Intent: research
The integration of video games and interactive technology into pediatric healthcare represents one of the most significant evolutions in how hospitals support young patients’ emotional, psychological, and physical wellbeing during medical treatment. What began as informal efforts to provide entertainment and distraction has transformed into evidence-based therapeutic gaming programs with measurable impacts on patient outcomes, pain management, medication utilization, mental health indicators, and overall healthcare experiences.
This research report synthesizes current data on therapeutic gaming programs in children’s hospitals across the United States and internationally. Through analysis of published studies, hospital program statistics, patient outcome metrics, and implementation benchmarks, this comprehensive examination provides healthcare administrators, child life professionals, grant funders, and technology providers with defensible data about the current state and proven benefits of video games in pediatric healthcare settings.
Research Methodology: This report analyzes data from multiple sources including peer-reviewed studies published in medical journals through 2026, operational statistics from hospital therapeutic gaming programs, grant program data from Child's Play Charity and similar organizations, patient outcome measurements from Seattle Children's Hospital, Mary Bridge Children's Hospital, CHRISTUS Children's, and other leading programs, and systematic reviews examining therapeutic gaming effectiveness across multiple healthcare settings and patient populations.
Key Findings Overview: Video games in children's hospitals demonstrate measurable benefits including 1.6-2.3 point reductions in patient-reported pain scores, an average reduction of 7 morphine boluses per day among pediatric patients utilizing therapeutic gaming, modest but significant reductions in ADHD and depression symptoms (effect size of .28 in both conditions), 70% of pediatric gaming program participants reporting increased happiness and reduced anxiety, and rapidly expanding program implementation with approximately 50-60 therapeutic gaming specialists now working in hospitals compared to fewer than five professionals in this role as recently as 2018.
The Evolution of Video Games in Pediatric Healthcare: Historical Context and Current Landscape
Understanding the current state of therapeutic gaming programs requires examining how video games transitioned from informal entertainment to evidence-based therapeutic interventions within pediatric healthcare settings.
Early Adoption and Informal Implementation (2003-2015)
Video games first entered children’s hospitals primarily through charitable donations and parent advocacy rather than formal hospital programming or clinical integration.
Charitable Foundation and Grassroots Origins
Child’s Play Charity, founded in 2003 by Mike Krahulik and Jerry Holkins (creators of the Penny Arcade webcomic), pioneered large-scale efforts to deliver gaming equipment and technology to pediatric hospitals. As of 2026, Child’s Play has processed over $67 million in donations since inception and maintains partnerships with over 140 hospitals worldwide, having powered over 1 million hours of play in pediatric healthcare settings.
During this early period, video games in hospitals functioned primarily as entertainment and distraction provided by child life departments without systematic integration into treatment protocols, clinical outcome measurement, or therapeutic programming. Gaming equipment typically consisted of donated consoles placed in playrooms or wheeled to patient rooms on an ad-hoc basis when available.
Emergence of Evidence Base
A systematic review published in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine examining studies from 2000-2010 identified emerging evidence that video games could serve roles beyond entertainment, particularly in pain management and procedural distraction. This early research established foundations for subsequent clinical integration by demonstrating that interactive technology engagement could produce measurable impacts on patient experiences and some clinical indicators.
However, most hospitals during this period lacked dedicated staff focused on therapeutic gaming, standardized protocols for game selection and utilization, outcome measurement systems assessing gaming program effectiveness, or integration between gaming resources and broader treatment planning. Gaming remained a peripheral amenity rather than a core therapeutic modality.

Professionalization and Clinical Integration (2016-2020)
The period from 2016-2020 witnessed significant professionalization as hospitals began creating dedicated therapeutic gaming specialist positions and integrating gaming more systematically into treatment protocols.
Creation of Therapeutic Gaming Specialist Roles
Seattle Children’s Hospital launched one of the first formal therapeutic gaming programs in 2018, creating dedicated therapeutic gaming specialist positions responsible for managing device distribution and maintenance of more than 100 devices daily, conducting an average of 200 patient visits monthly, collaborating with medical teams to integrate gaming into treatment plans, assessing individual patient needs and recommending appropriate gaming experiences, and tracking utilization patterns and patient outcome data.
According to program leaders, when Seattle Children’s therapeutic gaming program started, only three other hospitals employed dedicated gaming specialists. This pioneering program demonstrated that professional staffing dedicated to therapeutic gaming significantly increased utilization rates, improved appropriate matching of gaming experiences to patient needs and therapeutic goals, and enhanced outcome measurement and program evaluation compared to ad-hoc gaming access without specialized staff support.
Expanding Clinical Applications
During this period, therapeutic gaming applications expanded beyond distraction and entertainment to include more specific clinical purposes including procedural support during anxiety-inducing or painful medical procedures, physical rehabilitation through motion-based gaming requiring therapeutic movements, cognitive rehabilitation following brain injury or during neurological treatment, social-emotional skill development for patients with developmental or psychiatric needs, and education about medical conditions and treatment protocols through specially designed therapeutic games.
Research published during this period provided growing evidence for these expanded applications. Studies demonstrated that video games requiring active participation led to reduced pain perception at central nervous system levels, not merely distraction from existing pain but actual reduction in pain signal processing.
Rapid Expansion and Evidence Accumulation (2021-2026)
The most recent period has witnessed dramatic expansion in therapeutic gaming program implementation across pediatric hospitals nationwide and internationally, supported by accumulating research evidence demonstrating program effectiveness.
Program Growth Statistics
The number of therapeutic gaming specialists working in hospitals has increased approximately 10-15x in recent years. One specialist noted joining the field in 2018 when approximately five people held formal therapeutic gaming positions, with that number growing to approximately 60 worldwide by 2026. This represents roughly 1,200% growth in dedicated professional positions over six years.
Hospital program implementation has similarly expanded with notable programs launched including Mary Bridge Children’s therapeutic gaming program (2026), described as the nation’s first “second-generation” pediatric gaming program building on lessons learned from pioneering efforts, CHRISTUS Children’s gaming specialist position (February 2026), CS Mott Children’s Hospital therapeutic gaming and digital technology program at University of Michigan Medicine, and OHSU Doernbecher Children’s Hospital therapeutic gaming initiatives, among many others establishing formal programs during this period.
Funding Infrastructure Development
Child’s Play Charity has significantly expanded support for therapeutic gaming infrastructure beyond equipment donations to include capacity building grants for pediatric hospitals to strengthen and expand Child Life centers, funding for Pediatric Gaming and Technology Specialists positions (44 positions funded as of 2026), and long-term investment funding supporting sustained program operations rather than only equipment purchases.
This shift from equipment-focused charitable giving to infrastructure and personnel funding reflects maturation of the field and recognition that professional expertise and program integration matter as much as hardware availability.

Research Evidence on Patient Outcomes: Quantitative Findings from Clinical Studies
The therapeutic gaming field has accumulated substantial research evidence demonstrating measurable impacts on multiple patient outcome domains including pain management, mental health indicators, medication utilization, and overall patient experience.
Pain Management and Procedural Support Outcomes
Pain represents one of the most rigorously studied outcome domains for therapeutic gaming interventions, with multiple studies demonstrating significant effects.
Quantitative Pain Reduction Data
Research published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research examining video game interventions for pediatric pain management found statistically significant pain score reductions of 1.6-2.3 points on standard pain assessment scales among patients utilizing gaming during medical procedures or while experiencing disease-related pain. This effect size represents clinically meaningful pain reduction comparable to some pharmacological interventions, particularly for mild to moderate pain intensities.
The same study documented reduced opioid medication requirements among pediatric patients who engaged with therapeutic gaming, with patients utilizing gaming requiring an average of 7 fewer morphine boluses per day compared to control periods or comparison groups without gaming access. This medication reduction carries significant clinical implications including reduced risk of opioid-related side effects such as constipation, nausea, and respiratory depression, decreased total opioid exposure during hospitalization potentially reducing dependence risk, lower medication costs for hospital systems and families, and improved post-discharge pain management when patients require less total opioid exposure during acute hospitalization.
Mechanisms of Pain Reduction
Research examining why video games reduce pain perception has identified multiple contributing mechanisms including attentional distraction drawing cognitive resources away from pain signal processing, gate control theory mechanisms where competing sensory input from gaming reduces pain signal transmission, emotional regulation through positive gaming experiences modulating pain-related emotional distress, sense of control and agency when gaming provides patient autonomy during otherwise disempowering medical experiences, and social connection when multiplayer gaming reduces isolation contributing to pain experience amplification.
Importantly, studies indicate that interactive gaming produces stronger pain reduction effects than passive entertainment like television viewing, suggesting that active engagement and agency represent important components of gaming’s therapeutic effects beyond simple distraction.
Procedural Anxiety and Distress Reduction
Beyond ongoing pain management, therapeutic gaming demonstrates particular effectiveness for reducing anxiety and distress during medical procedures. Studies examining gaming during procedures such as IV insertions, dressing changes, blood draws, imaging procedures, and pre-operative preparation document reduced behavioral distress indicators including decreased crying, reduced need for physical restraint, improved cooperation with medical staff, and lower scores on validated pediatric anxiety assessment instruments.
Healthcare providers report that reduced patient anxiety during procedures improves procedural success rates (successful IV insertion on first attempt, for example), decreases procedure duration when patients cooperate more readily, reduces staff stress and moral distress associated with causing patient suffering, and improves overall quality of care delivery in pediatric settings.
Mental Health Outcomes and Psychological Wellbeing
Beyond acute pain and procedural support, therapeutic gaming demonstrates measurable impacts on mental health indicators and psychological wellbeing among hospitalized pediatric patients.
Clinical Mental Health Symptom Reduction
A comprehensive systematic review published in JAMA Pediatrics in September 2026 analyzed 27 randomized clinical trials examining therapeutic gaming interventions for pediatric mental health conditions. The analysis included 2,911 participants aged six to 17 across studies from the United States and internationally, representing the most comprehensive evidence synthesis available on this topic.
The review found that video games specifically designed to address ADHD symptoms produced modest but statistically significant symptom reductions with an effect size of .28 compared to control conditions. Similarly, games designed to address pediatric depression demonstrated comparable effect sizes (.28) in reducing depressive symptoms. While .28 represents a small-to-moderate effect size in statistical terms, the clinical significance becomes meaningful when considering that an estimated 20% of children and teenagers ages three to 17 in the United States are affected by mental health conditions that could potentially benefit from these low-cost, accessible interventions.
The researchers noted that therapeutic gaming interventions offer several advantages over traditional mental health treatments including reduced stigma compared to traditional psychotherapy that some families resist, high engagement and treatment adherence due to gaming’s inherent appeal to young people, accessibility and scalability with potential to reach underserved populations, and cost-effectiveness compared to intensive clinical interventions, making these approaches valuable components of comprehensive pediatric mental health treatment strategies.
Emotional Wellbeing and Quality of Life Indicators
Beyond clinical mental health diagnoses, studies examining general emotional wellbeing among hospitalized children utilizing therapeutic gaming programs report substantial improvements across multiple indicators. Data from hospital therapeutic gaming programs document that 70% of pediatric gaming program participants reported increased happiness during and after gaming sessions, 70% experienced reduced anxiety compared to baseline assessments, 60% noted decreased feelings of loneliness and isolation, and over 80% reported feeling less stress related to their hospitalization.
These emotional wellbeing improvements matter substantially for overall patient experience and recovery trajectories. Research in pediatric healthcare demonstrates connections between emotional wellbeing during hospitalization and outcomes including improved treatment adherence when patients feel emotionally supported, better appetite and nutrition intake supporting physical recovery, improved sleep quality facilitating healing processes, enhanced engagement with physical therapy and rehabilitation activities, and reduced post-hospitalization psychological trauma and medical anxiety affecting future healthcare encounters.
Social Connection and Peer Interaction
Hospitalization frequently isolates children from their normal social networks including school friends, sports teams, extracurricular activities, and community connections. Therapeutic gaming, particularly multiplayer and online gaming experiences, can partially mitigate this social isolation through continued connection with friends outside the hospital via online multiplayer gaming, peer connections with other hospitalized children through hospital-based multiplayer gaming, shared experiences with family members who play games together during hospital visits, and connections with gaming specialists and child life staff building therapeutic relationships through shared gaming experiences.
Research on socialization benefits of gaming in hospitals identifies increased cooperation, support, helping behaviors, and civic engagement among pediatric patients participating in multiplayer therapeutic gaming, along with reduced loneliness and isolation that commonly exacerbate emotional distress during hospitalization.

Rehabilitation and Functional Recovery Outcomes
Therapeutic gaming increasingly serves roles in physical and cognitive rehabilitation for pediatric patients recovering from injuries, surgeries, or neurological conditions.
Physical Rehabilitation Applications
Motion-based gaming platforms such as Nintendo Switch, Xbox Kinect (in facilities still utilizing this discontinued platform), and virtual reality systems enable therapeutic gaming to support physical rehabilitation goals including range of motion exercises disguised as gaming activities increasing patient engagement, strengthening exercises through repeated game-required movements, balance and coordination training particularly valuable for neurological rehabilitation, and bilateral coordination development for patients with hemiplegia or unilateral weakness.
Physical therapists and occupational therapists report that gaming-based rehabilitation produces higher patient engagement and motivation compared to traditional exercise protocols, particularly for pediatric patients who may resist conventional therapy. Research comparing gaming-based rehabilitation to traditional approaches finds comparable or superior functional outcomes, with the primary advantage being improved adherence and practice volume when patients willingly engage in gaming-based therapy compared to conventional exercises they resist or minimize.
Cognitive Rehabilitation and Educational Applications
For patients experiencing cognitive impacts from brain injury, chemotherapy, neurological conditions, or developmental disabilities, therapeutic gaming can support cognitive rehabilitation through attention and concentration training via games requiring sustained focus, executive function skill development through games involving planning and strategy, memory enhancement through games incorporating memory challenges and recall, and processing speed improvement through timed gaming activities requiring rapid responses.
Educational gaming applications help patients maintain academic progress during extended hospitalizations, learn about their medical conditions and treatment protocols, develop health literacy and self-management skills, and build life skills and coping strategies applicable beyond healthcare contexts.
Implementation Benchmarks: Program Structures and Operational Models
Understanding how successful therapeutic gaming programs structure their operations provides valuable benchmarks for hospitals considering program development or enhancement.
Staffing Models and Professional Roles
Therapeutic gaming programs utilize various staffing approaches depending on hospital size, patient volume, budget resources, and program maturity.
Dedicated Therapeutic Gaming Specialist Positions
Comprehensive programs at major pediatric hospitals typically employ dedicated therapeutic gaming specialists (also called pediatric gaming specialists or gaming and technology specialists) with responsibilities including device management and maintenance ensuring equipment functionality, patient assessment and game matching to recommend appropriate gaming experiences for individual needs, direct patient engagement conducting gaming sessions and teaching patients to use platforms, collaboration with medical teams to integrate gaming into treatment planning, family training and support helping parents understand and facilitate therapeutic gaming, outcome tracking and program evaluation documenting utilization and impacts, and community building organizing multiplayer sessions and peer connections among patients.
These specialists typically hold backgrounds in child life, recreational therapy, psychology, education, or related fields, though the role remains new enough that standardized credentials and training pathways are still developing. Salaries for therapeutic gaming specialist positions typically range from $40,000-$65,000 annually depending on geographic location, hospital size, required education, and experience levels.
Integration with Child Life Programs
Many hospitals integrate therapeutic gaming within existing child life departments rather than creating entirely separate programs. In these models, certified child life specialists receive training in therapeutic gaming principles and platforms, dedicating portions of their time to gaming-specific interventions while maintaining traditional child life responsibilities including procedural preparation and support, play therapy, family education, and developmental programming.
This integration approach offers advantages of leveraging existing child life expertise and relationships with medical teams, utilizing established departmental infrastructure and budgets, and ensuring gaming integration with comprehensive child life philosophy and approach. However, the trade-off is that child life specialists managing broad responsibilities may have limited time for deep gaming expertise development and specialized program building compared to dedicated gaming specialists.
Volunteer and Student Programs
Some hospitals supplement professional staff through trained volunteer programs including college students studying child development, education, or healthcare fields, gaming industry professionals volunteering specialized expertise, community volunteers trained in therapeutic gaming principles, and peer mentors (often former patients) connecting with current pediatric patients.
Volunteers extend program reach and provide valuable person-hours for gaming facilitation, though they require appropriate training, supervision, and boundaries to ensure clinical appropriateness and patient safety. Volunteer programs work best as supplements to rather than replacements for professional staff oversight.

Technology Infrastructure and Device Management
Successful therapeutic gaming programs require substantial technology infrastructure beyond just gaming consoles.
Device Inventories and Platform Diversity
Comprehensive programs maintain diverse gaming platform inventories to match varied patient ages, abilities, interests, and therapeutic goals including mobile devices (tablets and smartphones) for portable, bedside gaming, traditional gaming consoles (PlayStation, Xbox, Nintendo Switch) for full-featured gaming experiences, handheld gaming devices for patients with mobility limitations, virtual reality systems for immersive experiences and specific therapeutic applications, and adaptive gaming equipment enabling access for patients with disabilities.
Seattle Children’s therapeutic gaming program, for example, manages distribution and maintenance of more than 100 devices on any given day, reflecting the substantial technology inventory required to serve a large pediatric hospital population. Device quantities required scale with patient census, facility size, and program ambitions.
Infection Control and Device Hygiene Protocols
Healthcare environments require rigorous hygiene protocols that significantly impact gaming equipment management including regular disinfection procedures between patient uses, protective covers and cases reducing contamination risk, dedicated devices for immunocompromised or isolation patients avoiding cross-contamination, and disposal or deep cleaning protocols for devices used by patients with specific infectious conditions.
These infection control requirements create substantial operational burden for gaming programs including staff time for cleaning and disinfection, equipment replacement costs when devices cannot be adequately disinfected, and logistical systems tracking device cleaning status and patient-appropriate assignment.
Technical Support and Maintenance
Gaming equipment requires ongoing technical support including software updates and troubleshooting, hardware repairs and replacement, network connectivity management for online gaming, account management and parental controls ensuring appropriate content access, and accessibility configuration for patients with disabilities.
Some programs employ dedicated technical support staff, while others train gaming specialists in basic technical management and contract with hospital IT departments or external vendors for complex technical issues.
Program Funding and Financial Sustainability
Therapeutic gaming program funding comes from multiple sources with implications for program sustainability and scope.
Philanthropic Support and Grant Funding
Many programs initially launch through philanthropic support including Child’s Play Charity capacity building grants (both equipment and specialist position funding), foundation grants from organizations focused on pediatric healthcare or technology access, corporate sponsorships from gaming industry companies and technology firms, and individual donor campaigns including memorial funds or family-directed giving.
Child’s Play Charity has been particularly influential, having funded 44 Pediatric Gaming and Technology Specialist positions as of 2026, representing substantial infrastructure investment beyond equipment donations. However, grant-dependent programs face sustainability challenges when initial funding periods end, requiring either renewed grant funding, transition to operational budget support, or program reduction or elimination.
Hospital Operational Budget Integration
Mature programs increasingly secure hospital operational budget support recognizing therapeutic gaming as core patient care services similar to other child life and recreational therapy services. Budget justification strategies include demonstrating medication cost reductions from decreased opioid utilization, showing reduced procedure times and increased efficiency when patients cooperate more readily, documenting improved patient satisfaction scores affecting hospital reputation and competitive position, presenting evidence of reduced patient anxiety and distress supporting staff wellbeing and retention, and highlighting marketing and community relations value of innovative pediatric programs.
Programs secured within operational budgets demonstrate greater long-term sustainability than grant-dependent initiatives, though initial establishment often requires philanthropic funding to demonstrate value justifying permanent budget allocation.
Estimated Program Costs
Hospital administrators planning therapeutic gaming programs should anticipate costs including initial technology inventory of $15,000-$50,000 depending on device quantities and platform selection, annual equipment replacement and upgrade budgets of $5,000-$15,000 accounting for device depreciation and technology evolution, therapeutic gaming specialist salary and benefits of $45,000-$75,000 annually (or equivalent FTE if integrating within existing child life positions), software subscriptions and digital content purchases of $2,000-$8,000 annually, and administrative support, supplies, and operational overhead.
A modest program at a smaller pediatric hospital might launch with $25,000-$40,000 startup investment and $60,000-$100,000 annual operating costs, while comprehensive programs at major children’s hospitals can exceed $150,000-$300,000 in annual program costs supporting multiple specialist positions and extensive technology infrastructure.
Technology Platforms and Game Selection: Clinical and Practical Considerations
Therapeutic gaming effectiveness depends substantially on appropriate technology platform selection and thoughtful game choice matching patient needs, ages, abilities, and therapeutic goals.
Gaming Platform Analysis and Clinical Applications
Different gaming platforms offer distinct advantages and limitations affecting clinical appropriateness for various patient populations and therapeutic applications.
Mobile Gaming (Tablets and Smartphones)
Mobile devices represent the most widely utilized platform in pediatric healthcare settings due to their portability for bedside use with patients unable to leave rooms, intuitive touch interfaces accessible to young children and patients with limited gaming experience, extensive game libraries including many free or low-cost options, easy disinfection with protective cases and wipeable surfaces, and lower acquisition costs compared to dedicated gaming consoles.
Clinical applications where mobile gaming excels include brief distraction during procedures or medical visits, bedside entertainment for patients with mobility restrictions, casual gaming for patients with limited energy or attention spans, and educational game delivery for health literacy and academic support.
However, mobile gaming limitations include smaller screen size potentially problematic for visual engagement during pain management, limited physical interaction reducing effectiveness for rehabilitation applications, battery life constraints requiring charging infrastructure, and potential for inappropriate content access without adequate parental controls and monitoring.
Console Gaming (PlayStation, Xbox, Nintendo Switch)
Traditional gaming consoles provide immersive experiences with applications including playroom or common area gaming for ambulatory patients, physical rehabilitation through motion-based games (particularly Nintendo Switch), multiplayer experiences facilitating social connection, and extended engagement for patients experiencing prolonged hospitalizations requiring sustained entertainment options.
Console advantages include large screen presentations for immersive experiences, high-quality game libraries with content appealing to diverse ages and interests, multiplayer capabilities supporting social connection, and motion-based gaming options for rehabilitation applications. Limitations include reduced portability requiring dedicated play spaces or room-based installation, higher costs for hardware and software, infection control challenges with controllers requiring frequent disinfection, and complex setup potentially requiring technical expertise.
Virtual Reality Systems
Virtual reality represents the newest frontier in therapeutic gaming with particularly strong applications in procedural support and pain management due to highly immersive experiences that effectively capture attention, anxiety reduction through calming virtual environments, physical rehabilitation through VR movement requirements, and cognitive therapy applications addressing phobias or providing exposure therapy.
Research specifically examining VR in pediatric healthcare settings demonstrates effectiveness for reducing procedural anxiety and pain during IV insertions, blood draws, wound care, and similar procedures. However, VR adoption remains limited due to higher costs compared to traditional gaming platforms, hygiene challenges with headsets contacting patient faces, age restrictions (most VR manufacturers recommend ages 13+), and technical complexity requiring specialized training and support.
Game Selection Criteria and Therapeutic Matching
Appropriate game selection significantly impacts therapeutic effectiveness, requiring systematic approaches to matching games with patient needs and clinical goals.
Age-Appropriate Content and Developmental Matching
Games must match patient developmental stages and cognitive abilities including simple cause-and-effect games for toddlers and preschoolers, skill-building games for school-age children developing mastery and competence, narrative and role-playing games for adolescents interested in complex stories and characters, and adaptive content complexity for patients with developmental delays or cognitive impairments.
Content rating systems (ESRB ratings in North America) provide initial guidance, though therapeutic gaming specialists develop more nuanced understanding of which games succeed with specific patient populations based on program experience.
Therapeutic Goal Alignment
Game selection should align with specific therapeutic objectives including calming, non-violent games for anxiety reduction and procedural support, physically active games requiring movement for rehabilitation applications, cognitively engaging games supporting attention and executive function, social multiplayer games facilitating peer connection, and educational games supporting health literacy or academic continuity.
Child’s Play Charity and the University of California San Diego collaborated with gaming market research firm Circana to develop a Therapeutic Video Game Guide helping hospitals and families select games aligned with specific therapeutic goals including coping with pain, addressing sadness, managing anxiety, and reducing boredom. This evidence-informed game selection resource provides hospitals with systematic approaches to matching games to patient needs beyond informal trial-and-error.
Cultural Sensitivity and Inclusivity
Game selection should reflect diverse patient populations including representation of diverse racial and ethnic backgrounds in game characters, gender-inclusive content avoiding stereotypes, accommodation of various family structures and backgrounds, religious and cultural sensitivity in game themes and content, and accessibility features supporting players with disabilities.
Gaming specialists report that patients engage more deeply when they see themselves represented in gaming content, making cultural representation an important consideration beyond just avoiding overtly inappropriate content.
Connecting Therapeutic Gaming with Broader Recognition Technology: Cross-Sector Applications
While therapeutic gaming in children’s hospitals represents a specialized healthcare application, the underlying technology and engagement principles connect to broader interactive digital recognition platforms serving diverse institutional contexts including schools, athletic programs, and community organizations.
Shared Technology Platforms and Interactive Engagement Principles
Therapeutic gaming programs and digital recognition systems share fundamental technology approaches and user engagement principles applicable across healthcare, educational, and community contexts.
Touchscreen Interactive Display Technology
Both therapeutic gaming and digital recognition platforms utilize intuitive touchscreen interfaces enabling user agency and self-directed exploration. In hospital settings, touchscreen gaming provides patients with autonomy and control during otherwise disempowering medical experiences. In educational and community settings, interactive touchscreen displays enable students, alumni, and community members to explore historical content, achievements, and recognition at their own pace.
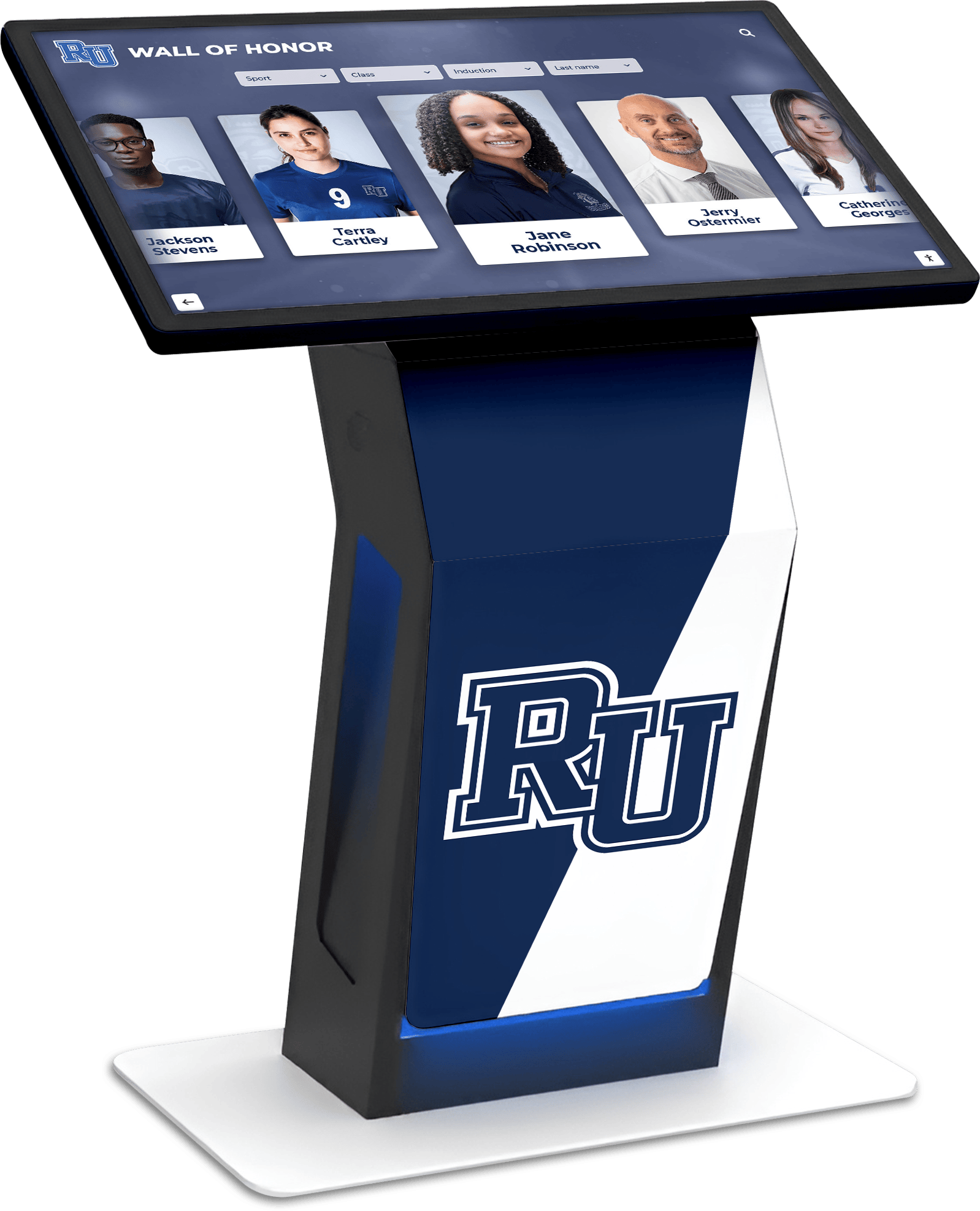
The principle remains consistent across applications: interactive technology that responds to user input creates more engaging and meaningful experiences compared to static displays or passive media consumption. Solutions like Rocket Alumni Solutions leverage this engagement principle by providing touchscreen platforms where users actively explore content, search for individuals or achievements, and discover stories that matter to them personally.
User-Centered Design and Accessibility Considerations
Both therapeutic gaming and recognition technology must prioritize intuitive user experience and accessibility for diverse user populations. Hospitals designing gaming programs for children across wide age ranges with varying abilities mirror challenges faced by schools implementing digital recognition displays serving diverse community members including young students, elderly alumni, and visitors with disabilities.
Best practices in both domains include multi-modal content presentation (visual, audio, text options), adjustable interface complexity matching user technical comfort, accessibility features supporting users with disabilities, and culturally responsive content representing diverse populations. Technology providers developing platforms for either application benefit from expertise in the other domain, as user-centered design principles apply across contexts.
Data-Driven Outcome Assessment and Continuous Improvement
Progressive therapeutic gaming programs track utilization data, patient outcomes, and program effectiveness to demonstrate value and guide continuous improvement. Similarly, effective digital recognition systems measure user engagement, community impact, and institutional outcomes to justify investments and optimize content and functionality.
Both applications benefit from analytics capabilities tracking user interactions, measuring engagement patterns, assessing program reach across diverse populations, identifying underutilized content or features requiring revision, and demonstrating value to administrators and funding sources. Organizations implementing either therapeutic gaming or recognition technology should establish clear metrics and systematic evaluation processes informing evidence-based program enhancement.
Recognition of Wellness Achievements and Holistic Student Support
The connection between therapeutic gaming and recognition technology extends beyond shared technical platforms to encompass broader institutional philosophies about holistic youth support and comprehensive achievement recognition.
Expanding Recognition Beyond Traditional Achievement Metrics
Just as therapeutic gaming programs recognize that pediatric patient wellbeing encompasses emotional, social, and psychological dimensions beyond just physical health metrics, progressive educational institutions recognize that student achievement extends beyond academic grades and athletic victories. Comprehensive digital recognition platforms can celebrate diverse accomplishments including academic recognition programs honoring scholastic excellence across various domains, wellness and resilience achievements recognizing students who overcome challenges or demonstrate personal growth, leadership and service contributions beyond traditional achievement measures, and creative and artistic accomplishments in performing arts, visual arts, and other creative domains.
Healthcare institutions that invest in therapeutic gaming demonstrate commitment to treating the whole child—emotional, social, and psychological wellbeing alongside physical health. Similarly, educational institutions implementing comprehensive recognition systems demonstrate commitment to supporting the whole student across multiple development domains rather than narrowly defining success through test scores and athletic championships.
Technology Supporting Youth Wellbeing Across Institutional Contexts
Therapeutic gaming specialists in hospitals recognize that technology can serve as a tool supporting youth mental health, social connection, and emotional regulation. Similar principles apply to educational technology implementation in schools where digital platforms can support student wellness initiatives by connecting current students with alumni mentors who navigated similar challenges, showcasing diverse pathways to success reducing narrow definition pressure, highlighting accomplishments in wellness, service, and character development, and providing resources and information about support services available to students.
Organizations implementing recognition technology should consider how platforms can support youth wellbeing beyond just celebrating past achievements—for example, by featuring mental health resources, connecting struggling students with peer support or adult mentors, or celebrating resilience and growth alongside traditional accomplishments.

Future Directions: Emerging Technologies and Research Priorities
The therapeutic gaming field continues evolving rapidly with emerging technologies, expanding research priorities, and growing recognition of gaming’s potential in pediatric healthcare.
Artificial Intelligence and Personalized Therapeutic Gaming
Artificial intelligence technologies offer potential to enhance therapeutic gaming through personalized game selection and adaptation based on individual patient characteristics, preferences, and therapeutic goals, real-time difficulty adjustment maintaining optimal engagement without frustration or boredom, pattern recognition identifying which game features produce strongest therapeutic effects for specific patient populations, and predictive analytics anticipating patient needs and proactively recommending gaming interventions.
Research exploring AI-enhanced therapeutic gaming remains early-stage but shows promise for optimizing clinical effectiveness through more precise matching of gaming interventions to individual patient needs compared to current manual game selection approaches.
Extended Reality (XR) and Immersive Therapeutic Environments
Beyond current VR applications, extended reality technologies including augmented reality and mixed reality offer future possibilities such as AR overlays in hospital rooms creating engaging visual environments without headset requirements, mixed reality experiences blending physical and digital elements for rehabilitation activities, spatial computing enabling intuitive interaction with digital content, and social XR experiences connecting hospitalized children with peers, friends, and family through shared immersive environments.
As XR technologies mature and costs decrease, healthcare applications will likely expand substantially from current limited VR implementations to more comprehensive immersive therapeutic environments.
Expansion to Adult Healthcare Settings
While therapeutic gaming initially focused on pediatric populations, growing evidence supports applications in adult healthcare including pain management during acute hospitalization or chronic pain treatment, mental health interventions for anxiety, depression, and PTSD, cognitive rehabilitation following stroke or brain injury, physical rehabilitation particularly for older adults who may engage more readily with gaming-based therapy, and distraction during procedures for adults experiencing medical anxiety.
Research examining therapeutic gaming effectiveness in adult populations remains less developed than pediatric evidence but represents a significant growth area as the current generation of digitally native young adults ages into periods of higher healthcare utilization.
Research Priorities and Knowledge Gaps
Despite substantial evidence accumulation, important research gaps remain requiring continued investigation including dose-response relationships (optimal gaming duration, frequency, and intensity for various therapeutic goals), mechanism studies clarifying how gaming produces observed effects to optimize intervention design, long-term outcome research examining whether acute benefits translate to lasting impacts on wellbeing, cost-effectiveness analyses comparing therapeutic gaming to alternative interventions, and equity research ensuring gaming programs serve diverse patient populations effectively without exacerbating existing healthcare disparities.
Healthcare systems and researchers should prioritize these knowledge gaps through systematic program evaluation, collaboration between clinical programs and academic researchers, multi-site studies enabling larger sample sizes and diverse populations, and publication of findings in peer-reviewed literature advancing the field’s evidence base.

Practical Implementation Guidance for Healthcare Administrators
Healthcare leaders considering therapeutic gaming program development or enhancement can follow structured implementation approaches based on lessons learned from successful programs.
Needs Assessment and Program Planning
Effective programs begin with systematic needs assessment including analysis of current patient population characteristics (age distribution, common diagnoses, typical length of stay, special needs populations), existing child life and recreational therapy resources and potential integration opportunities, facility infrastructure including available space, network connectivity, and technology support capacity, and stakeholder perspectives from medical staff, child life professionals, patients, families, and administrators about gaming program priorities and concerns.
This assessment informs program scope decisions including whether to start with modest pilot programs or comprehensive implementations, which patient populations and clinical applications to prioritize initially, what staffing model best fits institutional context and budget, and which technology platforms and gaming content align with identified needs.
Funding and Resource Development
Program funding typically requires multi-pronged approaches combining available resources including grants from Child’s Play Charity or other gaming and healthcare philanthropy organizations, hospital foundation fundraising campaigns positioning therapeutic gaming as innovative patient care enhancement, operational budget allocation demonstrating return on investment through outcome data, in-kind donations of gaming equipment from technology companies or community members, and volunteer program development extending staff capacity through trained community volunteers.
Healthcare administrators should develop clear financial sustainability plans extending beyond initial startup funding to ensure programs can maintain operations, replace equipment, and support staff positions over time. Programs launched enthusiastically with grant funding but lacking long-term financial sustainability plans frequently struggle when initial grant periods end.
Staff Recruitment and Professional Development
Program success depends heavily on hiring and supporting skilled staff including recruitment of gaming specialists or child life professionals with gaming expertise and enthusiasm, clear position descriptions and performance expectations, competitive compensation attracting and retaining qualified professionals, ongoing professional development through conferences, training, and peer learning opportunities, and connection to emerging professional communities like the Therapeutic Gaming Interest Group within child life professional associations.
As the therapeutic gaming field matures, clearer professional pathways, specialized training programs, and potential credentialing will likely emerge, enabling more standardized professional development compared to current pioneer generation largely learning through practice and peer exchange.
Outcome Measurement and Program Evaluation
Demonstrating program value requires systematic outcome measurement including utilization tracking (patient visits, device loans, program participation rates), patient satisfaction assessment through surveys or interviews, clinical outcome measurement where feasible (pain scores, anxiety ratings, medication utilization), stakeholder feedback from medical staff and families, and cost analysis examining expenses and potential cost offsets from medication reduction or improved efficiency.
Healthcare administrators should establish evaluation frameworks before program launch, enabling baseline data collection and longitudinal tracking demonstrating program impact over time. This evidence proves essential for securing continued funding, operational budget integration, and program expansion.
Conclusion: Video Games as Evidence-Based Therapeutic Tools in Pediatric Healthcare
The substantial evidence examined in this research report demonstrates conclusively that video games in children’s hospitals have evolved from informal entertainment amenities to evidence-based therapeutic interventions with measurable impacts on patient outcomes, pain management, mental health, rehabilitation, and overall healthcare experience quality.
Key Findings Summary:
Quantitative outcome data shows 1.6-2.3 point reductions in patient-reported pain scores, average reductions of 7 morphine boluses daily among gaming participants, modest but significant improvements in ADHD and depression symptoms, and 70-80% of participants reporting improved emotional wellbeing including increased happiness, reduced anxiety, decreased loneliness, and reduced stress.
Program implementation has expanded dramatically with approximately 50-60 therapeutic gaming specialists now working in hospitals compared to fewer than five professionals in this role as recently as 2018, representing roughly 1,200% growth. Child’s Play Charity has funded 44 specialist positions and processed over $67 million in donations supporting over 140 hospital partnerships worldwide.
Clinical applications now extend beyond entertainment and distraction to include pain management during procedures and treatment, mental health interventions for anxiety, depression, and emotional wellbeing, physical rehabilitation through motion-based gaming, cognitive rehabilitation and educational support, and social connection facilitating peer relationships and reducing isolation.
Implications for Healthcare Administrators:
Healthcare leaders should recognize therapeutic gaming as evidence-based patient care warranting serious consideration and investment rather than optional amenity or purely recreational activity. Successful implementation requires dedicated professional staffing (either specialized gaming specialists or trained child life professionals), diverse technology infrastructure matching varied patient ages and needs, systematic program evaluation measuring utilization and outcomes, sustainable funding plans extending beyond initial grants, and integration with broader patient care planning and medical team collaboration.
Institutions currently lacking formal therapeutic gaming programs should examine the compelling evidence and consider how gaming interventions might enhance patient care quality, improve clinical outcomes, support institutional missions of comprehensive pediatric care, and provide competitive differentiation in healthcare markets where patients increasingly have institutional choices.
Connections to Broader Youth Support and Recognition Technology:
The principles underlying therapeutic gaming success—interactive technology that provides agency and engagement, user-centered design serving diverse populations, holistic support addressing multiple wellbeing dimensions, and systematic outcome measurement—apply equally to digital recognition platforms serving educational institutions and youth-serving organizations. Healthcare institutions investing in therapeutic gaming demonstrate commitment to treating the whole child, while educational institutions implementing comprehensive recognition systems demonstrate commitment to supporting whole students across multiple development domains.
Technology providers developing platforms for healthcare, educational, or community applications should recognize shared principles and opportunities for cross-sector learning, ensuring solutions serve diverse institutional missions while maintaining user-centered design, accessibility, and measurable impact on the populations served.
Future Research and Program Development Priorities:
The therapeutic gaming field requires continued research examining optimal implementation approaches, long-term outcome sustainability, cost-effectiveness compared to alternative interventions, equity and access ensuring programs serve diverse patient populations, expansion to adult healthcare settings, and integration of emerging technologies including AI personalization and extended reality platforms.
Healthcare systems should view therapeutic gaming programs as ongoing learning laboratories, systematically evaluating outcomes, contributing findings to the professional literature, and participating in collaborative research advancing the field’s evidence base. Only through continued rigorous evaluation and knowledge sharing will therapeutic gaming achieve its full potential as evidence-based therapeutic intervention serving pediatric patients across diverse healthcare settings.
Every child facing hospitalization deserves comprehensive support addressing not only physical health but also emotional, psychological, and social wellbeing during challenging medical journeys. Therapeutic gaming programs represent healthcare institutions’ commitment to treating whole patients and recognizing that meaningful healing encompasses far more than clinical interventions alone. The compelling evidence reviewed in this report should encourage healthcare leaders to seriously consider how therapeutic gaming can enhance their institutions’ patient care and fulfill missions of comprehensive, compassionate pediatric healthcare.
Frequently Asked Questions About Video Games in Children’s Hospitals
What evidence demonstrates that video games are effective for pain management in pediatric patients?
Research published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research provides robust evidence of gaming’s pain management effectiveness. Studies document statistically significant pain score reductions of 1.6-2.3 points on standard pain assessment scales among patients utilizing gaming during medical procedures or while experiencing disease-related pain. The same research found that pediatric patients engaging with therapeutic gaming required an average of 7 fewer morphine boluses per day compared to control periods without gaming access. These reductions carry meaningful clinical implications including reduced opioid-related side effects, decreased total opioid exposure potentially reducing dependence risk, and lower medication costs. The mechanism appears to involve multiple factors including attentional distraction drawing cognitive resources away from pain signal processing, gate control theory mechanisms where competing sensory input reduces pain transmission, emotional regulation through positive gaming experiences, and sense of control during otherwise disempowering medical experiences. Importantly, interactive gaming produces stronger pain reduction than passive entertainment like television, suggesting active engagement represents an important therapeutic component beyond simple distraction.
How many hospitals currently have formal therapeutic gaming programs and specialists?
The therapeutic gaming field has experienced dramatic expansion in recent years. Approximately 50-60 therapeutic gaming specialists now work in hospitals worldwide, compared to fewer than five professionals in formal gaming specialist roles as recently as 2018—representing approximately 1,200% growth in dedicated professional positions over six years. Child’s Play Charity, a leading funder of therapeutic gaming infrastructure, has funded 44 Pediatric Gaming and Technology Specialist positions as of 2026 and maintains partnerships with over 140 hospitals worldwide. Notable programs operate at Seattle Children’s Hospital (established 2018), Mary Bridge Children’s Hospital (established 2026 as the nation’s first “second-generation” program), CHRISTUS Children’s (specialist position created February 2026), CS Mott Children’s Hospital at University of Michigan Medicine, OHSU Doernbecher Children’s Hospital, and many others. However, these formal programs represent a small fraction of pediatric hospitals nationwide, indicating substantial room for continued expansion. Many additional hospitals provide gaming resources through child life departments without dedicated gaming specialists, offering less comprehensive programming than facilities with specialized staff positions.
What types of mental health benefits do video games provide for hospitalized children?
A comprehensive systematic review published in JAMA Pediatrics in September 2026 analyzed 27 randomized clinical trials examining therapeutic gaming for pediatric mental health across 2,911 participants. The review found video games specifically designed to address ADHD produced modest but statistically significant symptom reductions (effect size .28), with similar effects for games addressing depression. Beyond clinical diagnoses, hospital program data shows 70% of gaming participants reported increased happiness, 70% experienced reduced anxiety, 60% noted decreased loneliness, and over 80% felt less stress. These emotional wellbeing improvements significantly impact recovery including enhanced treatment adherence, better appetite and nutrition, improved sleep quality, increased engagement with rehabilitation, and reduced post-hospitalization medical anxiety. Gaming also provides social connection benefits particularly important during hospitalization including continued connection with outside friends through online multiplayer gaming, peer connections with other hospitalized children, shared experiences with visiting family members, and therapeutic relationships with gaming specialists and child life staff. Research identifies that gaming increases cooperation, support, helping behaviors, and civic engagement while reducing isolation that commonly exacerbates emotional distress during hospitalization.
What are the typical costs for hospitals to establish therapeutic gaming programs?
Program costs vary substantially based on scope and institutional size. Initial technology inventory typically requires $15,000-$50,000 depending on device quantities and platform selection (mobile devices, consoles, VR systems). Annual equipment replacement and upgrade budgets of $5,000-$15,000 account for device depreciation and technology evolution. The largest ongoing expense involves therapeutic gaming specialist salary and benefits at $45,000-$75,000 annually for full-time positions, though some hospitals integrate gaming within existing child life specialist positions rather than creating separate roles. Additional costs include software subscriptions and digital content ($2,000-$8,000 annually) plus administrative support and operational overhead. A modest program at a smaller pediatric hospital might launch with $25,000-$40,000 startup investment and $60,000-$100,000 annual operating budget, while comprehensive programs at major children’s hospitals can exceed $150,000-$300,000 annually supporting multiple specialist positions and extensive technology infrastructure. Funding typically combines grants from organizations like Child’s Play Charity (which has funded 44 specialist positions), hospital foundation fundraising campaigns, operational budget allocation, and in-kind equipment donations. Programs should develop long-term financial sustainability plans extending beyond initial grant funding to ensure sustained operations.
How do therapeutic gaming programs measure their effectiveness and demonstrate value to hospital administrators?
Comprehensive evaluation tracks multiple outcome dimensions demonstrating program impact. Utilization metrics show patient engagement including total visits, percentage of patient population served, visit frequency patterns, and service-specific usage rates. Clinical outcome measures assess health impacts through patient-reported pain scores comparing gaming participants to control periods, medication utilization particularly opioid requirements, procedural success rates and durations, and standardized anxiety and mental health assessments. Patient satisfaction data gathered through surveys, interviews, and feedback forms reveal perceived value and program quality. Healthcare provider perspectives from nurses, physicians, child life staff, and therapists provide important context about how gaming affects workflow, patient cooperation, and care quality. Cost analysis examines program expenses against potential cost offsets including medication reductions, improved procedure efficiency, enhanced patient satisfaction scores affecting hospital reputation, and reduced staff stress supporting retention. Programs should establish evaluation frameworks before launch enabling baseline data collection and longitudinal tracking. Publishing findings in professional literature or presenting at conferences contributes to the broader evidence base while demonstrating institutional commitment to evidence-based practice and program excellence.
What gaming platforms and content work best for different therapeutic goals in hospital settings?
Platform selection depends on patient age, therapeutic goals, mobility status, and clinical context. Mobile devices (tablets and smartphones) excel for bedside distraction during procedures, patients with mobility restrictions, brief gaming sessions, and young children needing intuitive touch interfaces, though smaller screens may limit immersiveness for pain management applications. Console gaming (PlayStation, Xbox, Nintendo Switch) provides advantages for playroom or common area gaming with ambulatory patients, physical rehabilitation through motion-based games particularly Nintendo Switch, multiplayer social experiences, and extended engagement during prolonged hospitalizations, though they’re less portable and involve higher costs. Virtual reality shows particular promise for procedural pain management and anxiety reduction due to highly immersive experiences but faces limitations including higher costs, hygiene challenges with headsets, age restrictions (typically 13+), and technical complexity. Game content selection should match therapeutic goals—calming non-violent games for anxiety reduction, physically active games for rehabilitation, cognitively engaging games for attention and executive function, social multiplayer games for peer connection, and educational games for health literacy or academic continuity. The Therapeutic Video Game Guide developed through collaboration between Child’s Play Charity, Circana market research, and University of California San Diego mental health professionals provides evidence-informed game selection resources helping hospitals match specific games to therapeutic objectives including coping with pain, addressing sadness, managing anxiety, and reducing boredom.
Disclaimer and Research Transparency:
This report synthesizes publicly available information current as of November 2026. Research findings and statistics represent published studies and hospital program data available through peer-reviewed journals, hospital communications, and charitable organization reports. Healthcare institutions should conduct independent evaluation of therapeutic gaming appropriateness for their specific patient populations, clinical contexts, and operational capabilities. All trademarks and program names belong to their respective owners. This research analysis was produced to inform healthcare administrators, child life professionals, and other stakeholders about therapeutic gaming program evidence and implementation considerations.
Sources:
- Gaming in Hospitals: More Than A Distraction | Starlight Children’s Foundation
- Seattle Children’s Therapeutic Gaming Program
- Press play, not pause: Gaming program at Mary Bridge Children’s
- Specially Designed Video Games May Benefit Mental Health | Johns Hopkins Medicine
- Child’s Play Charity
- ‘Gaming Guy’ at CHRISTUS Children’s
- The Power of Play Through Gaming | Games for Change