Selecting the right screen for your digital signage project can make the difference between a captivating display that engages viewers and an underwhelming investment that fails to deliver results. With the global digital signage market projected to reach $32.8 billion by 2027, understanding screen technology options has never been more important for organizations planning recognition displays, wayfinding systems, or interactive kiosks.
The screen you choose affects everything from image quality and visibility to energy costs and maintenance requirements. Whether you’re creating a digital hall of fame for your school, implementing wayfinding displays in a corporate office, or installing outdoor advertising screens, matching screen technology to your specific use case ensures optimal performance and return on investment.
Understanding Commercial-Grade vs. Consumer Displays
Before diving into specific screen technologies, it’s essential to understand why commercial-grade displays differ from consumer TVs—and why this distinction matters for digital signage applications.
Why Consumer TVs Fall Short for Digital Signage
Consumer televisions are designed for home entertainment with specific usage patterns: a few hours daily in controlled lighting conditions with moderate ambient temperatures. These design parameters make consumer displays unsuitable for most commercial digital signage applications.
Key Limitations of Consumer TVs:
Limited Operating Hours: Consumer displays are rated for approximately 8-10 hours of daily operation. Digital signage applications often require 16-18 hours daily or even continuous 24/7 operation. Running consumer TVs beyond their design specifications leads to premature failure, often within 12-18 months rather than the 5-7 year lifespan typical of commercial displays.
Heat Management Issues: Consumer televisions lack the robust thermal management systems commercial displays feature. Extended operation causes heat buildup that degrades components, particularly in enclosed installations or warm environments. Commercial displays include enhanced cooling systems, temperature sensors, and thermal protection features enabling extended operation without overheating.
Inadequate Brightness: Consumer TVs typically produce 250-350 nits of brightness, suitable for controlled home lighting but insufficient for well-lit commercial spaces or locations with natural light. Commercial displays deliver 500-700 nits for indoor applications and 2,500+ nits for outdoor installations.
Limited Warranty Coverage: Consumer TV warranties specifically exclude commercial use. Organizations that deploy consumer displays in digital signage applications void warranties and receive no manufacturer support when units fail prematurely.
Missing Commercial Features: Consumer displays lack essential commercial capabilities: remote management systems, portrait orientation support, lockable inputs, ruggedized construction, and commercial-grade mounting options.
Commercial Display Advantages
Commercial-grade digital signage displays are purpose-built for business applications with features addressing the specific demands of continuous operation in public spaces.
Commercial Display Benefits:
- Extended operating hours: Rated for 16/7, 18/7, or 24/7 operation depending on the model series
- Enhanced durability: Ruggedized components and construction withstand commercial environments
- Superior brightness: Higher nit ratings ensure visibility in various lighting conditions
- Advanced thermal management: Sophisticated cooling systems enable continuous operation
- Commercial warranties: Coverage designed for business use with appropriate support
- Remote management capabilities: Network-based monitoring, configuration, and content management
- Orientation flexibility: Support for portrait, landscape, and tilted installations
- Longer lifespan: Expected operational life of 70,000-100,000 hours (8-11 years of continuous use)

LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) Screens
LCD technology represents the most widely deployed screen type in digital signage applications, offering an excellent balance of image quality, reliability, and cost-effectiveness for indoor installations.
How LCD Technology Works
LCD displays use a backlight (typically LED-based) shining through liquid crystal cells that twist to allow or block light passage. Color filters create the full-color images viewers see. This light-modulating approach differs fundamentally from emissive display technologies like LED or OLED where pixels produce their own light.
LCD Display Components:
- LED backlight array: Provides uniform illumination across the display panel
- Liquid crystal layer: Microscopic crystals that twist to control light passage
- Color filter array: Red, green, and blue filters creating full-color images
- Polarizing filters: Control light orientation for proper LCD operation
- TFT (thin-film transistor) matrix: Individual transistors controlling each pixel
LCD Display Advantages
LCD screens offer compelling benefits making them the dominant technology for indoor digital signage applications.
Key LCD Strengths:
Cost Effectiveness: LCD displays deliver the lowest cost per inch among commercial display technologies. Large-format LCD panels (50-86 inches) provide excellent value for organizations with budget constraints while still delivering commercial-grade performance.
Proven Reliability: Decades of LCD technology refinement have produced highly reliable displays with predictable performance characteristics. Commercial LCD panels routinely deliver 60,000-70,000 hours of operation before brightness degrades to 50% of original output.
Energy Efficiency: Modern LED-backlit LCD displays consume significantly less power than previous CCFL-backlit LCD technology or plasma displays. A typical 55-inch commercial LCD display draws 150-200 watts during operation, contributing to lower operational costs over time.
Wide Availability: LCD displays are available in virtually every size category from small 32-inch displays to massive 98-inch panels. This size flexibility accommodates diverse application requirements from desktop information displays to large-format video walls.
Excellent Resolution Options: LCD technology supports Full HD (1920x1080), 4K UHD (3840x2160), and even 8K (7680x4320) resolutions, enabling sharp, detailed imagery appropriate for content ranging from text-heavy wayfinding information to high-resolution photographs.
Minimal Burn-in Risk: Unlike OLED displays, LCD screens face negligible risk of image retention or burn-in even when displaying static content for extended periods. This characteristic makes LCD ideal for applications displaying consistent branding elements, menus, or wayfinding information.
LCD Display Limitations
While LCD technology offers numerous advantages, certain limitations make alternative technologies preferable for specific applications.
LCD Challenges:
Limited Viewing Angles: Despite advances in IPS (In-Plane Switching) panel technology, LCD displays show color shift and brightness reduction when viewed from extreme angles. Premium commercial LCD displays with IPS panels typically offer 178-degree viewing angles, but image quality still degrades compared to straight-on viewing.
Black Level Performance: Because LCD displays require backlighting even for black content, they cannot achieve true black levels. Light leakage through liquid crystals in the “off” state creates gray appearance rather than deep blacks. This limitation reduces contrast ratio compared to emissive display technologies.
Backlight Uniformity Challenges: Some LCD displays exhibit brightness variation across the screen surface, particularly noticeable when displaying uniform colors or solid backgrounds. Commercial-grade displays minimize this issue through precise backlight calibration, but perfect uniformity remains challenging.
Outdoor Visibility: Standard LCD displays lack sufficient brightness for direct sunlight environments. While high-brightness LCD variants exist (1,500-5,000 nits), they command premium pricing and increased power consumption.
Ideal LCD Applications
LCD displays excel in specific digital signage scenarios where their advantages align with application requirements.
Best Use Cases for LCD:
- Indoor digital signage: Retail displays, corporate lobbies, educational institutions, healthcare facilities
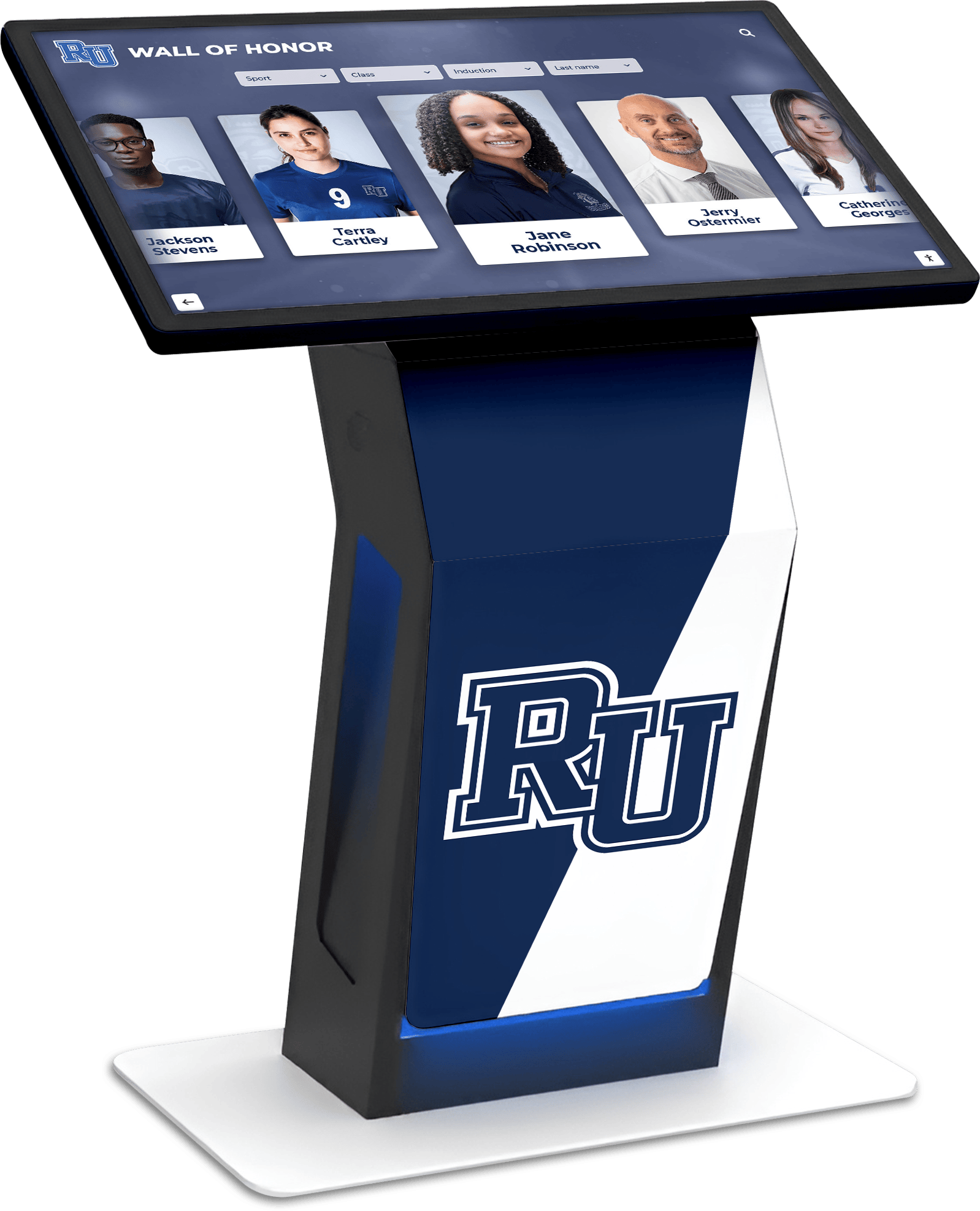
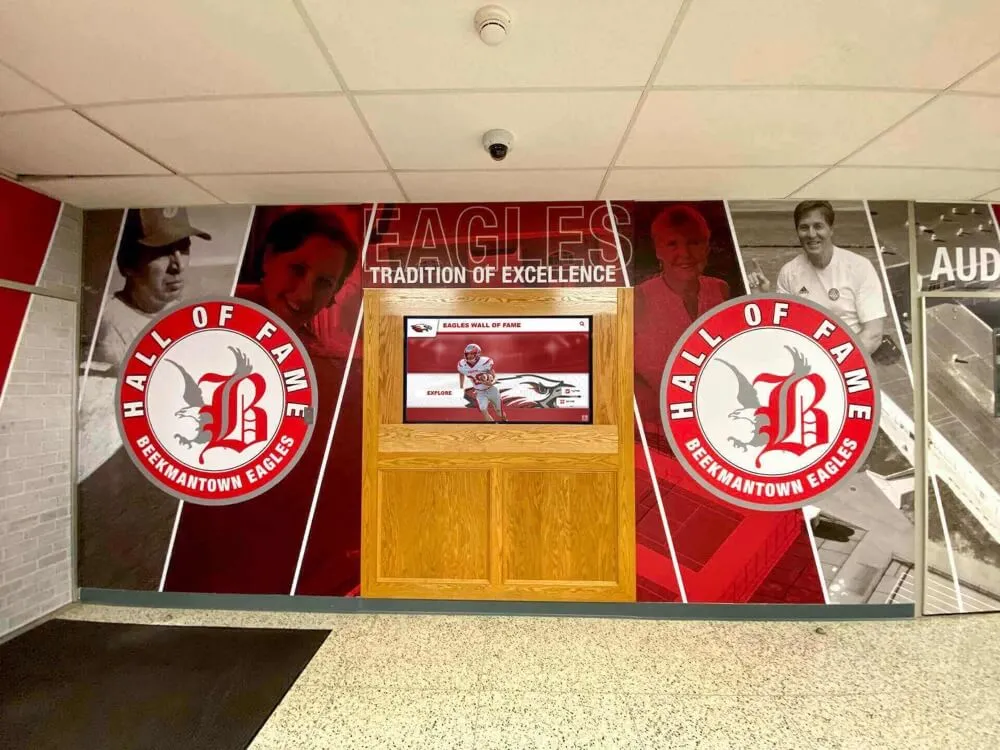
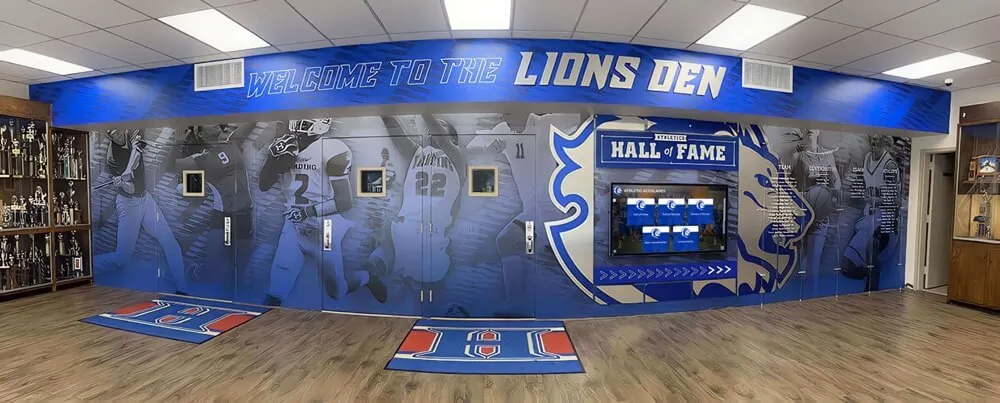
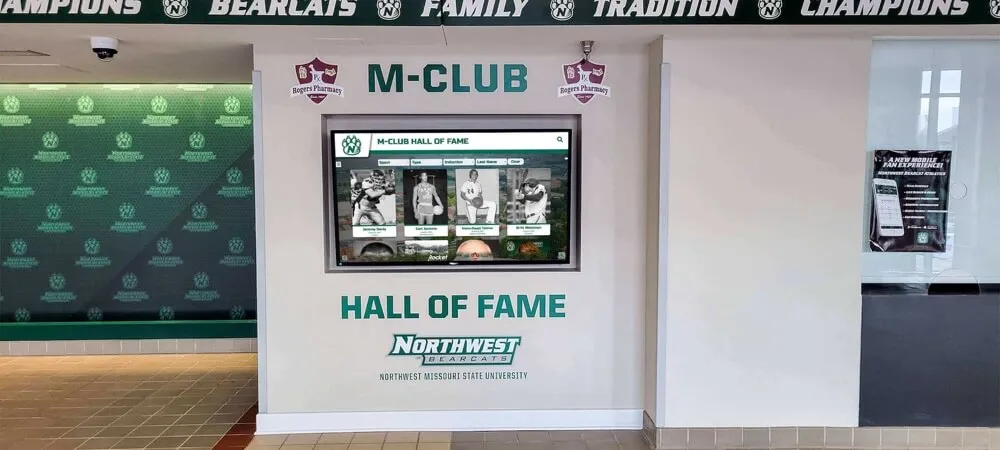
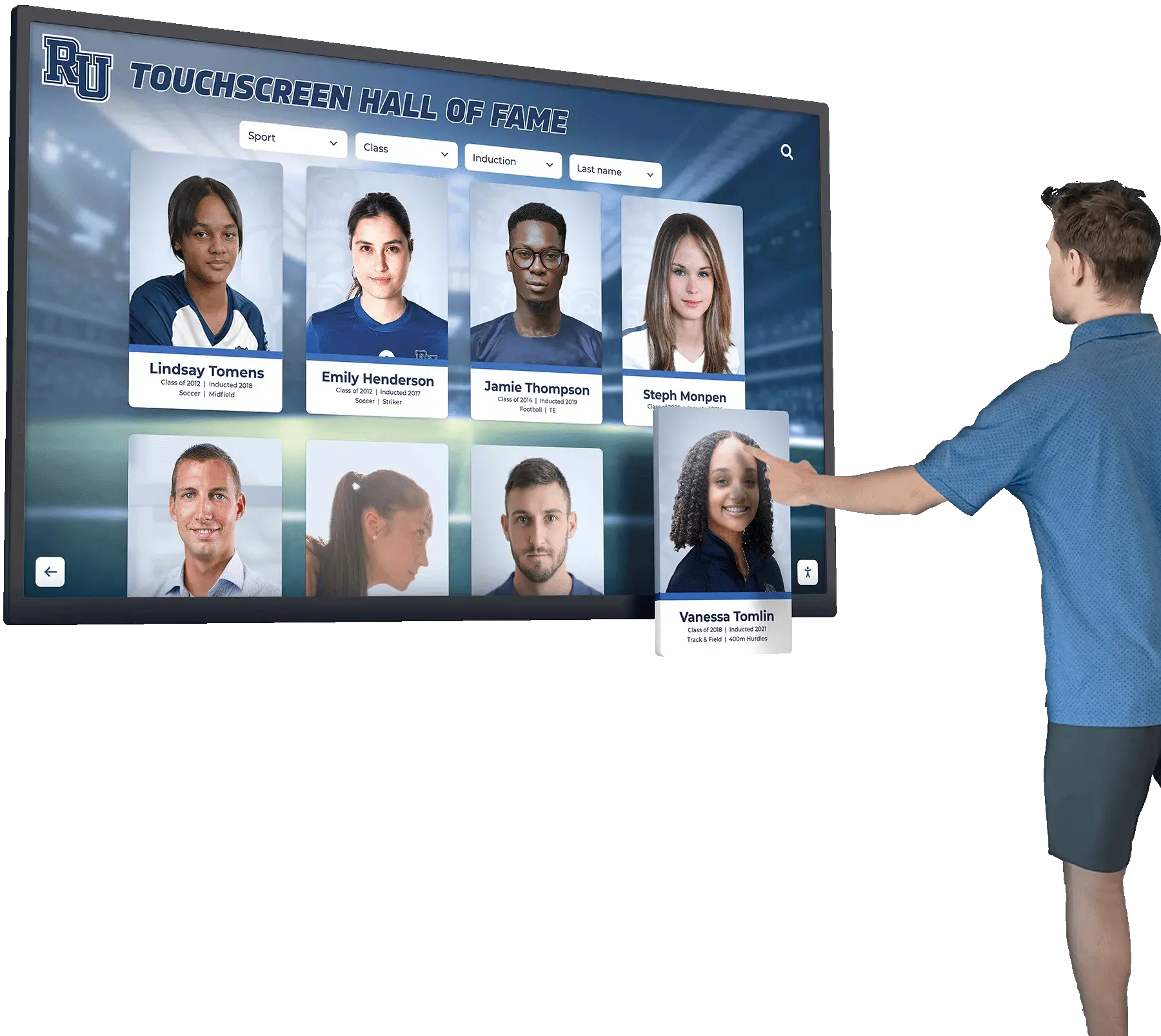
- Recognition displays: Digital halls of fame, employee recognition, alumni walls where interactive touchscreen displays showcase achievements
- Menu boards: Restaurants, cafeterias, and food service locations with controlled lighting
- Wayfinding systems: Directional signage in buildings where viewing angles remain relatively straight-on
- Conference room displays: Presentation screens, scheduling panels, and video conferencing applications
- Video walls: Multi-panel installations creating large-format display surfaces with narrow bezel designs
LCD Pricing Considerations
LCD display pricing varies significantly based on size, resolution, brightness, features, and brand positioning.
LCD Cost Factors:
Entry-Level Commercial LCD (32-43 inches): Basic commercial-grade LCD displays start around $400-$800 depending on specifications. These displays offer 16/7 operation ratings suitable for retail or corporate environments with moderate usage requirements.
Mid-Range Commercial LCD (50-65 inches): Professional-grade displays in this size range typically cost $1,200-$3,500. These panels feature enhanced brightness (500-700 nits), longer warranties, and advanced features like integrated media players or touchscreen capabilities.
Large-Format Commercial LCD (75-98 inches): Premium large-format displays command $4,000-$12,000+ depending on resolution and features. These displays serve applications requiring maximum impact or viewing from significant distances.
High-Brightness LCD for Windows/Outdoors: Specialized high-brightness LCD displays (1,500-5,000 nits) for window-facing or semi-outdoor applications cost 2-3x standard display prices due to enhanced backlight systems and protective coatings.

LED (Light-Emitting Diode) Display Panels
LED display technology in digital signage typically refers to direct-view LED panels where thousands of individual light-emitting diodes create images, distinct from LED-backlit LCD displays. These modular panels offer unique advantages for large-scale installations and demanding environments.
Understanding Direct-View LED Technology
Direct-view LED displays consist of modules containing clusters of red, green, and blue LED lamps. These LEDs illuminate directly to create images without backlighting or light-modulating layers. The spacing between LED clusters—called pixel pitch—determines resolution and optimal viewing distance.
LED Display Architecture:
LED Modules: Individual cabinet panels typically measuring 500mm x 500mm or 1000mm x 500mm contain LED clusters. These modules connect together creating displays of virtually any size or shape without bezels interrupting the image.
Pixel Pitch: The distance between LED cluster centers determines resolution. Common pixel pitches range from 0.9mm (fine pitch for close viewing) to 10mm+ (coarse pitch for viewing from distance). Smaller pixel pitches enable closer viewing distances but increase cost significantly.
SMD (Surface-Mount Device) LED: Modern LED displays use SMD packaging where red, green, and blue LED chips are mounted on a single package. This approach enables finer pixel pitches than older DIP (Dual In-line Package) LED technology while improving color uniformity and viewing angles.
LED Display Advantages
Direct-view LED displays offer compelling benefits for specific digital signage applications where their unique characteristics provide value.
LED Display Strengths:
Exceptional Brightness: LED displays deliver brightness levels far exceeding LCD or OLED technology, commonly reaching 5,000-10,000 nits or higher. This extreme brightness enables excellent visibility in ambient light conditions including direct sunlight, making LED ideal for outdoor applications.
Seamless Large-Format Displays: Because LED displays consist of modular panels without bezels, they create truly seamless large-format displays without the grid lines characteristic of LCD video walls. This seamlessness proves particularly valuable for immersive installations or applications where uninterrupted images matter.
Virtually Unlimited Size: LED display size is limited only by budget and physical space constraints rather than panel manufacturing limitations. Organizations can create massive displays spanning entire building facades or irregularly shaped installations following architectural features.
Excellent Viewing Angles: LED displays maintain brightness and color consistency across extremely wide viewing angles, often 160-170 degrees both horizontally and vertically. This characteristic makes LED ideal for locations where viewers approach from various angles.
Long Lifespan: Quality commercial LED displays deliver 100,000+ hours of operation before brightness degradation becomes noticeable. This extended lifespan—equivalent to over 11 years of continuous operation—reduces long-term replacement costs despite higher initial investment.
Weather Resistance: Outdoor-rated LED displays feature weatherproof enclosures protecting against rain, snow, dust, and temperature extremes. These displays operate reliably in environments that would destroy standard LCD displays within hours.
LED Display Limitations
Despite significant advantages, LED display technology presents challenges that make alternatives preferable for certain applications.
LED Challenges:
Higher Initial Cost: LED displays command premium pricing, particularly fine-pitch models suitable for indoor close-viewing applications. A fine-pitch LED display can cost 5-10x more per square foot than equivalent LCD video walls, though this cost differential narrows for very large installations.
Resolution Limitations at Close Range: Pixel pitch constraints mean LED displays viewed from typical indoor viewing distances (3-10 feet) show visible pixelation unless using extremely fine-pitch (and expensive) models. This limitation makes LED less suitable than LCD for applications requiring close viewing of detailed content.
Complex Installation: LED displays require specialized installation expertise including power distribution, signal processing, module alignment, and color calibration. This complexity increases installation costs and necessitates working with experienced integrators.
Power Consumption: High-brightness LED displays consume substantial power, particularly for outdoor installations. A large outdoor LED display might draw 25,000+ watts when displaying bright white content, creating significant operational electricity costs.
Maintenance Considerations: While individual LED modules can be replaced if damaged, servicing requires technical expertise and access to compatible spare parts. Organizations should establish maintenance agreements with qualified providers for mission-critical LED installations.
Ideal LED Applications
LED display technology excels in scenarios where its unique characteristics provide clear advantages over LCD alternatives.
Best Use Cases for LED:
- Outdoor digital signage: Building facades, roadside advertising, stadium perimeter boards requiring extreme brightness and weather resistance
- Large-format installations: Massive displays where seamless appearance matters and viewing distances exceed 15-20 feet
- Architectural integration: Curved displays, irregular shapes, or installations following building contours
- High-ambient-light environments: Windows, atriums, or locations with significant natural light where LCD brightness proves insufficient
- Sports facilities: Scoreboards, ribbon boards, and center-hung displays in arenas where brightness and wide viewing angles matter
- Retail flagship locations: Premium brand installations where seamless appearance and visual impact justify premium investment
LED Pricing Considerations
LED display pricing depends heavily on pixel pitch, size, indoor vs. outdoor rating, and installation complexity.
LED Cost Factors:
Indoor Fine-Pitch LED (1.2-2.5mm pitch): Suitable for indoor viewing from 6+ feet, fine-pitch LED displays typically cost $800-$2,500 per square foot for panels alone, with additional costs for control systems, installation, and calibration.
Indoor Standard-Pitch LED (2.6-5mm pitch): Appropriate for indoor viewing from 10+ feet, these displays cost $300-$800 per square foot, making them more accessible for large installations where close viewing isn’t required.
Outdoor LED (5-10mm pitch): Weatherproof outdoor LED displays for viewing from significant distances (15+ feet) typically cost $400-$1,200 per square foot depending on brightness, resolution, and protective features.
Ultra-Fine-Pitch LED (0.9-1.1mm): Premium indoor displays for close viewing applications can exceed $3,000-$5,000 per square foot, positioning them as alternatives to LCD only in applications where seamless appearance justifies extreme cost.

OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) Displays
OLED technology represents the premium display option offering superior image quality characteristics, though availability in large commercial formats remains limited and pricing stays elevated compared to LCD alternatives.
How OLED Technology Works
OLED displays use organic compounds that emit light when electricity is applied. Unlike LCD displays requiring backlighting, each OLED pixel produces its own light. This self-emissive characteristic enables unique performance benefits including perfect black levels and extremely thin form factors.
OLED Display Characteristics:
Self-Emissive Pixels: Each pixel generates its own light rather than modulating light from a backlight. When displaying black content, pixels simply turn off completely, eliminating light leakage and enabling infinite contrast ratios.
Thin, Flexible Substrates: OLED displays can be manufactured on flexible substrates enabling curved displays, transparent panels, or ultra-thin installations impossible with rigid LCD technology.
Wide Color Gamut: OLED displays typically cover wider color spaces than standard LCD panels, delivering more vivid, saturated colors particularly beneficial for advertising content, artistic displays, or premium brand installations.
OLED Display Advantages
OLED technology delivers image quality characteristics that position it as the premium option for specific high-value digital signage applications.
OLED Strengths:
Perfect Black Levels: Because OLED pixels turn off completely for black content, these displays achieve absolute black and infinite contrast ratios. This characteristic creates stunning image depth particularly noticeable when displaying high-contrast content like white text on black backgrounds or cinematic content with dark scenes.
Superior Color Accuracy: OLED displays deliver exceptional color accuracy and saturation across the color spectrum. This color performance makes OLED particularly attractive for applications where precise color reproduction matters: art galleries, luxury retail, photography displays, or brand installations with strict color requirements.
Extremely Wide Viewing Angles: OLED displays maintain color and brightness consistency across virtually any viewing angle without the color shift characteristic of LCD technology. This benefit proves valuable in installations where viewers approach from diverse angles.
Ultra-Thin Form Factor: OLED panels measure only a few millimeters thick, enabling sleek wall-mounted installations where minimal protrusion matters. Some OLED displays can be mounted flush against walls appearing almost painted-on.
Fast Response Time: OLED pixels transition between states nearly instantaneously without the motion blur that can affect LCD displays when showing fast-moving content. This characteristic benefits applications displaying video, animation, or rapidly changing content.
Transparent Display Options: Unique to OLED technology, transparent displays allow viewing content overlaid on visible backgrounds. These specialized displays create attention-grabbing installations in retail windows or museum cases where transparency provides design value.
OLED Display Limitations
Despite superior image quality, OLED technology presents significant limitations currently restricting widespread digital signage adoption.
OLED Challenges:
Limited Large-Format Availability: Commercial OLED displays remain largely limited to 55-65 inch sizes with only limited availability of larger formats. Organizations requiring displays exceeding 65 inches must generally choose LCD or LED alternatives.
Burn-In Risk: OLED displays face image retention (temporary) or burn-in (permanent) when showing static content elements for extended periods. This vulnerability makes OLED problematic for applications displaying consistent logos, menus, or interface elements that occupy fixed screen positions.
Lower Brightness: OLED displays typically deliver 300-500 nits brightness, significantly less than commercial LCD displays. This limitation restricts OLED to controlled-lighting environments and makes them unsuitable for high-ambient-light locations or window-facing installations.
Premium Pricing: OLED displays command 2-4x the cost of equivalent LCD panels while offering fewer size options and shorter operational lifespans. This price premium limits OLED adoption to applications where superior image quality justifies additional investment.
Shorter Lifespan: OLED displays degrade faster than LCD alternatives, with brightness reducing to 50% of original output after approximately 30,000-50,000 hours depending on usage patterns. This shorter lifespan increases long-term total cost of ownership.
Limited Brightness Sustainability: OLED displays showing bright content (particularly full white screens) for extended periods can experience accelerated degradation. This characteristic makes OLED less suitable for applications requiring sustained high brightness.
Ideal OLED Applications
OLED technology serves niche digital signage applications where its superior image quality provides clear value despite limitations and premium pricing.
Best Use Cases for OLED:
- Luxury retail: Premium brand installations where superior image quality reinforces brand positioning
- Art galleries and museums: Interactive museum displays where accurate color reproduction and perfect blacks enhance artistic content
- Executive spaces: Corporate reception areas, executive offices, or boardrooms where premium aesthetics justify additional investment
- Product showcases: High-end product displays where image quality influences purchasing decisions
- Transparent display applications: Retail windows or showcase installations leveraging transparent OLED technology
- Temporary installations: Short-term premium installations where limited lifespan concerns matter less
OLED Pricing Considerations
OLED display pricing reflects premium positioning with limited commercial availability in large formats.
OLED Cost Factors:
Commercial OLED Displays (55-65 inches): Professional-grade OLED displays in available sizes typically cost $3,500-$8,000, representing 2-3x the cost of equivalent commercial LCD panels. These displays target applications where image quality justifies premium investment.
Transparent OLED Displays: Specialized transparent OLED panels command even higher pricing, often $8,000-$15,000 for 55-inch displays due to limited production volumes and unique characteristics.
Larger Format Limitations: Very limited availability of commercial OLED displays exceeding 77 inches, with extremely high pricing (often $20,000+) making LCD or LED alternatives more practical for large-format requirements.

Specialized Display Technologies
Beyond mainstream LCD, LED, and OLED options, several specialized display technologies serve specific digital signage niches with unique requirements.
E-Paper and Electronic Ink Displays
E-paper displays use electronic ink technology that reflects ambient light rather than emitting light, creating paper-like readability with exceptional energy efficiency.
E-Paper Characteristics:
- Ultra-low power consumption: Displays maintain static images without power, consuming energy only during image updates
- Excellent sunlight readability: Reflective technology works better in bright conditions rather than worse like emissive displays
- Limited refresh rate: Slow transition speeds (typically 1-2 seconds) restrict e-paper to static or infrequently changing content
- Monochrome or limited color: Most e-paper displays show grayscale, though color e-paper options exist with limited color gamut
- Ideal applications: Outdoor menu boards, transportation schedules, meeting room booking displays, retail shelf labels, or any application with static content and outdoor visibility requirements
Transparent LED Displays
Transparent LED displays feature see-through construction allowing viewing of content while maintaining visibility through the display to backgrounds behind.
Transparent LED Benefits:
- Architectural integration: Window installations that don’t block natural light or views
- Attention-grabbing aesthetics: Unique visual impact distinguishes transparent displays from conventional screens
- Dual functionality: Maintain window transparency while displaying dynamic content
- Reduced brightness perception: See-through construction reduces brightness perception from behind while maintaining viewing from front
- Ideal applications: Retail windows, building facades, interior architectural glass, automotive showrooms, or any installation where transparency provides value
Projection Displays
While not screens themselves, projection systems serve many digital signage applications through large-format image projection onto walls or specialized surfaces.
Projection Display Considerations:
Advantages:
- Extremely large image sizes: Project 100+ inch images more cost-effectively than equivalent direct-view displays
- Flexible installation: Project onto various surfaces including walls, floors, irregular surfaces, or specialized projection screens
- Interactive capabilities: Add interactivity through interactive projection systems detecting touch or gesture input
- Portable options: Some projection applications benefit from portable projector configurations
Limitations:
- Ambient light sensitivity: Projection quality degrades significantly in well-lit environments
- Lamp replacement: Projector lamps require periodic replacement adding maintenance costs and potential downtime
- Viewing angle constraints: Projected images wash out when viewing from extreme angles
- Space requirements: Front-projection requires clear space between projector and screen; rear-projection needs depth behind screen
Ideal Applications: Conference rooms, auditoriums, temporary installations, very large format displays in controlled lighting, or interactive floor projections
High-Brightness Window Displays
Specialized high-brightness displays designed for window-facing installations bridge the gap between standard LCD displays and outdoor LED panels.
Window Display Features:
- 2,500-5,000 nit brightness: Sufficient for visibility in window locations with direct sunlight exposure
- Optical bonding: Reduced reflections and glare through optical bonding of glass layers
- Enhanced thermal management: Robust cooling systems handling heat from both high-brightness backlights and solar heat gain
- Auto-brightness sensors: Automatic brightness adjustment based on ambient light conditions optimizing visibility while managing power consumption
- Ideal applications: Retail window displays, bank branch windows, quick-service restaurant menu boards in window locations
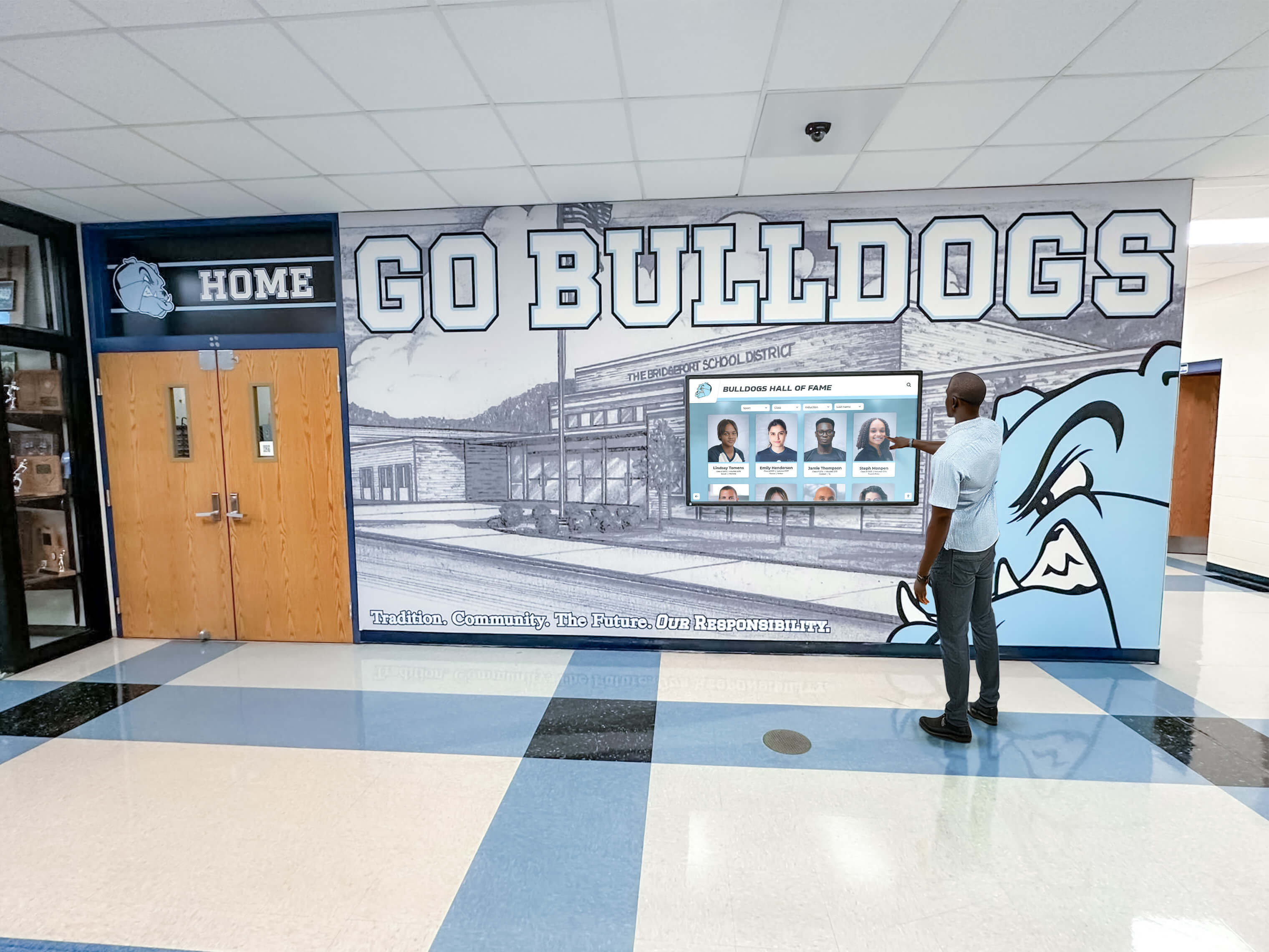

Touchscreen Technology Options
Many digital signage applications benefit from interactive touchscreen capabilities enabling user engagement beyond passive content viewing. Several touchscreen technologies exist, each with distinct characteristics.
Infrared (IR) Touch
Infrared touch systems use an invisible IR grid across the display surface detecting interruptions caused by touches.
Infrared Touch Characteristics:
Advantages:
- Excellent optical clarity: No overlay attenuating display brightness or affecting image quality
- Any input method: Responds to fingers, gloves, styluses, or any object interrupting IR beams
- Durable: No surface coating to wear or scratch over time
- Large format support: IR touch scales effectively to very large displays without performance degradation
Limitations:
- Frame around display: IR emitters and receivers create a frame projecting slightly beyond screen surface
- Susceptible to debris: Dust or debris on screen surface can trigger false touches
- Limited multi-touch: Most IR touch systems support 2-10 touch points rather than extensive multi-touch
Best Uses: Digital hall of fame displays, wayfinding kiosks, educational exhibits, or applications requiring large format touchscreens
Projected Capacitive (PCAP) Touch
Projected capacitive technology—the same technology used in smartphones and tablets—offers responsive, precise multi-touch capabilities.
PCAP Touch Characteristics:
Advantages:
- Excellent responsiveness: Highly accurate, fast response with smooth gesture recognition
- Extensive multi-touch: Support for 10+ simultaneous touch points enabling sophisticated gestures
- Sleek appearance: Smooth glass surface with no visible frame or gaps
- Durable glass surface: Hardened glass provides scratch resistance and easy cleaning
Limitations:
- Touch input requirements: Requires conductive input (bare fingers or capacitive stylus); doesn’t work with gloves or non-conductive objects
- Size limitations: Large format PCAP touch becomes expensive; practical size limits around 55-65 inches
- Higher cost: Premium pricing compared to resistive or IR alternatives
Best Uses: Interactive exhibits, retail product configurators, building directories, or applications requiring smartphone-like touch experience
Resistive Touch
Resistive touch technology uses pressure-sensitive overlays detecting physical pressure applied to screen surface.
Resistive Touch Characteristics:
Advantages:
- Any input method: Works with fingers, gloves, styluses, or any object applying pressure
- Lower cost: Generally less expensive than capacitive or IR alternatives
- Dirt/moisture tolerance: Continues working with dirty, wet, or gloved hands
Limitations:
- Reduced optical clarity: Touch overlay reduces display brightness and clarity
- Limited multi-touch: Most resistive touch supports single touch only
- Pressure requirement: Requires deliberate pressing rather than light touch
- Durability concerns: Overlay surface can wear or get damaged with heavy use
Best Uses: Industrial settings, outdoor kiosks in harsh environments, applications requiring gloved operation, or budget-conscious interactive installations
Optical Touch
Optical touch systems use cameras detecting touch positions through optical sensing without requiring any overlay on display surface.
Optical Touch Characteristics:
Advantages:
- Perfect optical clarity: No overlay affecting display brightness or image quality
- Extensive multi-touch: Support for numerous simultaneous touch points
- Large format capability: Scales effectively to very large displays
- Any input method: Responds to fingers, gloves, stylus, or any object
Limitations:
- Bezel requirements: Requires bezels around display housing camera systems
- Viewing angle sensitivity: Touch accuracy can degrade at extreme viewing angles
- Higher cost: Premium pricing compared to some alternatives
Best Uses: Large-format interactive displays, video walls with touch capabilities, museum installations, or applications where optical clarity and multi-touch matter

Screen Selection Criteria for Different Applications
Choosing the optimal screen technology requires matching technical characteristics with specific application requirements, environmental conditions, and budget parameters.
Educational Institution Digital Signage
Schools, colleges, and universities implement digital signage for diverse applications from academic recognition to wayfinding to event promotion.
Educational Environment Considerations:
Screen Technology Recommendations:
- Main hallway recognition displays: 55-65 inch commercial LCD displays with IR touchscreen capabilities provide excellent balance of cost, durability, and interactive engagement
- Cafeteria menu boards: Multiple 43-55 inch commercial LCD displays in portrait or landscape orientation offer clear visibility from dining areas
- Entrance wayfinding: Large-format 75-86 inch commercial LCD displays with high brightness (500+ nits) ensure visibility in naturally lit entrance areas
- Classroom scheduling: Small 10-15 inch commercial displays or e-paper panels outside classrooms showing schedules with minimal power consumption
Key Selection Factors:
- Durability for high-traffic environments: Commercial-grade construction withstanding bumps, vibration, and heavy use
- Easy content management: User-friendly content management systems allowing faculty and staff to update information without technical expertise
- Appropriate viewing distances: Interactive touchscreen displays positioned at accessible heights with screen sizes appropriate for typical viewing distances
- Budget considerations: Educational institutions often need cost-effective solutions balancing quality with fiscal constraints
Corporate Office Digital Signage
Corporate environments use digital signage for employee communication, visitor management, meeting room scheduling, and workplace recognition.
Corporate Environment Considerations:
Screen Technology Recommendations:
- Lobby recognition displays: 55-75 inch premium commercial LCD displays or OLED panels creating sophisticated first impressions
- Internal communications: Multiple networked 43-55 inch commercial LCD displays throughout office spaces sharing company news and metrics
- Conference room scheduling: 10-15 inch tablet-sized displays or e-paper screens outside meeting rooms showing real-time booking status
- Employee recognition walls: Large-format touchscreen displays (65-75 inches) with IR or PCAP touch technology enabling interactive employee profiles
Key Selection Factors:
- Professional aesthetics: Slim bezels, clean mounting, and modern appearance supporting corporate brand image
- Network integration: Seamless integration with calendar systems, communication platforms, and employee databases
- Remote management: IT department ability to manage content, monitor display health, and troubleshoot remotely
- Conference room compatibility: Integration with scheduling systems and video conferencing platforms
Retail Digital Signage
Retail environments leverage digital signage for advertising, product information, promotional content, and interactive product exploration.
Retail Environment Considerations:
Screen Technology Recommendations:
- Window displays: High-brightness LCD (2,500+ nits) or transparent LED displays maintaining visibility in direct sunlight
- In-store advertising: Commercial LCD displays ranging from 43-75 inches positioned throughout retail spaces
- Interactive product kiosks: 32-55 inch PCAP touchscreen displays enabling product configuration and detailed information
- Video walls: LCD video walls with ultra-narrow bezels or fine-pitch LED displays creating impactful visual statements
Key Selection Factors:
- Brightness for window visibility: Sufficient brightness overcoming ambient light and direct sunlight exposure
- Content flexibility: Ability to quickly update promotional content, pricing, and seasonal campaigns
- Integration with point-of-sale: Connections to inventory systems, pricing databases, and sales platforms
- Attention-grabbing impact: High image quality and appropriate size creating stopping power in competitive retail environments
Healthcare Facility Digital Signage
Healthcare environments use digital signage for wayfinding, patient education, wait time information, and recognition of donors or medical staff.
Healthcare Environment Considerations:
Screen Technology Recommendations:
- Main lobby wayfinding: 55-75 inch commercial LCD displays or touchscreen kiosks providing directory and navigation information
- Waiting room content: Multiple 43-55 inch commercial LCD displays sharing patient education content and facility information
- Department recognition: Donor recognition displays using 55-65 inch touchscreen LCD panels highlighting supporter contributions
- Corridor wayfinding: Smaller 32-43 inch commercial displays at decision points providing directional guidance
Key Selection Factors:
- Infection control considerations: Smooth touchscreen surfaces allowing effective cleaning and sanitization protocols
- HIPAA compliance: Secure content management systems protecting patient information privacy
- Accessibility requirements: ADA-compliant mounting heights, text sizes, and contrast levels accommodating diverse patient populations
- Calming aesthetics: Professional appearance supporting healing environments rather than adding visual stress
Outdoor Digital Signage
Outdoor applications face extreme environmental challenges requiring specialized display technology and protective enclosures.
Outdoor Environment Considerations:
Screen Technology Recommendations:
- Direct sunlight locations: LED displays (5,000-10,000 nits) or high-brightness LCD displays (2,500-5,000 nits) providing visibility in brightest conditions
- Semi-outdoor/covered areas: High-brightness commercial LCD displays (1,500-2,500 nits) in weatherproof enclosures
- Outdoor menu boards: High-brightness LCD displays with weatherproof enclosures and thermal management systems
- Building facades: Large-format LED displays with appropriate pixel pitch for viewing distances and weatherproof construction
Key Selection Factors:
- Extreme brightness: Sufficient nit rating overcoming direct sunlight exposure
- Temperature management: Operating range covering extreme cold and heat with appropriate cooling/heating systems
- Weather protection: IP65 or higher rating protecting against rain, snow, dust, and humidity
- Vandalism resistance: Robust construction and protective measures preventing damage from vandalism or environmental impacts

Technical Specifications to Consider
Beyond basic display technology, numerous technical specifications impact display performance and suitability for specific applications.
Resolution and Pixel Density
Display resolution determines image sharpness and the amount of detail visible at various viewing distances.
Resolution Standards:
Full HD (1920x1080): Sufficient for most digital signage applications where viewing distances exceed 6-8 feet. Provides good text readability and image quality at reasonable cost points.
4K UHD (3840x2160): Beneficial for applications requiring close viewing (3-6 feet), very large displays where resolution must scale, or content with fine detail. 4K enables crisp text legibility and detailed imagery but requires appropriate content creation.
8K (7680x4320): Emerging resolution offering exceptional detail but limited content availability and significantly higher costs. Currently benefits only specialized applications requiring extreme close-up viewing of massive displays.
Resolution Selection Guidelines:
- Consider typical viewing distance: farther viewing distances make high resolutions unnecessary
- Match content resolution to display resolution to avoid scaling artifacts
- Balance resolution benefits against increased cost and content creation requirements
- Ensure media players and content delivery infrastructure support chosen resolution
Brightness Specifications
Display brightness directly impacts visibility in various ambient light conditions and determines appropriate installation locations.
Brightness Levels by Application:
300-400 nits: Suitable only for controlled-lighting environments with minimal ambient light. Adequate for residential use but insufficient for most commercial applications.
500-700 nits: Standard brightness for commercial indoor digital signage in typical ambient lighting. Appropriate for locations away from windows or bright overhead lighting.
1,000-1,500 nits: Enhanced brightness for challenging indoor environments with significant natural light or bright ambient lighting. Suitable for window-adjacent installations or brightly lit retail spaces.
2,500-5,000 nits: High brightness for window-facing displays, semi-outdoor locations, or direct sunlight exposure. Requires enhanced thermal management and increased power consumption.
5,000-10,000+ nits: Extreme brightness for outdoor LED displays requiring visibility in direct sunlight from significant distances.
Contrast Ratio
Contrast ratio measures the difference between brightest whites and darkest blacks, affecting image depth and perceived quality.
Contrast Considerations:
LCD displays: Typically offer 1,000:1 to 5,000:1 contrast ratios with higher numbers generally correlating with better image quality
OLED displays: Achieve infinite contrast ratios due to perfect black levels from turned-off pixels
Practical impact: Higher contrast ratios create more dynamic, engaging images particularly beneficial for video content and photography
Environment interaction: Ambient light reduces effective contrast ratio regardless of specifications; controlled lighting maximizes contrast benefits
Viewing Angles
Viewing angle specifications indicate how far off-axis viewers can be positioned before image quality degrades noticeably.
Viewing Angle Technologies:
TN (Twisted Nematic) Panels: Budget LCD technology with limited viewing angles (typically 90-120 degrees). Not recommended for digital signage where viewing from angles commonly occurs.
IPS (In-Plane Switching) Panels: Premium LCD technology offering wide viewing angles (typically 178 degrees). Standard for commercial digital signage applications requiring consistent image quality from various viewing positions.
VA (Vertical Alignment) Panels: Mid-range LCD technology offering better contrast than IPS but somewhat narrower viewing angles. Suitable for applications where straight-on viewing predominates.
LED and OLED: Excellent viewing angles maintaining brightness and color across wide viewing positions.
Response Time and Refresh Rate
Response time affects motion clarity while refresh rate impacts video smoothness and flicker perception.
Response Time:
- Measured in milliseconds (ms) indicating how quickly pixels change states
- Most commercial displays offer 6-12ms response time sufficient for digital signage content
- Critical primarily for video-intensive applications rather than static or slowly changing content
Refresh Rate:
- Typically 60Hz for commercial displays providing smooth motion for standard video content
- Higher refresh rates (120Hz+) benefit specialized applications like sports venues but unnecessary for most digital signage
Lifespan and Reliability Ratings
Commercial displays specify expected operational hours providing insight into long-term reliability and replacement planning.
Operational Hour Ratings:
Consumer TV (not recommended): 30,000-40,000 hours equivalent to 3-4 years of 24/7 operation but typically failing much sooner in commercial use
Commercial LCD 16/7: 60,000-70,000 hours designed for 16-hour daily operation equating to approximately 10 years of rated use
Commercial LCD 24/7: 70,000-100,000 hours designed for continuous operation equating to 8-11 years of constant use
LED displays: 100,000+ hours equivalent to over 11 years of continuous operation before brightness degrades to 50% of original output
Brightness half-life: Time until display brightness reduces to 50% of original output—the practical definition of lifespan

Installation and Integration Considerations
Successful digital signage implementation extends beyond screen selection to encompass mounting, connectivity, content management, and ongoing maintenance.
Mounting and Installation
Proper mounting ensures safety, optimal viewing angles, and professional appearance while accommodating accessibility requirements.
Mounting Options:
Wall Mounting: Most common installation method using commercial-grade wall mounts supporting display weight with appropriate security. Consider stud location, wall material, and future serviceability during planning.
Ceiling Mounting: Suspends displays from ceilings in locations where wall mounting proves impractical. Requires careful consideration of viewing angles, accessibility for maintenance, and structural support.
Floor Standing: Freestanding kiosks or pedestal mounts provide flexibility for locations where wall mounting isn’t feasible. Particularly common for interactive touchscreen applications requiring accessible positioning.
Video Wall Mounting: Specialized mounting systems for multi-display video walls ensure precise alignment, minimal bezels, and structural support for the cumulative weight of multiple displays.
Key Installation Factors:
- ADA compliance: Appropriate mounting heights and reach ranges for accessible installations
- Viewing angle optimization: Position displays accounting for typical viewer positions and sightlines
- Service accessibility: Allow access to display connections, power, and components for maintenance without complete removal
- Security considerations: Anti-theft mounting hardware and cable management preventing tampering
Content Management Systems
Effective content management systems enable easy content creation, scheduling, distribution, and monitoring across single displays or extensive networks.
CMS Capabilities:
Content Creation Tools: Integrated design tools allowing creation of content directly within CMS or import of content from design applications.
Scheduling and Playlisting: Ability to schedule content appearing at specific times, dates, or triggered by external conditions. Create playlists rotating through multiple content pieces.
Multi-Display Management: Centralized control enabling content distribution across multiple displays with grouping, targeting, and individual display control.
Remote Monitoring: Real-time monitoring of display status, health metrics, and playback confirmation from central management dashboard.
Integration Capabilities: Connections to external data sources like weather feeds, social media, databases, or scheduling systems enabling dynamic content.
User Permissions: Role-based access controls allowing appropriate users content editing capabilities while restricting system configuration to administrators.
Organizations like schools implementing comprehensive recognition display systems benefit significantly from robust content management enabling faculty and staff to easily update achievement information without technical expertise.
Power and Connectivity Requirements
Digital signage installations require careful planning of electrical power distribution and data connectivity.
Power Considerations:
Electrical Requirements:
- Ensure adequate power capacity at installation locations accounting for display power consumption plus media players and accessories
- Consider UPS (uninterruptible power supply) backup for critical applications requiring continuity during power interruptions
- Plan electrical outlet locations appropriately positioned for display installation
Energy Efficiency:
- Commercial displays with auto-brightness and scheduling features reduce operational costs through intelligent power management
- Consider total cost of ownership including electricity consumption over display lifespan
Connectivity Options:
Wired Connectivity: Ethernet connections provide reliable network connectivity for content delivery, remote management, and monitoring without wireless interference concerns.
Wireless Connectivity: WiFi connectivity offers installation flexibility but may face reliability or bandwidth challenges in some environments.
Video Inputs: HDMI, DisplayPort, or SDI connections from media players or other video sources with appropriate cable lengths and signal distribution for video walls.
USB and Additional Interfaces: USB ports for touchscreen connectivity, external storage, or peripheral devices.
Media Player and PC Requirements
Digital signage displays require media players or embedded computing systems for content playback and management.
Media Player Options:
Standalone Media Players: Dedicated external devices connecting to displays via HDMI providing content playback from network, USB, or internal storage. Offers flexibility to upgrade media players independently of displays.
System-on-Chip (SoC) Displays: Displays with integrated computing capabilities eliminating external media players. Simplified installation but potential limitations in computing power compared to standalone players.
PC-Based Systems: Full computers providing maximum flexibility and computing power for complex interactive applications or resource-intensive content. Higher cost and maintenance requirements than dedicated media players.
Selection Considerations:
- Match computing power to content complexity: video resolution, animations, interactivity
- Ensure compatibility with chosen content management system
- Consider management capabilities: remote configuration, monitoring, updates
- Evaluate total cost including hardware, software licensing, and ongoing support
Making the Right Choice: Decision Framework
Selecting optimal screen technology requires systematic evaluation of technical requirements, environmental conditions, budget parameters, and application-specific needs.
Assessment Questions
Application Requirements:
- What is the primary purpose? (Recognition, wayfinding, advertising, information, entertainment)
- Will users interact with displays or view passively?
- What type of content will display? (Static images, video, detailed text, simple graphics)
- How frequently will content change?
Environmental Factors:
- Indoor or outdoor installation?
- What are ambient lighting conditions? (Natural light, bright overhead lighting, controlled lighting)
- What are temperature conditions? (Climate-controlled or temperature extremes)
- What is the expected viewing distance range?
- What are viewing angles? (Straight-on only or wide angles required)
Technical Specifications:
- What size display(s) are appropriate for space and viewing distance?
- What resolution provides sufficient detail at viewing distance?
- What brightness level ensures visibility in ambient lighting?
- What operational hours are required? (8/5, 16/7, 24/7)
Budget Considerations:
- What is the initial hardware budget per display?
- What are acceptable operational costs for electricity and maintenance?
- What is the expected display lifespan and replacement cycle?
- Are interactive capabilities required, and if so, what touch technology fits needs and budget?
Integration Requirements:
- What content management capabilities are needed?
- What data sources or systems require integration?
- What remote management capabilities are necessary?
- What network infrastructure exists or needs implementation?
Technology Selection Matrix
For Indoor Commercial Applications (Schools, Offices, Retail): Commercial LCD displays with 500-700 nit brightness, Full HD or 4K resolution, IPS panels, and 24/7 or 16/7 ratings provide optimal balance of cost, performance, and reliability for most applications.
For Interactive Recognition Displays: 55-75 inch commercial LCD displays with infrared or PCAP touchscreen technology offer excellent user experience for digital halls of fame, alumni recognition, or donor walls. Solutions like Rocket Alumni Solutions provide comprehensive packages including hardware, software, content design, and ongoing support specifically optimized for recognition applications.
For Large-Format Impressive Installations: LED video walls or LCD video walls with ultra-narrow bezels create impactful large-format displays for atriums, lobbies, or flagship locations where visual statement justifies investment.
For Window or High-Brightness Applications: High-brightness LCD displays (2,500-5,000 nits) in weatherproof enclosures provide visibility in challenging lighting conditions for window displays or semi-outdoor locations.
For Outdoor Digital Signage: Direct-view LED displays with appropriate pixel pitch, extreme brightness (5,000+ nits), and weatherproof ratings withstand outdoor conditions while delivering visibility in direct sunlight.
For Premium Image Quality Applications: OLED displays deliver superior image quality with perfect blacks and exceptional colors for luxury retail, art galleries, or executive spaces where image quality justifies premium investment and shorter lifespan.
For Budget-Conscious Implementations: Entry-level commercial LCD displays in smaller sizes (32-43 inches) provide commercial-grade reliability at accessible price points for organizations with budget constraints.
Conclusion: Investing in the Right Screen Technology
Selecting appropriate screen technology for digital signage represents a strategic investment impacting daily operations, user experience, and long-term costs for years following initial installation. The decision extends well beyond comparing specifications to understanding how technical characteristics align with specific application requirements, environmental conditions, budget realities, and organizational objectives.
While consumer TVs might appear to offer cost savings, commercial-grade displays provide superior reliability, appropriate brightness, longer operational lifespans, and essential features justifying their investment through years of dependable service. The difference between a display failing after 18 months versus performing reliably for 8-10 years dramatically impacts total cost of ownership beyond initial purchase price differences.
For most indoor digital signage applications, commercial LCD displays deliver an excellent balance of image quality, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. LED displays serve specific scenarios requiring extreme brightness, seamless large-format installations, or outdoor durability. OLED technology remains a premium niche option for applications where superior image quality justifies additional investment and operational considerations.
Interactive touchscreen capabilities transform passive digital signage into engaging experiences particularly valuable for recognition displays, wayfinding applications, or information kiosks. Selecting appropriate touch technology—infrared, capacitive, resistive, or optical—depends on specific application requirements including display size, budget, user expectations, and environmental conditions.
Key Principles for Screen Selection Success:
- Match technology to application: Choose screen characteristics aligned with specific viewing conditions, content types, and user interactions rather than selecting based on specifications alone
- Prioritize commercial-grade displays: Invest in displays designed for commercial applications rather than consumer TVs regardless of claimed compatibility
- Consider total cost of ownership: Evaluate not just purchase price but operational costs, expected lifespan, maintenance requirements, and replacement cycles
- Plan for integration: Ensure screen selection aligns with available mounting options, network infrastructure, content management systems, and organizational technical capabilities
- Future-proof investments: Select technology and infrastructure supporting growth, content evolution, and emerging capabilities over multi-year operational horizons
Organizations planning recognition displays for schools, alumni centers, corporate offices, or community spaces benefit from comprehensive solutions integrating appropriate screen technology with purpose-built software, content design, and ongoing support. Specialized providers understand the unique requirements of recognition applications and deliver turnkey solutions eliminating the complexity of independently sourcing displays, developing software, designing content, and managing ongoing operations.
Ready to implement professional digital signage that engages visitors and celebrates achievements for years to come? Partner with experts who understand both the technology and the specific needs of recognition displays, ensuring your investment delivers maximum value through superior hardware, intuitive software, compelling content design, and reliable support.