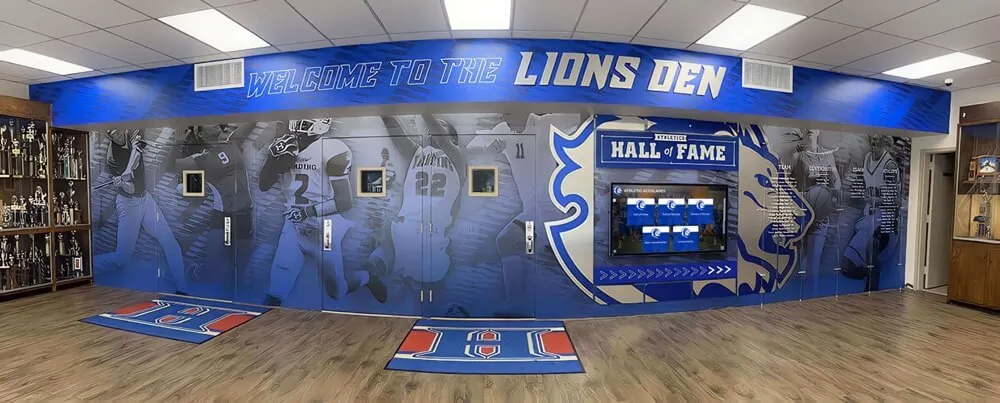
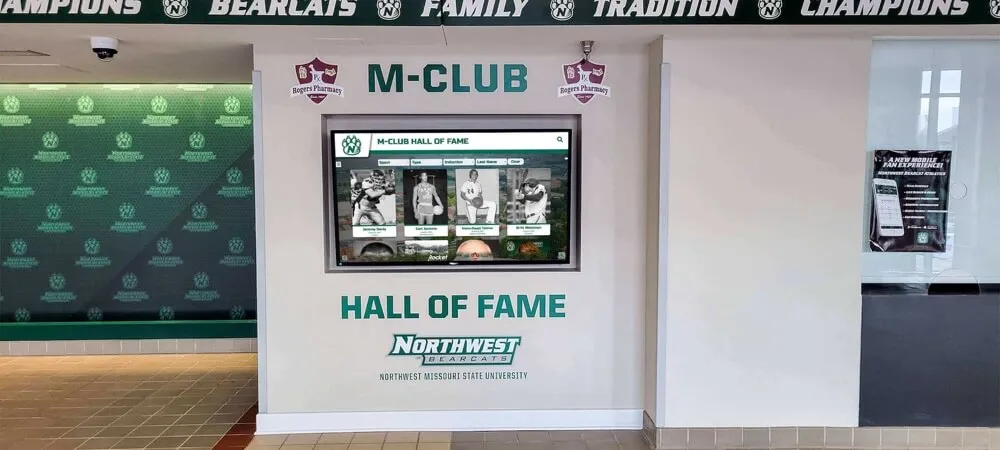
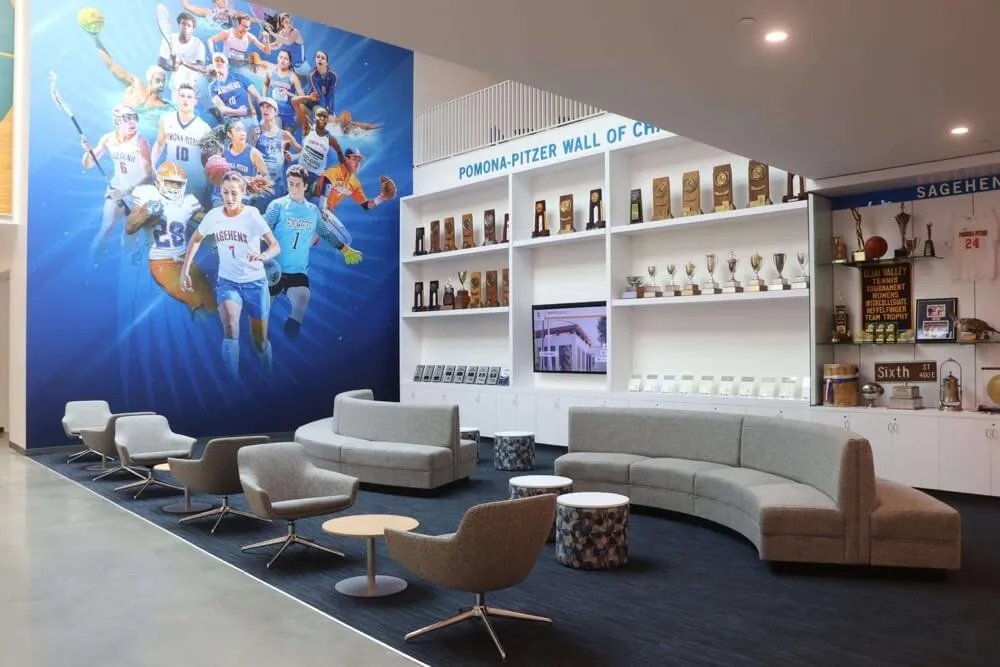
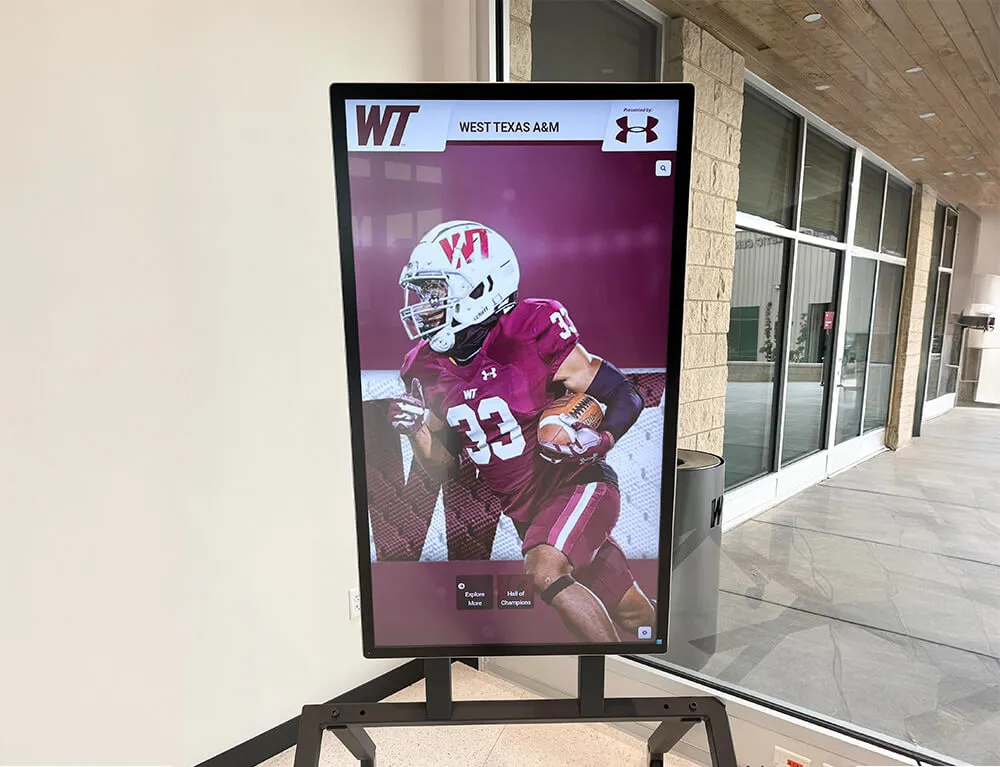
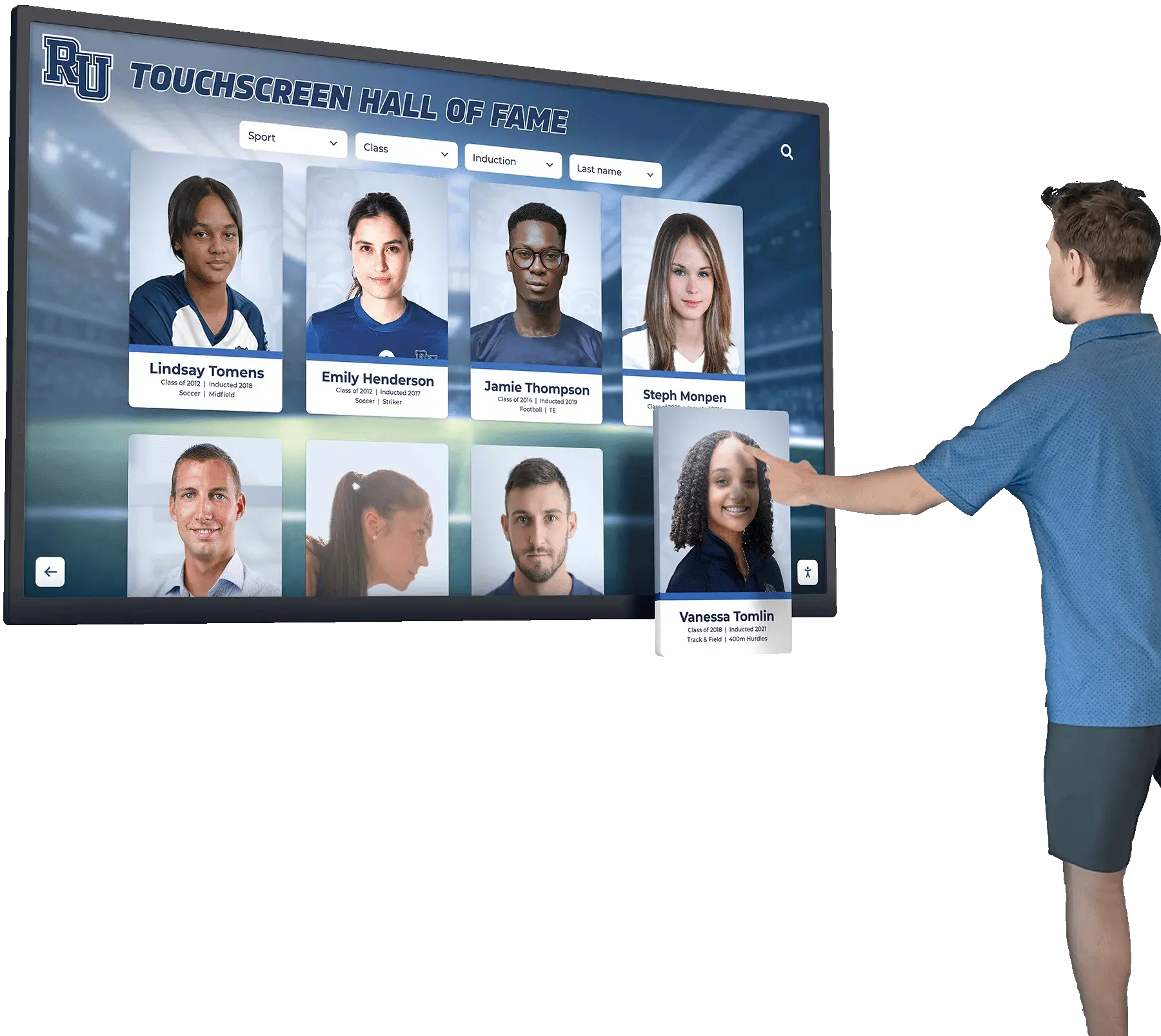
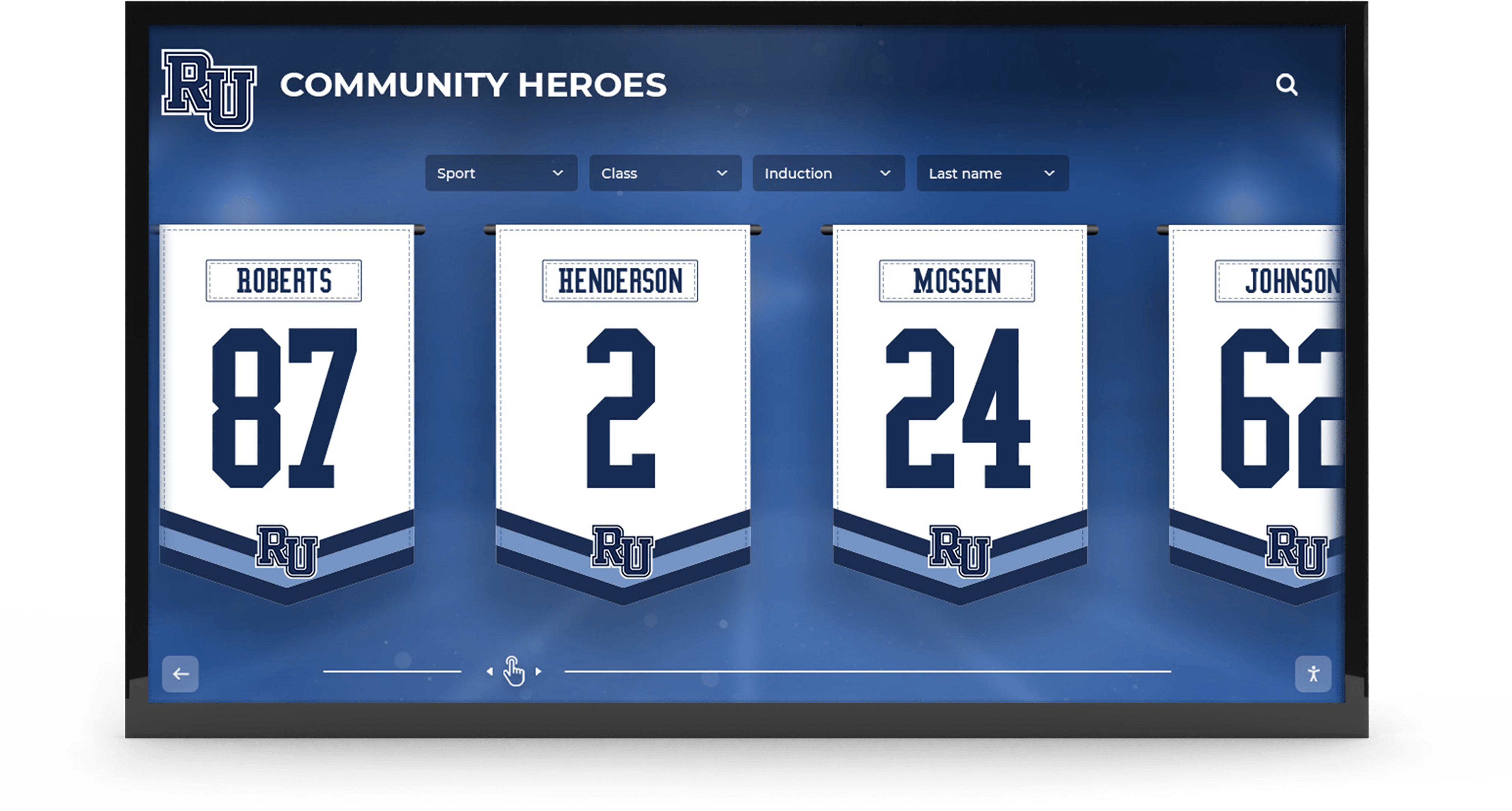
Digital Recognition Platforms for Youth Sports
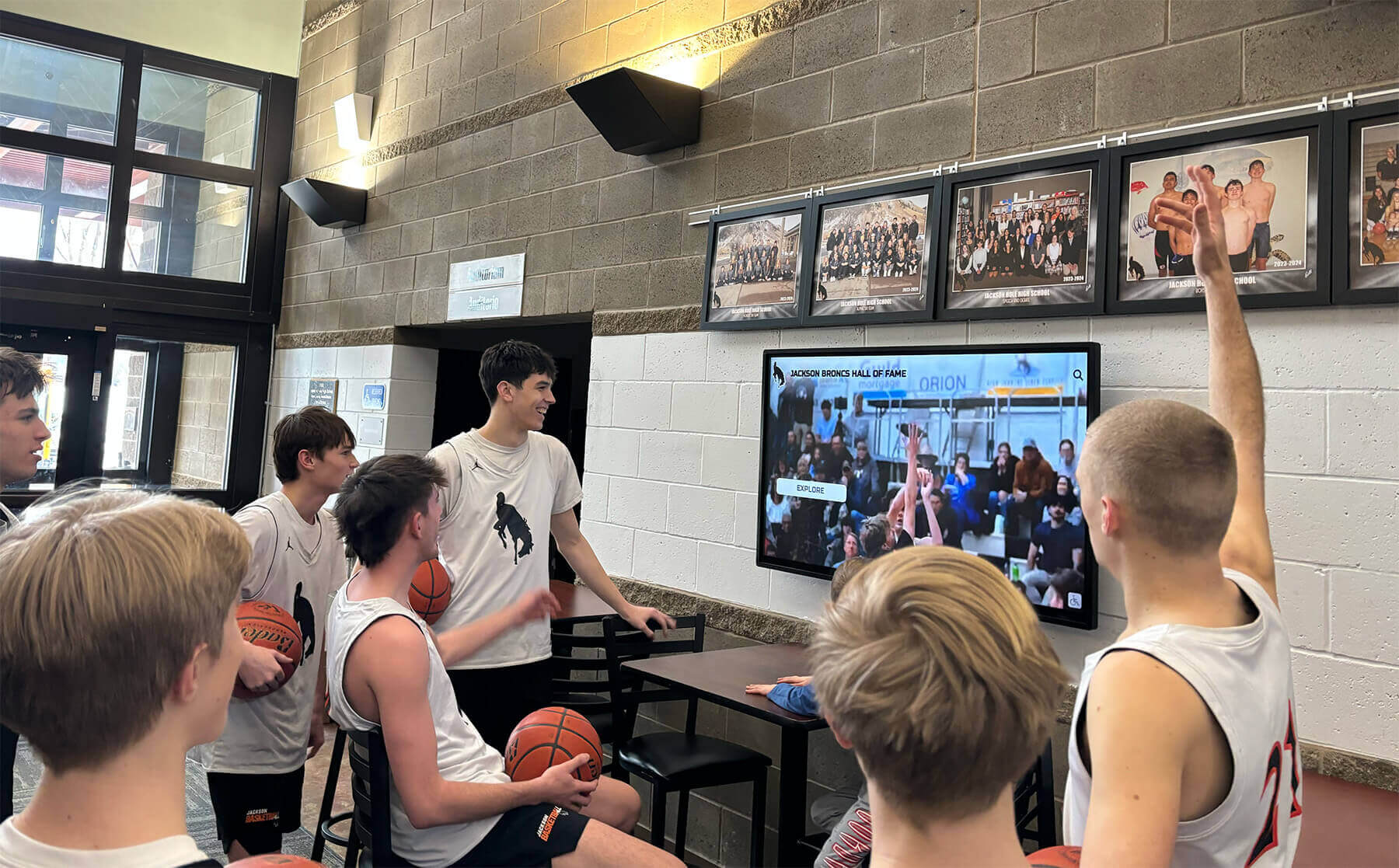
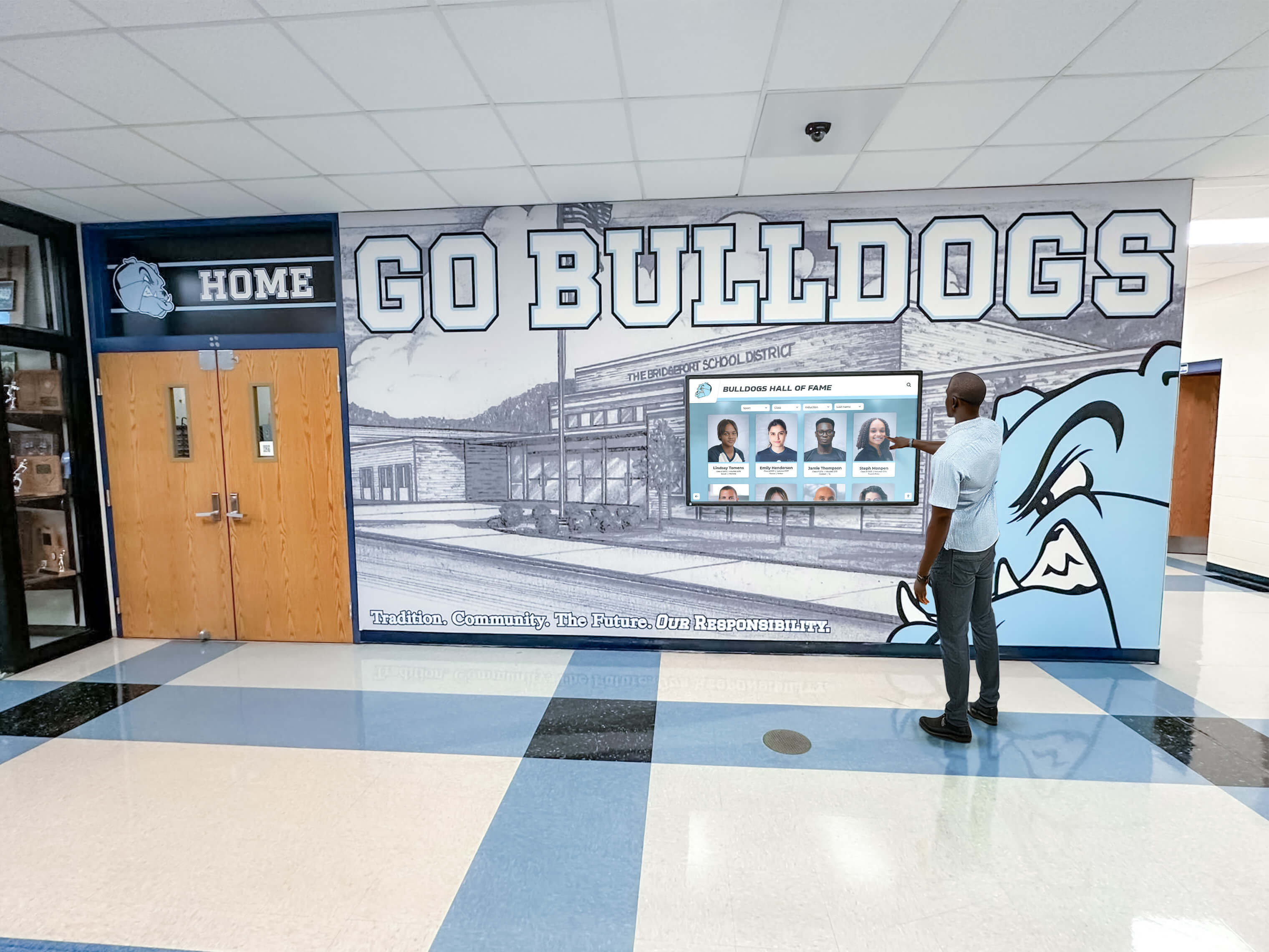
Forward-thinking youth sports organizations increasingly implement digital recognition systems showcasing athlete achievements, team accomplishments, and program history through interactive displays positioned in athletic facilities, community centers where leagues operate, school lobbies for school-affiliated programs, or recreation center entrances serving league headquarters.
These digital platforms provide capabilities traditional approaches cannot match including unlimited recognition capacity without physical space constraints, instant updates ensuring recognition remains current throughout seasons, rich multimedia profiles featuring photos, statistics, and achievement details, interactive exploration engaging athletes and families actively, web accessibility enabling sharing with extended family and community, and historical archives building comprehensive program documentation.
Content to Include in Youth Sports Recognition
Effective recognition profiles should showcase individual athlete achievements including statistical leaders, improvement awards, character recognition, and all-star selections; team accomplishments including championships, tournament results, and season records; coach recognition celebrating volunteer contributions; program milestones documenting league history and development; and participant contributions from all program levels ensuring diverse recognition across ability spectrums.
Strategic Recognition Placement
Position recognition displays where athletes, families, and community members naturally gather including entrance areas creating first impressions about program culture, spectator areas where families wait before and after practices or games, multi-purpose spaces used for meetings and events, and connection points between different program areas or facilities.
Recognition Supporting High School Feeder Systems
Many youth sports leagues serve as feeder programs for high school athletics. Recognition systems can strengthen these pipelines by showcasing progression pathways from youth through high school programs, highlighting former youth league participants who achieved high school success, documenting connections between youth program participation and later achievement, and building aspirational examples inspiring current youth participants toward continued athletic development.
Solutions like Rocket Alumni Solutions enable communities to create comprehensive recognition spanning youth programs through high school athletics, documenting complete athletic journeys while showcasing how early youth participation leads to later success. These integrated systems help youth leagues demonstrate their value within broader athletic development ecosystems while motivating young athletes through visible pathways to future opportunities.
Common Challenges Facing Youth Sports Leagues
Understanding typical challenges enables leagues to address issues proactively rather than reactively when problems threaten program sustainability or participant experiences.
Overemphasis on Competition and Winning
Perhaps the most common challenge facing youth sports involves organizations losing sight of developmental goals by overemphasizing competitive outcomes inappropriate for children’s developmental levels.
Warning Signs
Programs may be overemphasizing competition when coaches experience pressure to win games over developing all players, playing time becomes heavily concentrated among top players, team selection involves cutting younger athletes before high school, parent behavior becomes overly intense with yelling or confrontational interactions, children express reluctance to attend activities they previously enjoyed, or organizations measure success primarily through win-loss records rather than participant development.
Corrective Approaches
Leagues should establish clear philosophies prioritizing age-appropriate development, implement playing time policies ensuring equitable participation, train volunteers in positive coaching emphasizing improvement over outcomes, educate parents about appropriate support and behavior, recognize diverse achievements beyond just competitive success, and regularly evaluate whether operations align with stated developmental priorities.

Volunteer Burnout and Leadership Succession
Youth sports leagues depend heavily on volunteer leadership that can experience burnout when demands become unsustainable or concentrate on too few individuals.
Prevention Strategies
Distribute responsibilities across multiple volunteers rather than relying on few individuals handling everything, establish reasonable time boundaries preventing volunteer obligations from becoming overwhelming, provide administrative support reducing tedious tasks volunteers must handle, recognize and appreciate contributions regularly rather than only at season conclusions, create clear succession plans identifying and training future leaders, and build institutional knowledge through documented procedures surviving individual leadership transitions.
Cost Barriers and Accessibility Challenges
Rising youth sports costs increasingly exclude lower-income families, contradicting leagues’ stated missions of providing opportunities for all children.
Addressing Accessibility
Leagues should keep base registration fees as low as possible by managing costs aggressively, implement robust scholarship programs funded through dedicated fundraising, create equipment-lending libraries preventing equipment costs from excluding participants, pursue facility partnerships reducing rental expenses, seek business sponsorships offsetting costs, and consider sliding scale fee structures based on family circumstances.
Safety Concerns and Injury Prevention
Youth sports involve inherent injury risks that leagues must actively address through appropriate safety protocols, training, and equipment standards.
Safety Best Practices
All coaches should receive training in age-appropriate skills instruction, concussion recognition and response protocols, emergency action planning, and proper equipment fitting and maintenance. Leagues should maintain appropriate insurance coverage, establish relationships with medical providers for consultation and coverage, enforce pitch count limits for baseball/softball protecting developing arms, implement heading restrictions for younger soccer players, require appropriate protective equipment for all activities, and create cultures where safety concerns receive immediate attention rather than dismissal as over-cautiousness.
Building Community Through Youth Sports
Youth sports leagues serve as community focal points where families connect, volunteers contribute, and shared identity develops around common goals of supporting children’s development.
Creating Family Engagement Opportunities
Beyond just spectating at games, leagues can engage families through volunteer opportunities with varied time commitments, social events building relationships among families, education programs about child development and sports participation, communication systems keeping families informed and connected, and input mechanisms ensuring families feel heard regarding program decisions.
Connecting Youth Sports to Broader Community Goals
Youth sports programs often connect to broader community development priorities including youth development initiatives preventing behavioral problems, public health efforts addressing childhood obesity, education partnerships supporting academic achievement, recreation access ensuring all children have activity opportunities, and community building creating social connections across diverse populations.
Making these connections explicit helps leagues secure support from municipal governments, school districts, public health agencies, and community foundations by demonstrating how youth sports support multiple priorities beyond just athletics.
Documenting and Celebrating Program History
Long-running youth sports leagues build rich histories worth documenting and celebrating. Comprehensive digital recognition systems enable leagues to preserve historical records including founding stories and program evolution, decade-by-decade participation statistics, notable alumni and their later achievements, championship teams and tournament results, and volunteer contributors who built programs over years or decades.
This historical documentation serves multiple purposes including building program identity and pride, demonstrating longevity and stability to prospective families, honoring past participants and volunteers, and providing context showing how current participants fit within broader legacy narratives.
The Future of Youth Sports Leagues
Youth sports continue evolving in response to changing family structures, technology integration, developmental research, and shifting priorities among children and families.
Technology Integration
Modern youth sports leagues increasingly leverage technology for registration and payment processing streamlining administrative burdens, communication platforms coordinating schedules and sharing updates, performance tracking documenting skill development and achievement, digital recognition showcasing accomplishments permanently, and virtual instruction supplementing in-person practice.
While technology offers significant benefits, leagues must balance convenience with maintaining personal connections and ensuring technology enhances rather than replaces human interaction and relationship-building at the heart of effective youth sports experiences.

Addressing Mental Health and Wellbeing
Growing awareness of youth mental health challenges requires youth sports programs to consider emotional and psychological dimensions alongside physical development. Progressive leagues implement training for volunteers on recognizing mental health concerns, cultures emphasizing fun and development over pressure and stress, appropriate parental behavior standards, balanced competitive expectations, and connections to mental health resources when participants struggle.
Ensuring Inclusive Participation
Youth sports organizations increasingly prioritize inclusion ensuring programs serve diverse participants including children with physical or developmental disabilities through adaptive programming, lower-income families through scholarship and equipment programs, girls seeking equal opportunities and recognition, LGBTQ+ youth requiring safe and welcoming environments, and children from minority communities historically underserved by youth sports infrastructure.
Conclusion: Communities Building Tomorrow’s Citizens Through Youth Sports
Youth sports leagues represent far more than scheduled games and trophy opportunities. When organized thoughtfully with age-appropriate structures emphasizing development over premature competition, trained volunteer leadership guided by positive coaching principles, sustainable funding enabling accessibility across socioeconomic diversity, and recognition systems celebrating achievement while ensuring all participants feel valued, these programs provide experiences shaping children’s entire lives.
The investment communities make in quality youth sports programs pays dividends across multiple domains. Children who participate regularly develop physical fitness habits influencing lifelong health, learn teamwork and social skills supporting academic and career success, build character traits including discipline, resilience, and work ethic, and establish positive associations with achievement and goal pursuit. Families benefit from social connections with other parents, volunteer opportunities contributing meaningfully to communities, and watching children develop confidence through competence. Communities gain social infrastructure bringing diverse populations together, youth development programming supporting broader goals, and shared identity around supporting young people’s growth.
Ready to strengthen recognition within your youth sports league? Modern solutions like Rocket Alumni Solutions provide comprehensive platforms designed specifically for youth athletic recognition, offering intuitive content management, engaging interactive displays, unlimited recognition capacity, and proven approaches helping leagues build recognition cultures their athletes deserve. From recreational programs celebrating every participant’s contribution to competitive organizations showcasing elite achievement, digital recognition extends visibility and impact far beyond traditional approaches while creating permanent documentation of program history and individual accomplishment.
Your young athletes invest countless hours developing skills, building character, and learning lessons that will serve them throughout entire lives. Comprehensive recognition ensures those achievements receive celebration and visibility that motivates continued participation while building program identity attracting future generations. The communities that build strong youth sports leagues today are investing in healthier, more connected, more resilient citizens tomorrow.