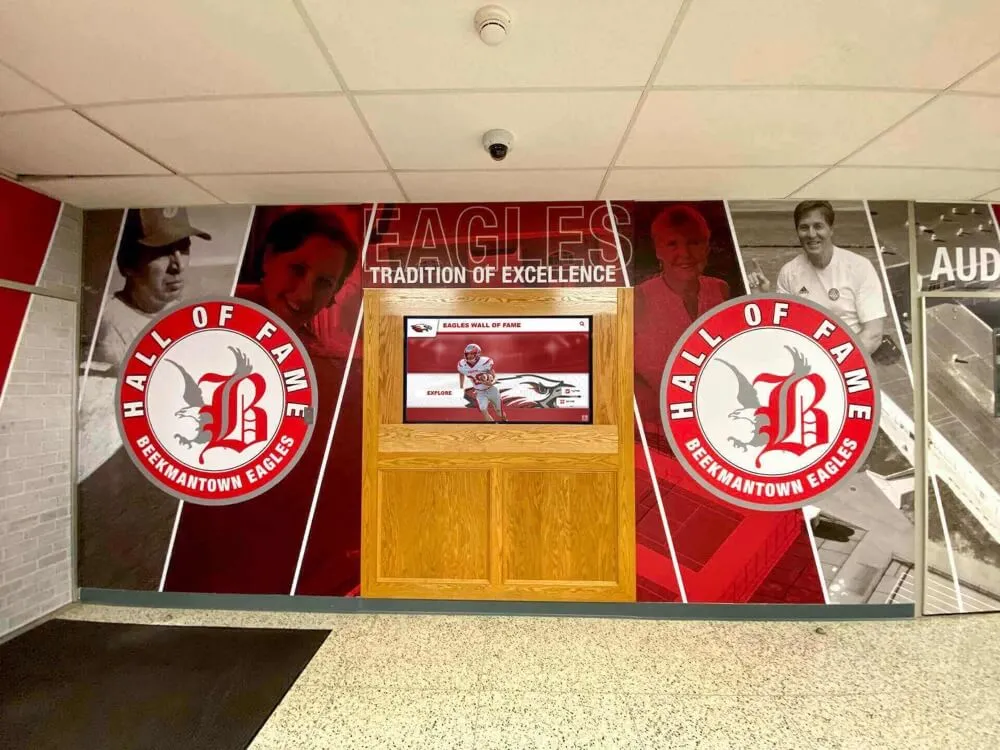
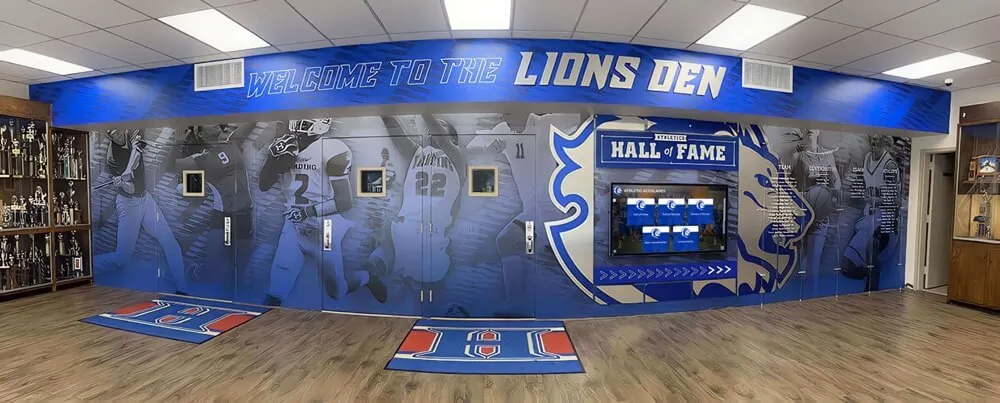
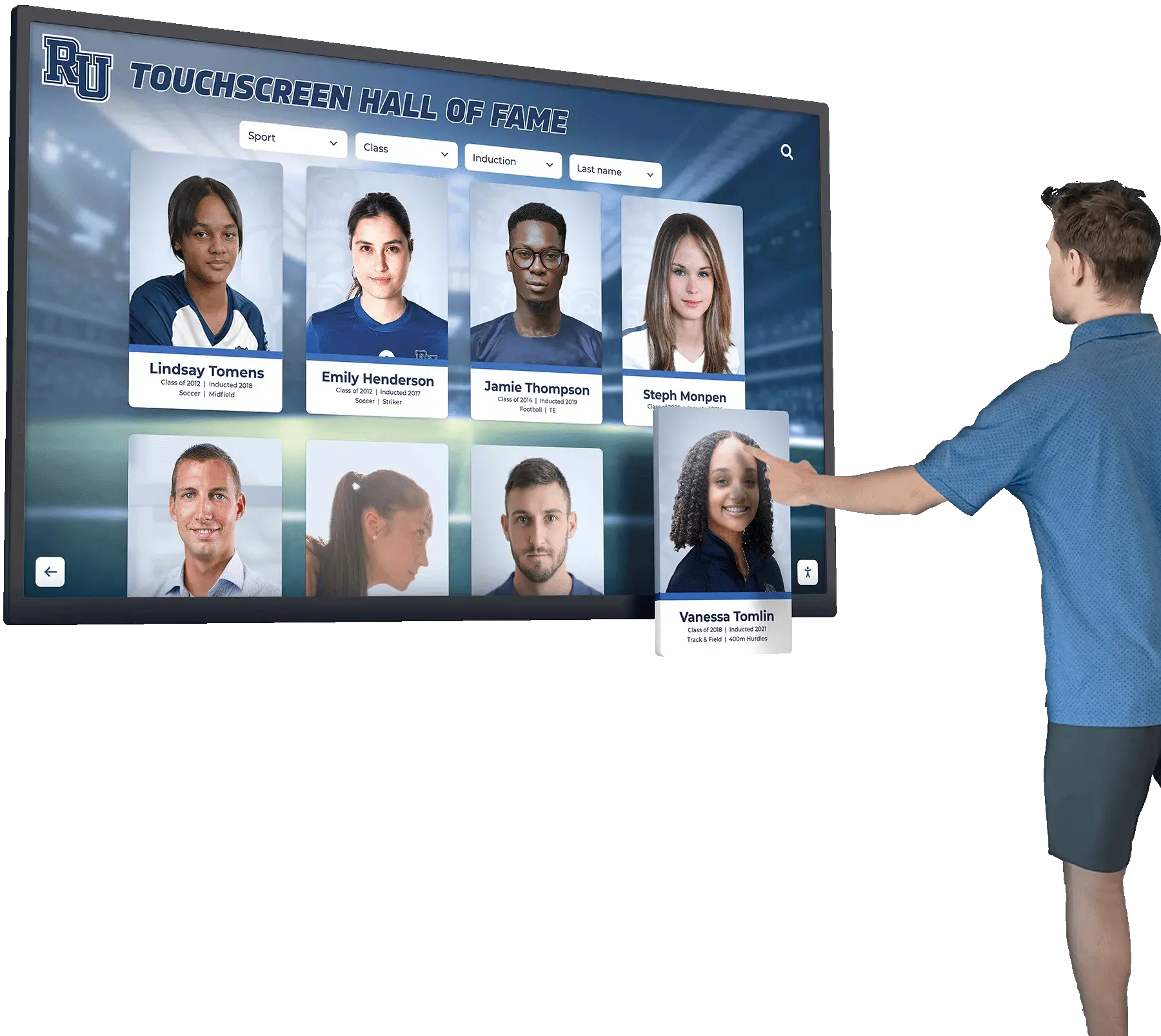
Statewide hall of fames represent the pinnacle of recognition within state communities, celebrating exceptional achievement across athletics, academics, public service, and cultural contributions. Unlike institution-specific programs, statewide halls of fame honor individuals whose excellence transcends individual schools or organizations to represent the best of what an entire state produces. From state athletic hall of fames recognizing championship coaches and legendary athletes to academic recognition programs celebrating educational pioneers, statewide recognition creates inspiring models of achievement while building community pride across diverse populations and geographic regions.
Whether you’re involved with an established state recognition program seeking to enhance capabilities, considering launching a new statewide hall of fame, or researching best practices for state-level recognition, this guide provides practical insights for creating meaningful celebration that honors achievement while strengthening community bonds across entire states.
Understanding Statewide Hall of Fame Programs
Statewide hall of fames operate at a unique scale, recognizing excellence that represents the best of what entire state communities produce across various achievement categories.
What Distinguishes State-Level Recognition
State hall of fames differ fundamentally from institutional programs in scope, selectivity, and purpose. They honor individuals whose achievements carry significance beyond single schools, teams, or organizations to represent state-level excellence worthy of celebration by entire communities.
Broader Geographic Reach: State programs draw candidates from across entire states, creating diverse inductee pools representing urban and rural communities, large and small institutions, and different demographic populations. This geographic diversity ensures recognition reflects complete state communities rather than specific regional achievements.
Higher Selectivity Standards: Because state halls of fame represent the highest tier of recognition within state communities, selection criteria typically prove more demanding than institutional programs. Inductees generally achieve at national or international levels, earn recognition that brings honor to their states, or demonstrate sustained excellence over extended careers that establish them as generational leaders within their fields.
Cross-Community Celebration: State recognition creates opportunities for communities that might not otherwise connect to celebrate shared excellence. Rural communities see their exceptional individuals honored alongside metropolitan achievers, creating pride that transcends typical urban-rural divides. Small schools gain equal representation with large programs when excellence meets established standards.
Historical Preservation at Scale: State programs preserve achievement histories that might otherwise fragment across hundreds of individual institutions. They create comprehensive records documenting how excellence in athletics, academics, service, or other categories has evolved across decades within specific states.

Common Types of Statewide Hall of Fame Programs
Different states implement various recognition programs celebrating diverse achievement categories based on state traditions, cultural priorities, and historical strengths.
State Athletic Hall of Fame Programs
Athletic recognition represents the most common type of statewide hall of fame, celebrating coaching excellence, exceptional student-athlete achievement, sports administration leadership, and significant contributions to athletic program development.
State athletic halls of fame typically recognize multiple categories including high school coaches whose career achievements and player development establish them as state legends, outstanding high school athletes who excelled at state level competition and often continued to collegiate or professional success, college coaches and athletes whose achievements brought recognition to state universities, professional athletes with state connections through birth, education, or residence, sports officials and administrators whose service elevated state athletic programs, and contributors whose support enabled athletic excellence across state communities.
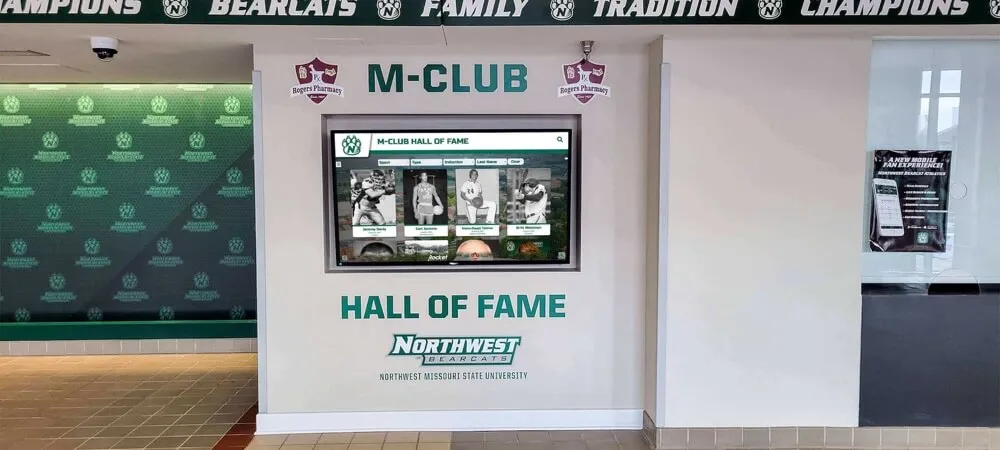
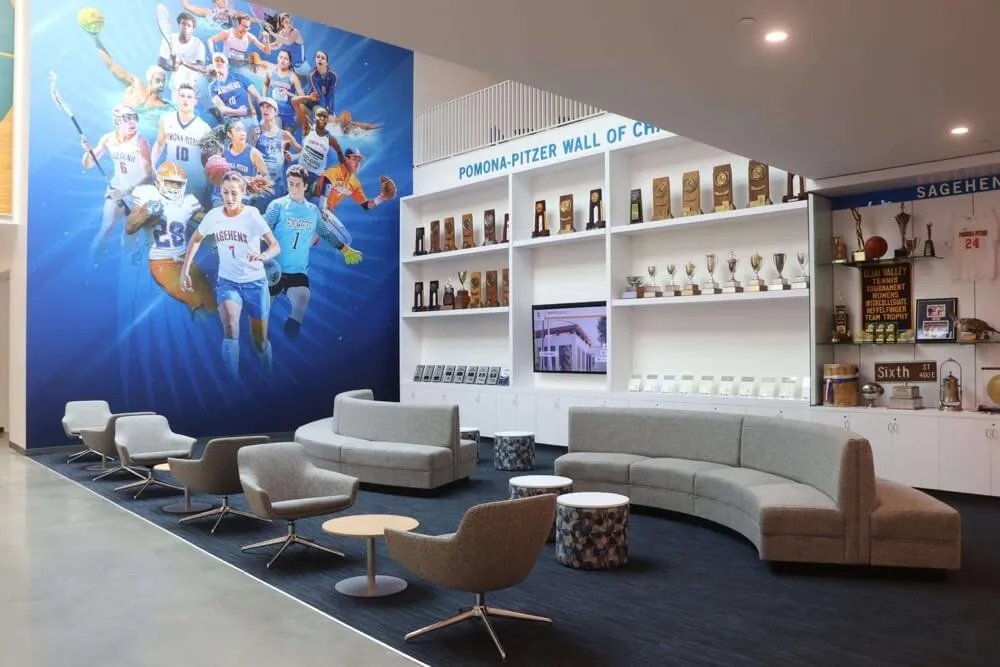
Many states maintain dedicated athletic hall of fame facilities—museums or recognition centers where visitors explore state sports history through interactive displays, archived photographs and memorabilia, video highlights of legendary performances, and comprehensive databases documenting recognized achievers.
Academic and Educational Recognition Programs
Some states implement academic hall of fame programs celebrating educational excellence including pioneering educators whose innovative methods influenced state education practices, educational administrators who advanced state school systems, researchers whose work brought recognition to state universities, and students whose academic achievements reached exceptional levels bringing honor to their states.
These programs prove less common than athletic recognition but serve important purposes in states valuing educational achievement alongside athletic success. They demonstrate that intellectual excellence deserves celebration equal to athletic accomplishment while inspiring current students to pursue academic goals with same dedication that athletes bring to sport.
State Sports-Specific Hall of Fame Programs
Certain states with strong traditions in particular sports maintain specialized recognition programs. States with dominant football traditions might operate dedicated football halls of fame, basketball-focused states celebrate hardwood legends separately, and states with strong baseball or wrestling heritage create sport-specific recognition.
Sport-specific programs enable deeper recognition within particular athletic categories, honoring achievements that might not reach the broad standards required for general state athletic halls of fame but deserve celebration within their specific sports. They create opportunities for specialized communities—football coaches, wrestling families, baseball enthusiasts—to celebrate shared traditions and excellence.
Public Service and Leadership Recognition
Some states implement hall of fame programs recognizing exceptional public service, governmental leadership, military service, or community contribution. These programs celebrate individuals whose service to state communities deserves permanent recognition alongside athletic and academic achievers.

Benefits of Statewide Hall of Fame Programs
State recognition systems deliver valuable benefits to multiple constituencies while serving important cultural and historical preservation functions.
Inspiring Achievement Across State Communities
State halls of fame create aspirational models demonstrating what’s possible for students, athletes, and professionals across entire state communities. When young people see that individuals from their specific towns, schools, or circumstances achieved recognition at state level, abstract possibilities become tangible goals.
Geographic Inspiration: Recognition showcasing achievers from diverse communities demonstrates that excellence can emerge anywhere. Rural students see that state recognition isn’t reserved for metropolitan areas. Small school athletes understand that program size doesn’t determine recognition eligibility when individual excellence meets established standards.
Pathway Documentation: State programs document developmental pathways showing how recognized achievers progressed from local success through state recognition to national or international achievement. These documented journeys provide inspiring examples for current students and athletes pursuing their own excellence.
Standards Clarification: State recognition establishes clear excellence benchmarks, helping students, athletes, coaches, and educators understand what achievement levels merit state-level celebration. These standards create concrete targets that inspire elevated performance across state programs.
Preserving State History and Heritage
Comprehensive state hall of fame programs create permanent records preserving achievement histories that might otherwise disperse across countless individual institutions as decades pass.
Centralized Historical Documentation: State programs aggregate achievement records that would otherwise exist only in scattered school archives, fading newspaper clippings, or personal memory. This centralization ensures that future generations can access complete state history rather than fragmented institutional records.
Cultural Continuity: Recognition programs document how achievement in athletics, academics, or service has evolved across generations within specific states. They show cultural continuity—how values around excellence, sportsmanship, education, or service have persisted even as achievement forms evolved with changing social contexts and opportunities.
Accessibility for Research: Centralized state recognition records support historical research, documentary production, educational program development, and cultural preservation projects that benefit from access to comprehensive achievement documentation spanning decades.
Building State Pride and Identity
State hall of fame programs strengthen community identity by celebrating shared excellence that transcends individual loyalties to specific schools, teams, or regions.
Shared Celebration: Recognition ceremonies and facilities create opportunities for diverse state communities to gather around shared celebration of excellence. These gatherings build social capital and strengthen state identity through positive shared experiences that unite rather than divide.
Positive State Representation: State halls of fame showcase positive state narratives highlighting achievement, dedication, and excellence rather than negative stereotypes or limitations. They demonstrate state quality through documented accomplishment across multiple domains.
Cross-Community Connection: State recognition connects communities that might not otherwise interact. When rural and urban communities, different demographic populations, or various geographic regions see their exceptional individuals honored together, they develop broader state identity beyond narrow local loyalties.
Solutions like Rocket Alumni Solutions provide digital platforms enabling state organizations to create comprehensive recognition programs that preserve history while building community engagement across diverse populations and geographic regions.

Establishing Effective Selection Criteria
Credible state hall of fame programs require clear, defensible selection criteria ensuring that recognition maintains meaningful standards while remaining accessible to deserving candidates regardless of school size, geographic location, or demographic background.
Defining Achievement Standards
State programs must balance selectivity that maintains recognition prestige with inclusiveness ensuring that excellence from all state communities receives consideration.
Quantifiable Achievement Thresholds: Effective criteria establish specific achievement benchmarks that prevent subjective decision-making while providing clear standards. Athletic programs might require state championship coaching records, All-American athlete selections, professional sport achievement, or statistical milestones. Academic programs establish GPA standards, research publication requirements, innovation documentation, or teaching excellence metrics.
Timing and Eligibility Windows: Most state programs require minimum waiting periods between achievement completion and hall of fame eligibility, typically 10-25 years depending on achievement category. These waiting periods ensure that recognition celebrates sustained excellence and lasting impact rather than recent accomplishment.
Categorical Recognition: State programs often establish multiple recognition categories ensuring diverse achievement types receive appropriate celebration. Athletic halls of fame might separately recognize coaches, athletes, and contributors. Academic programs distinguish researchers, teachers, and administrators. This categorical approach ensures that different contribution types receive evaluation against appropriate standards rather than competing against incomparable achievements.
Geographic and Institutional Balance: While criteria should remain purely achievement-focused, selection committees should monitor whether recognition patterns inadvertently favor particular regions or institution types. If metropolitan areas or large schools dominate inductee pools despite excellence existing across state communities, committees should examine whether criteria unconsciously disadvantage certain populations.
Character and Conduct Requirements
Beyond achievement standards, many state programs require that candidates maintain character and conduct standards reflecting state values and ensuring recognition celebrates complete excellence rather than just athletic or academic accomplishment.
Values Alignment: Programs typically require that candidates throughout their careers exemplified values like sportsmanship, integrity, leadership, and community service that align with state identity and organizational missions. This values emphasis ensures recognition celebrates individuals worthy of serving as role models beyond their specific achievement domains.
Post-Achievement Conduct: Some programs require that candidates maintain exemplary conduct after their primary achievement periods, preventing recognition of individuals whose later behavior contradicts values that hall of fame honor represents. This requirement proves occasionally controversial but protects program integrity.
Documented Evidence: Character requirements should rely on documented evidence rather than subjective opinion or unverified claims. Programs might consider formal disciplinary records, legal proceedings, verified ethical violations, or documented patterns of behavior rather than isolated incidents or unsubstantiated allegations.
Selection Committee Composition and Process
Effective selection processes require diverse committee representation, transparent procedures, and documented decision rationales maintaining community confidence in program integrity.
Representative Committee Structure: State programs should include committee members representing different geographic regions, institutional types, demographic populations, and expertise areas. This diversity ensures multiple perspectives inform selection decisions while preventing domination by particular constituencies or interest groups.
Rotating Membership: Regular committee rotation brings fresh perspectives while preventing entrenchment that might lead to predictable patterns favoring particular achievement types or candidate profiles. Staggered terms maintain institutional memory while ensuring consistent membership evolution.
Transparent Processes: Programs should publish selection criteria, nomination procedures, evaluation methods, and decision timelines enabling interested parties to understand processes and participate effectively. Transparency builds community confidence while reducing questions about decision fairness.
Documented Rationales: Recording selection rationales creates accountability while establishing precedents guiding future decisions. Documentation enables committees to explain selections when questioned and helps future committees understand past decision patterns.
Many state athletic recognition programs leverage these selection best practices to maintain credibility while celebrating diverse excellence across their communities.
Modern Recognition Technology for State Programs
Digital recognition technology has transformed state hall of fame capabilities, addressing space limitations of physical displays while enabling engagement features impossible with traditional plaques or trophy cases.
Overcoming Physical Display Limitations
Traditional state hall of fame facilities face inevitable space constraints as programs mature and inductee populations grow across decades. Physical museums accommodate only limited display space for plaques, photographs, and memorabilia. As inductee numbers grow, facilities must make difficult decisions about selective display, reduced space per inductee, or expensive facility expansion.
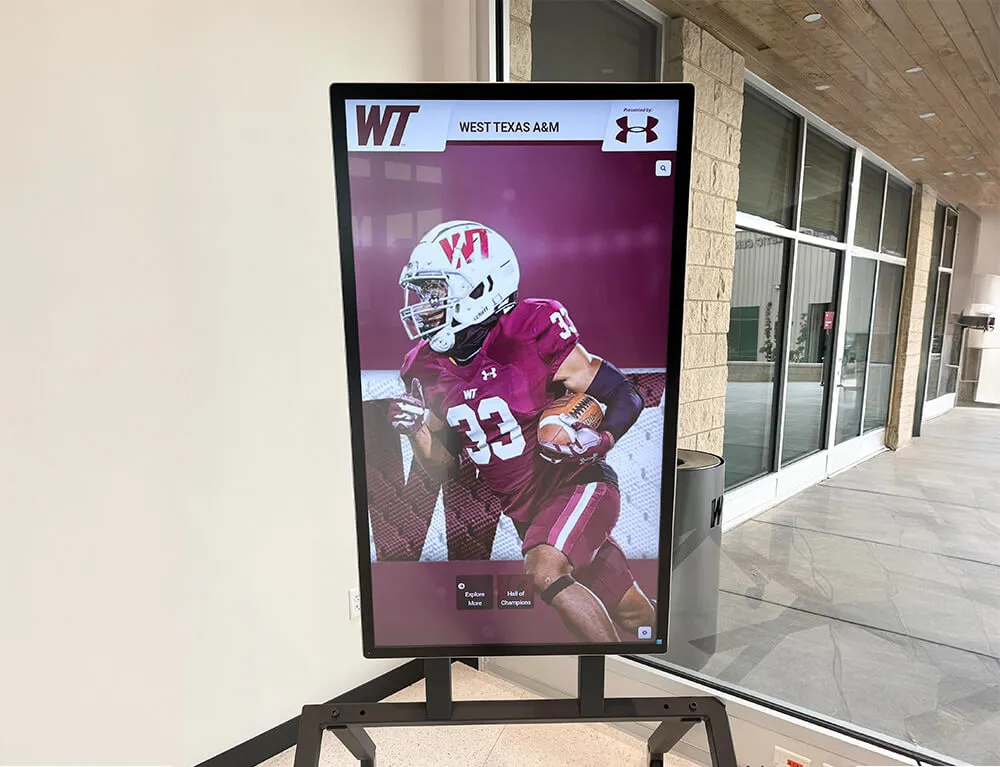
Unlimited Digital Capacity: Digital recognition systems eliminate space constraints entirely. State programs can honor unlimited inductees with comprehensive profiles including biographical information, achievement documentation, multimedia content, and historical context. Every deserving individual receives thorough recognition regardless of total inductee populations.
Scalable Implementation: Digital platforms scale effortlessly as programs grow. Adding new inductees requires simple content management system updates taking minutes rather than physical construction, fabrication, or installation taking months and incurring per-inductee costs.
Cost-Effective Long-Term Operation: While digital systems typically require larger initial investments than basic physical displays, over typical 10-20 year timespans they prove more economical. Physical programs incur ongoing costs for plaques, photographs, display updates, and periodic facility refreshing. Digital systems require only content development and software subscriptions—costs that often prove lower than repeated physical updates.
Interactive Engagement Features
Modern digital platforms transform passive recognition viewing into active exploration experiences encouraging extended engagement.
Advanced Search Capabilities: Visitors can search inductees by name, year, achievement category, hometown, school, sport, or other criteria. This search functionality enables families to quickly locate specific individuals while supporting exploration discovering new stories based on various criteria.
Multimedia Integration: Digital profiles incorporate photograph galleries showing inductees throughout their careers, video highlights capturing memorable performances, audio interviews providing personal perspectives, historical documents adding context, and interactive timelines connecting individual achievements to broader state history.
Story Connections: Digital storytelling features enable linking related profiles, showing mentorship chains, documenting collaborative achievements, and revealing influence networks. These connections transform isolated profiles into interconnected narratives demonstrating how excellence develops through community support and mentorship.
Remote Accessibility: Web-integrated platforms enable anyone worldwide to explore state hall of fame content, extending recognition reach far beyond physical facility visitors. Alumni who’ve relocated, researchers studying state history, and families researching ancestors can access comprehensive content regardless of geographic distance from facilities.

Analytics and Program Assessment
Digital platforms provide data about visitor engagement enabling evidence-based program improvements impossible with traditional displays.
Engagement Metrics: Track which inductees generate most interest, how visitors navigate content, session duration patterns, search behavior revealing what information visitors seek, and feature usage indicating which capabilities create value. These insights inform content development priorities and justify continued program investment.
Demographic Analysis: Understanding visitor demographics—ages, geographic origins, visit contexts—helps programs tailor content and outreach strategies serving diverse community needs. Schools might use data targeting youth engagement efforts, while historical societies focus on preservation priorities.
Impact Demonstration: Quantitative engagement data demonstrates program value to funding sources, supporting organizations, and legislative bodies. Rather than relying solely on anecdotal evidence, programs can present measurable metrics documenting community engagement and program reach.
Implementation Strategies for State Hall of Fame Programs
Launching effective statewide recognition programs requires systematic planning addressing governance, funding, content development, and community engagement.
Organizational Foundation and Governance
Organizational Structure: State programs typically operate through dedicated nonprofit organizations, state athletic associations, historical societies, or state government agencies. Structure selection depends on existing organizational relationships, funding sources, and administrative capabilities.
Board Development: Effective governance requires diverse board representation including current and former educators, coaches, athletes, business leaders, state officials, and community representatives from various geographic regions. Board diversity ensures multiple perspectives inform strategic decisions while building broad community support.
Staff and Volunteer Management: Programs need staff or volunteers managing operations including nomination processing, content development, event planning, facility operations, and community engagement. Clear role definition prevents operational bottlenecks while ensuring consistent quality.
Funding and Financial Sustainability
State programs require reliable funding supporting initial establishment and ongoing operations including facilities, content development, induction ceremonies, marketing, and administrative costs.
Diversified Revenue Streams: Sustainable programs develop multiple revenue sources including corporate sponsorships, individual donations, event ticket sales, merchandise revenue, facility rentals, and potentially state funding or grants. Revenue diversification protects programs from disruption if single sources decline.
Endowment Building: Long-term sustainability benefits from endowment development generating investment income supporting operations regardless of annual fundraising performance. Even modest endowments create financial stability while signaling program permanence.
Cost Management: Effective programs balance quality with financial sustainability. Digital recognition systems often prove more cost-effective than traditional museums requiring expensive physical facilities, climate control, security, and continuous maintenance.
Content Development and Historical Research
Comprehensive state programs require extensive content development documenting inductee achievements, gathering photographs and memorabilia, conducting interviews, and researching historical context.
Systematic Research Processes: Establish standardized approaches to inductee research including information gathering from candidates and families, institutional archive searches, newspaper and media research, interview scheduling and recording, and photograph collection and rights management.
Historical Context Addition: Effective recognition provides context helping visitors understand achievement significance. Document era-specific challenges candidates overcame, competitive landscapes they navigated, and how their achievements influenced subsequent generations.
Ongoing Content Enhancement: Programs should continuously enhance existing content as additional information surfaces. Alumni might contribute photographs decades after inductions, or researchers might discover historical details adding valuable context to profiles.
Resources on creating comprehensive hall of fame programs provide detailed frameworks for content development ensuring recognition honors inductees appropriately while engaging diverse audiences.

Engaging Communities Through State Recognition
Effective state programs actively engage communities rather than functioning as static display spaces visited occasionally.
Annual Induction Ceremonies and Events
Regular recognition events create ongoing community engagement opportunities while celebrating new inductees appropriately.
High-Profile Ceremonies: Annual induction banquets or ceremonies bring inductees, families, and communities together for formal celebration. These events should honor inductees meaningfully while creating networking opportunities connecting generations of excellence.
Geographic Distribution: Consider rotating event locations across different state regions ensuring that diverse communities have opportunities to host celebrations and participate without excessive travel. Geographic rotation demonstrates program commitment to representing entire states rather than specific regions.
Media Coverage: Develop relationships with state media generating coverage that amplifies recognition reach. Television features, newspaper stories, radio interviews, and social media content extend recognition impact far beyond event attendees.
Educational Programming and Youth Engagement
State programs should actively inspire current students and athletes rather than simply preserving historical achievements.
School Partnerships: Develop relationships with schools across states facilitating educational programming. Inductees might visit schools sharing their stories, speak at assemblies, or participate in classroom discussions about excellence, perseverance, and goal achievement.
Youth Programs: Create programs specifically engaging young people including essay contests about state sports history, art competitions honoring athletic heroes, student curator positions researching inductee stories, or youth advisory boards providing student perspectives.
Digital Engagement: Leverage social media, interactive websites, and virtual programming reaching youth who might never visit physical facilities but will engage enthusiastically with digital content accessible on devices they already use daily.
Alumni and Historical Society Collaboration
State programs benefit from partnerships with alumni associations, historical societies, and heritage organizations sharing missions around preserving state history and celebrating community achievement.
Resource Sharing: Historical societies often possess archives, photographs, and research capabilities supporting hall of fame content development. Alumni associations maintain networks facilitating inductee contact and gathering biographical information.
Joint Programming: Collaborative programming leverages combined resources creating richer experiences than single organizations could produce independently. Co-hosted events, shared exhibitions, or coordinated research projects benefit all participating organizations while serving communities more effectively.
Cross-Promotion: Organizations with overlapping missions should actively promote each other’s programs, events, and resources. Cross-promotion extends all organizations’ reach while building stronger ecosystems supporting state history preservation and community celebration.
Best Practices for Long-Term Program Success
Sustainable state recognition programs require ongoing attention ensuring that initial enthusiasm translates into lasting impact across decades.
Maintaining Selection Integrity
Program credibility depends on consistent application of selection criteria maintaining recognition standards regardless of external pressures.
Criteria Consistency: Resist temptations to relax standards accommodating particular candidates, responding to political pressure, or expanding inductee classes beyond program capacity. Consistency ensures all inductees meet equivalent standards maintaining recognition prestige.
Transparent Communication: When deserving candidates don’t receive selection, clear communication about evaluation processes and decision rationales helps nominees and their supporters understand decisions without damaging relationships or generating controversy.
Periodic Criteria Review: While consistency matters, programs should periodically review criteria ensuring standards remain appropriate as achievement contexts evolve. What constituted exceptional achievement three decades ago might require adjustment acknowledging how competition levels, training methods, or opportunity structures have changed.
Continuous Content Enhancement
Recognition quality shouldn’t decline as programs mature and inductee populations grow.
Equivalent Recognition Quality: Ensure recent inductees receive recognition quality equivalent to inaugural classes rather than diminished profiles resulting from content development fatigue. Set minimum standards for profile comprehensiveness ensuring all inductees receive thorough documentation regardless of induction timing.
Historical Profile Enhancement: Systematically enhance older profiles as additional content becomes available. Alumni might contribute photographs years after inductions, researchers might uncover historical details, or changing perspectives might add valuable context to earlier achievements.
Technology Currency: Plan for periodic technology refreshes maintaining modern user experiences. Digital displays and platforms eventually require updates ensuring recognition remains impressive rather than appearing dated or suffering failing equipment.
Building Sustainable Operations
Long-term success requires operational systems supporting consistent quality regardless of staff transitions or volunteer availability changes.
Documented Procedures: Develop written procedures for nomination processing, content development, event planning, and other core activities ensuring operations continue smoothly when specific individuals transition out of roles.
Volunteer Development: Build volunteer pools providing operational support reducing dependence on limited staff or small groups of highly committed individuals. Volunteer roles should accommodate diverse time commitments and skill levels maximizing participation.
Succession Planning: Identify and develop future leaders ensuring organizational continuity when current board members, staff, or key volunteers eventually transition. Formal succession planning prevents crisis scrambles when unexpected departures occur.
Programs implementing these best practices create recognition systems serving communities effectively across decades while maintaining standards, quality, and relevance. Resources on interactive hall of fame design provide additional guidance for programs seeking to enhance community engagement through strategic recognition approaches.
Addressing Common Challenges
State recognition programs face predictable challenges requiring proactive strategies preventing or mitigating difficulties.
Managing Geographic Representation
State programs must ensure recognition doesn’t inadvertently favor particular regions or institution types despite achievement-based selection criteria.
Monitoring Selection Patterns: Track inductee geographic origins, school sizes, and demographic characteristics identifying any patterns suggesting unintentional bias. If metropolitan areas or large schools dominate selections despite excellence existing statewide, investigate whether criteria unconsciously disadvantage certain populations.
Outreach Balance: Conduct nomination outreach ensuring all state regions understand processes and receive encouragement to nominate deserving candidates. Rural communities or small schools might assume state recognition remains beyond reach unless programs actively communicate that excellence from anywhere receives equal consideration.
Selection Committee Geographic Diversity: Ensure committees include representatives from diverse state regions providing perspective on excellence emerging from various contexts. Urban members might not recognize achievement significance in rural contexts without colleagues explaining competitive landscapes and resource limitations rural achievers overcame.
Balancing Selectivity and Inclusiveness
Programs face tension between maintaining high standards preserving recognition prestige and ensuring deserving individuals receive appropriate celebration.
Multiple Recognition Tiers: Some programs address this tension through tiered recognition—highly selective hall of fame induction representing top achievement level, broader recognition categories celebrating significant excellence not quite reaching hall of fame thresholds, and special recognition for particular achievement types deserving celebration separately from general hall of fame consideration.
Clear Criteria Communication: Transparent standards help communities understand selection requirements while managing expectations. When criteria clearly explain achievement thresholds, nominees and supporters better understand decisions without assuming bias or inappropriate exclusion.
Appeals and Reconsideration: Establish processes enabling reconsideration of selection decisions when new information emerges or nominees provide additional documentation addressing committee concerns. Appeals processes demonstrate fairness while potentially correcting initial oversights.
Maintaining Community Engagement
Initial program enthusiasm often wanes requiring strategies sustaining engagement across years.
Regular Content Updates: Continuously refresh content keeping programs dynamic rather than static. Add new inductee profiles, enhance existing content, create special exhibits, or develop thematic collections maintaining visitor interest beyond single visits.
Event Innovation: While annual induction ceremonies form program centerpieces, develop additional events maintaining year-round community engagement. Historical lectures, athletic clinics featuring inductee coaches, networking events connecting current students with accomplished alumni, or traveling exhibitions bringing recognition to various communities all extend program reach.
Youth Focus: Deliberately target youth engagement ensuring programs inspire current students rather than functioning primarily as nostalgia vehicles for older generations. Young people represent future donors, volunteers, and community supporters whose early engagement creates lasting connections.
Conclusion: Celebrating State Excellence Through Meaningful Recognition
Statewide hall of fame programs serve essential purposes within state communities—preserving achievement histories that might otherwise fragment across countless institutions, inspiring current students and athletes by showcasing what’s possible, building state pride through shared celebration of excellence transcending regional and institutional divides, and creating networks connecting accomplished individuals across generations and communities.
The most effective programs combine clear selection criteria maintaining recognition prestige while ensuring excellence from all state communities receives consideration, compelling content honoring inductees comprehensively through rich storytelling rather than just listing achievements, professional display systems whether traditional museums or modern digital platforms, consistent annual operations adding new inductees while enhancing existing content, and sustained community engagement ensuring programs actively inspire rather than functioning as static historical archives.
Modern digital recognition solutions offer particular advantages for state programs seeking comprehensive capabilities. Interactive systems eliminate space constraints preventing unlimited growth, enable rich multimedia content impossible with physical plaques, provide instant cost-effective updates when adding inductees, create engaging experiences encouraging exploration and discovery, deliver measurable analytics demonstrating program value, and extend recognition beyond physical facilities through web access reaching communities statewide and beyond.
Whether implementing inaugural state recognition programs or enhancing existing celebrations, core principles remain constant—honor achievement appropriately, maintain equitable recognition across all state regions and populations, create engaging experiences connecting current students to state traditions, preserve complete historical documentation for future generations, and demonstrate through consistent operations that excellence earns permanent acknowledgment regardless of where or when it occurs within state communities.
For state organizations committed to celebrating excellence while building sustainable recognition programs serving diverse communities across decades, comprehensive hall of fame initiatives represent essential investments delivering returns across multiple dimensions—enhanced youth inspiration, preserved historical knowledge, stronger state identity, engaged alumni networks, and celebrated achievement traditions demonstrating what state communities value most. Through thoughtful selection criteria, professional recognition displays, compelling content development, and consistent operations, state programs create lasting tributes to excellence while inspiring continued achievement across entire state communities.
Ready to discover how modern digital recognition can transform your state hall of fame program? Solutions like Rocket Alumni Solutions provide comprehensive platforms specifically designed for state-level recognition, offering unlimited capacity, engaging interactive features, and seamless content management supporting programs celebrating excellence across diverse state communities.