School administrators face a critical challenge when establishing athletic halls of fame: how to create recognition systems that authentically celebrate athletic excellence while remaining sustainable, fair, and meaningful for decades. An athletic hall of fame represents far more than a display of achievements—it embodies institutional values, strengthens school culture, engages alumni, and demonstrates sustained commitment to athletic excellence across generations.
This comprehensive guide provides school administrators with systematic frameworks for planning, implementing, and maintaining athletic halls of fame that serve your institution's unique needs. Whether you're establishing your first formal recognition program or modernizing existing traditions, this guide delivers practical strategies, proven selection criteria, and contemporary solutions that transform how schools honor athletic achievement.
School athletics generate remarkable stories of dedication, perseverance, and achievement. Student-athletes invest countless hours developing skills, supporting teammates, and representing school values through competition. Coaches dedicate careers to mentoring young people and building programs. Teams create bonds that last lifetimes while achieving victories that define institutional identity.
Yet many schools struggle to honor these achievements adequately. Traditional recognition methods—trophy cases, banners, plaques—impose severe limitations that force difficult decisions about which accomplishments deserve acknowledgment. Physical space constraints mean only the most prominent achievements receive recognition, while equally worthy individual accomplishments and team successes remain undocumented. Static displays become outdated quickly, and updating them proves expensive and time-consuming.
School administrators increasingly recognize that athletic recognition requires more thoughtful, comprehensive approaches. Modern athletic halls of fame serve multiple institutional objectives simultaneously: preserving program history for future generations, engaging alumni and strengthening fundraising relationships, demonstrating school values and athletic excellence to prospective families, building school pride and culture among current students and staff, and honoring the achievements of individuals and teams fairly and comprehensively.
This guide helps school administrators navigate every dimension of athletic hall of fame planning and implementation, from defining institutional objectives through selecting honorees and implementing recognition systems that deliver lasting value.

Defining Your Athletic Hall of Fame Purpose and Scope
Before addressing logistics, school administrators must clarify exactly what their athletic hall of fame should accomplish and which achievements warrant recognition.
Establishing Clear Institutional Objectives
Different schools emphasize different aspects of athletic recognition based on institutional history, values, and community expectations.
Historical Preservation and Legacy Documentation: Schools with long athletic traditions benefit from halls of fame that comprehensively document program history. This objective emphasizes preserving complete records of championship teams, tracking coaching legacies across decades, maintaining statistical records and achievement progressions, documenting facility evolution and program development, and capturing the connections between generations of athletes. Historical preservation proves particularly important for institutions where athletic tradition forms a core element of institutional identity.
Alumni Engagement and Development: Many schools view halls of fame primarily as alumni engagement tools supporting broader institutional advancement goals. This objective prioritizes creating opportunities for alumni reconnection with athletic programs, facilitating networking among former athletes across generations, demonstrating institutional appreciation for alumni contributions, and strengthening emotional connections that support fundraising efforts. When alumni engagement drives hall of fame purpose, selection criteria and implementation strategies shift to emphasize inclusive recognition and regular events bringing alumni back to campus.
Current Student Inspiration and Motivation: Halls of fame can serve as motivational tools demonstrating achievement possibilities for current student-athletes. This objective emphasizes creating role models current students can aspire to emulate, illustrating the rewards of dedication and athletic excellence, building program pride and competitive culture, and making excellence visible and celebrated throughout athletic facilities. Schools emphasizing this objective often include detailed achievement narratives showing the work behind success rather than simply listing accomplishments.
Community Pride and School Promotion: Athletic recognition communicates institutional quality to external audiences including prospective students and families, community members and supporters, media covering school athletics, and potential donors and sponsors. Halls of fame become marketing assets showing program excellence, competitive success, and institutional values. This objective influences display placement, content detail, and the prominence given to athletic recognition in school facilities.
Most effective halls of fame serve multiple objectives simultaneously, but clarifying which purposes matter most helps administrators make strategic decisions throughout planning and implementation.
Determining Recognition Scope
School administrators must define precisely which achievements and individuals their halls of fame will honor.
Individual Athletes vs. Teams: Some schools focus exclusively on individual athletic excellence, inducting standout athletes based on career achievements and post-high-school success. Others prioritize team accomplishments, recognizing championship squads and historically significant teams. Comprehensive approaches honor both dimensions, creating separate categories for individual and team recognition. The choice depends on institutional values, available resources, and the relative importance of individual versus collective achievement in school culture.
Recent vs. Historical Recognition: Newer schools with limited athletic history can establish halls of fame recognizing recent excellence, with shorter waiting periods between graduation and induction eligibility. Older institutions with decades or centuries of tradition face different challenges—comprehensive historical recognition requires substantial research documenting achievements from eras with incomplete records. Many schools implement phased approaches, initially focusing on recent well-documented achievements before systematically working backward through history as resources permit.
Multi-Sport Coverage: Comprehensive athletic programs fielding 15-30+ sports face difficult questions about equitable recognition across programs. Some schools establish minimum achievement thresholds that apply equally across all sports, while others create sport-specific criteria acknowledging different competitive landscapes. Schools must decide whether all sports receive equal representation or whether prominence in hall of fame induction reflects each sport’s relative importance within the broader athletic program.
Coaching and Contributor Recognition: Beyond athletes and teams, many halls of fame honor coaches, administrators, boosters, and other contributors who shaped athletic programs. This expanded scope acknowledges that program excellence depends on contributions beyond on-field performance. However, it also complicates selection processes and creates additional categories requiring separate criteria and selection procedures.
Clear scope definition prevents mission creep that makes halls of fame unwieldy while ensuring recognition systems align with institutional values and resources.

Establishing Selection Criteria and Governance
Selection processes fundamentally determine hall of fame credibility, fairness, and long-term sustainability.
Developing Objective Selection Standards
Clear, publicly documented criteria enable consistent decision-making and help stakeholders understand recognition requirements.
Quantitative Achievement Metrics: Measurable accomplishments provide objective foundations for selection. Common quantitative criteria include career statistical achievements and school records, championship participation and titles won, all-conference, all-state, or all-region recognition, individual awards and honors received during high school career, collegiate or professional athletic achievement after graduation, and years of participation and consistency across seasons.
These quantitative measures should reflect genuine athletic excellence rather than arbitrary thresholds. Schools must calibrate standards to their specific competitive context—achievement levels warranting recognition at small rural schools differ substantially from those at large suburban programs competing in elite conferences.
Qualitative Character Considerations: Most schools supplement quantitative achievement with character requirements ensuring inductees exemplify institutional values. Qualitative considerations might include sportsmanship and conduct during competition, leadership demonstrated on and off the field, academic achievement and citizenship, positive representation of school values, and contributions to team culture beyond individual performance.
Character criteria prove more challenging to assess objectively than statistics, requiring careful definition and documentation standards. Schools should establish what evidence supports character claims—coach recommendations, academic records, discipline history, and peer testimony all provide validation.
Post-Graduation Achievement Weight: Schools disagree about how heavily to weight post-high-school athletic achievement. Some prioritize high school accomplishments exclusively, while others emphasize collegiate, professional, or Olympic success as primary criteria. Many schools adopt hybrid approaches where exceptional high school performance alone qualifies athletes while post-graduation achievement provides alternative pathways to recognition.
This decision reflects fundamental questions about purpose—is the hall of fame recognizing high school achievement specifically, or celebrating all athletic excellence connected to the institution regardless of when it occurred?
Time-Based Eligibility Requirements: Nearly all halls of fame impose waiting periods between graduation and induction eligibility, typically ranging from 5-25 years. Waiting periods allow time for post-graduation achievement assessment, create emotional distance enabling objective evaluation, and prevent recent bias favoring fresh memories. However, they also delay recognition and risk losing touch with potential inductees. Schools should balance these considerations based on how heavily they weight post-graduation accomplishments in selection decisions.
Creating Effective Selection Committees
Selection committee composition and processes directly impact hall of fame credibility and fairness.
Committee Composition: Effective selection committees balance multiple perspectives and avoid concentration of authority. Common committee structures include athletic directors and senior athletic administrators, current coaching staff representation across multiple sports, faculty members familiar with student-athletes academically, alumni representatives with institutional perspective, community members providing external viewpoints, and current student-athlete representatives in some cases.
Committee size typically ranges from 7-15 members—large enough to represent diverse perspectives but small enough for productive deliberation. Terms should be staggered to maintain institutional knowledge while allowing regular rotation introducing fresh perspectives.
Nomination and Evaluation Processes: Systematic nomination and evaluation procedures ensure thorough, consistent assessment. Effective processes typically include open nomination periods accepting submissions from any community member, standardized nomination forms capturing required information consistently, preliminary screening verifying basic eligibility before full committee review, structured evaluation protocols applying selection criteria uniformly, and deliberation procedures facilitating discussion while maintaining confidentiality.
Documentation standards prove critical—committees should maintain detailed records justifying selections and demonstrating that established criteria were applied consistently. This documentation protects against claims of favoritism or bias while providing precedents guiding future decisions.
Transparency and Appeals: Published selection criteria, committee composition, and general process outlines build community confidence in hall of fame integrity. However, specific deliberations and individual votes should remain confidential to enable candid discussion. Schools should establish clear policies regarding whether unsuccessful nominees can be reconsidered in future years and under what circumstances, how selection decisions can be appealed if perceived as inconsistent with published criteria, and what information is shared publicly about selection processes versus what remains internal.
The athletic director guide to choosing digital hall of fame providers offers additional insights into governance considerations that support long-term hall of fame success.
Planning Physical and Digital Recognition Elements
Once selection frameworks are established, administrators must determine how inducted individuals and teams will actually be honored and displayed.
Traditional Physical Recognition Approaches
Despite digital innovations, many schools maintain traditional physical recognition elements valued for their permanence and tangible presence.
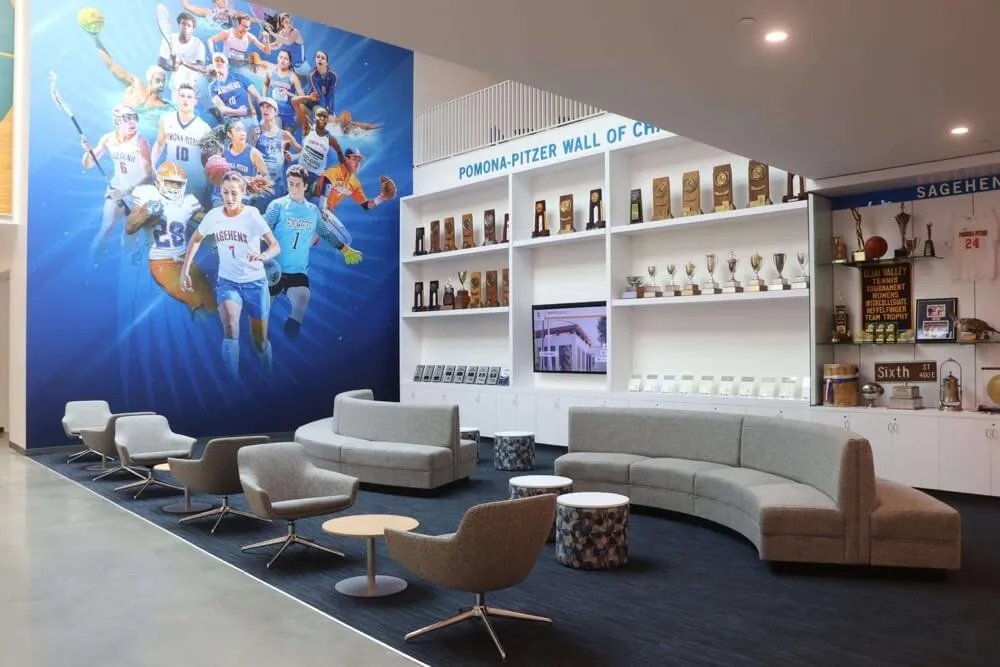
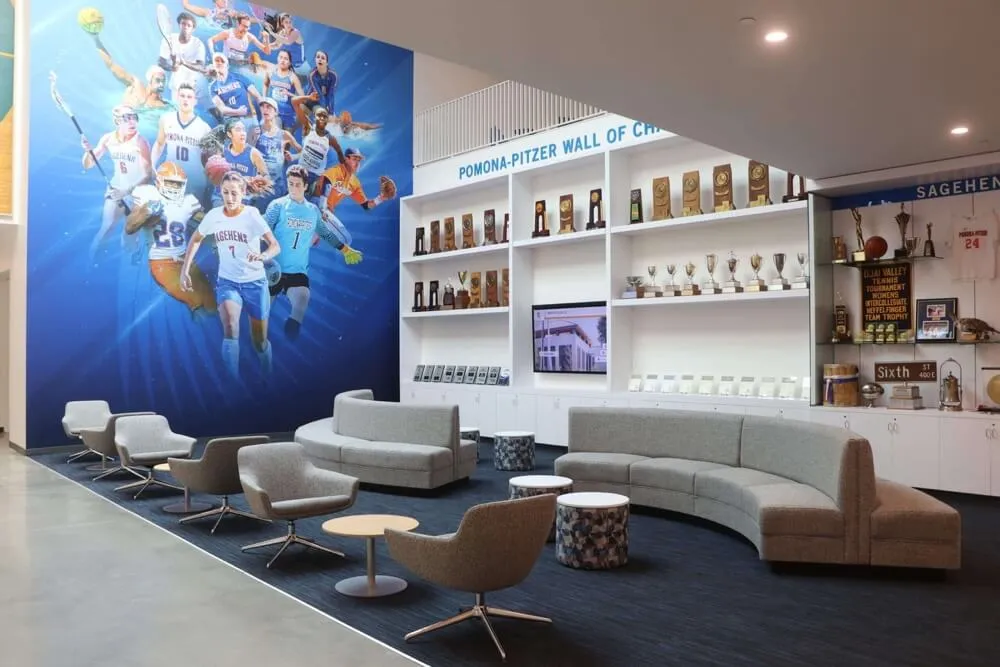
Trophy Cases and Display Areas: Dedicated trophy cases in prominent athletic facility locations provide centralized recognition. Effective trophy case implementations feature climate-controlled environments protecting artifacts, professional lighting highlighting displayed items, organized layouts grouping related achievements logically, regular rotation featuring different eras and programs, and integration with digital displays adding context and storytelling. Trophy cases work best when treated as curated exhibits rather than cluttered storage of every award.
Wall Plaques and Nameplates: Individual plaques mounted on dedicated walls provide permanent recognition requiring no power or maintenance. Quality plaque walls include consistent formatting creating visual coherence, organized arrangements (alphabetical, chronological, or by achievement category), room for expansion as future classes are inducted, professional engraving and mounting, and prominent placement in high-traffic areas. However, wall space limitations eventually constrain how many inductees can be recognized physically.
Banner and Pennant Programs: Hanging banners recognizing championship teams, retired jerseys, or hall of fame inductees provide highly visible recognition in gymnasiums and field houses. Banners work particularly well for team accomplishments and create impressive visual impact during athletic events. Considerations include weather-resistant materials for outdoor applications, consistent design standards across all banners, secure mounting preventing damage or falling, and regular replacement as materials deteriorate over years.
Bronze Plaques and Permanent Installations: Some schools create permanent bronze plaque installations or sculptural elements for the most significant recognitions. These premium options convey importance and permanence but require substantial investment and cannot easily be updated or corrected. They work best for the most exceptional achievements and most distinguished contributors.
Traditional physical elements provide tangible permanence that resonates particularly with older alumni who expect “real” recognition. However, they also impose severe space constraints and update difficulties that digital solutions address directly.

Digital Recognition Solutions
Digital recognition technologies enable comprehensive athletic halls of fame without traditional space limitations while adding engagement capabilities impossible with static displays.
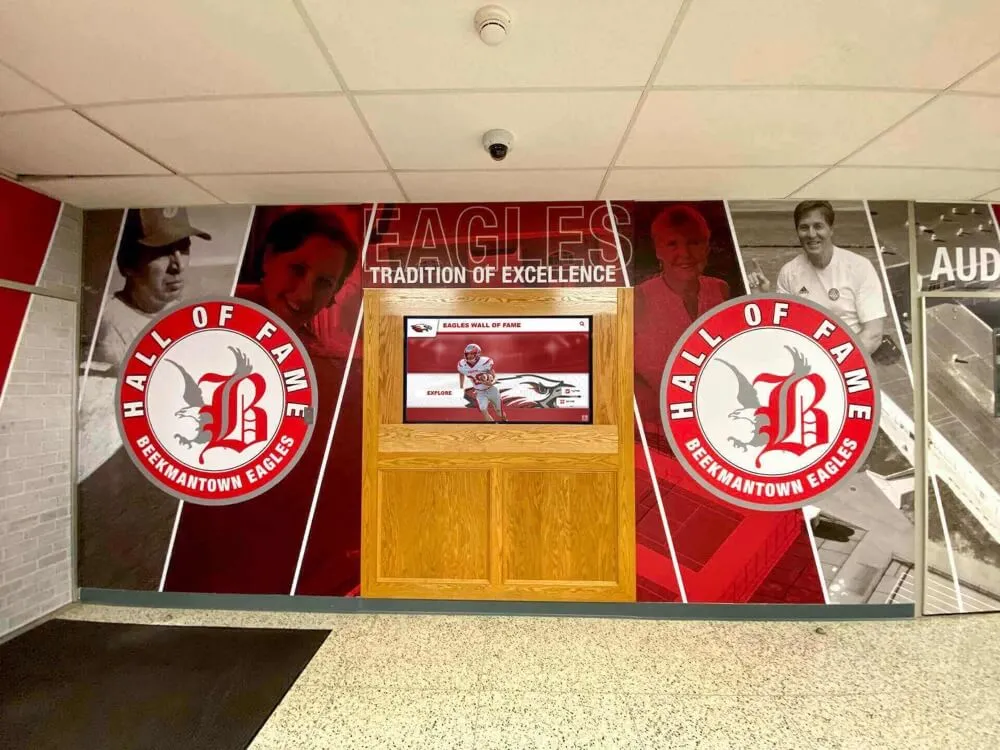
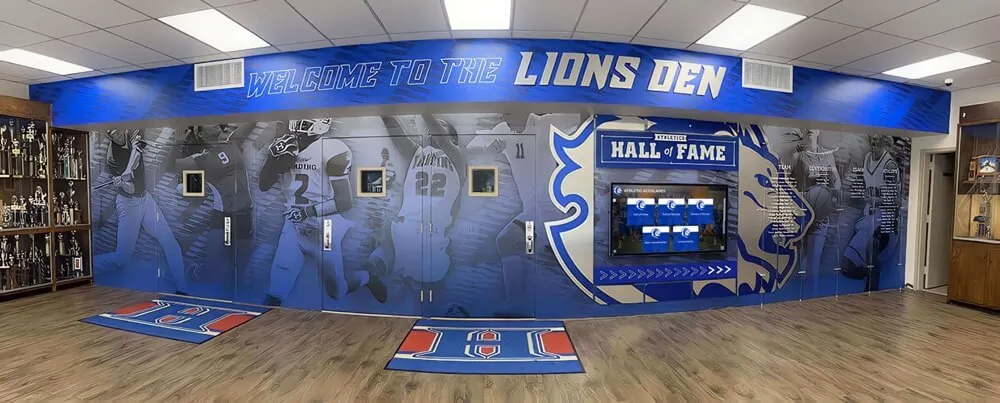
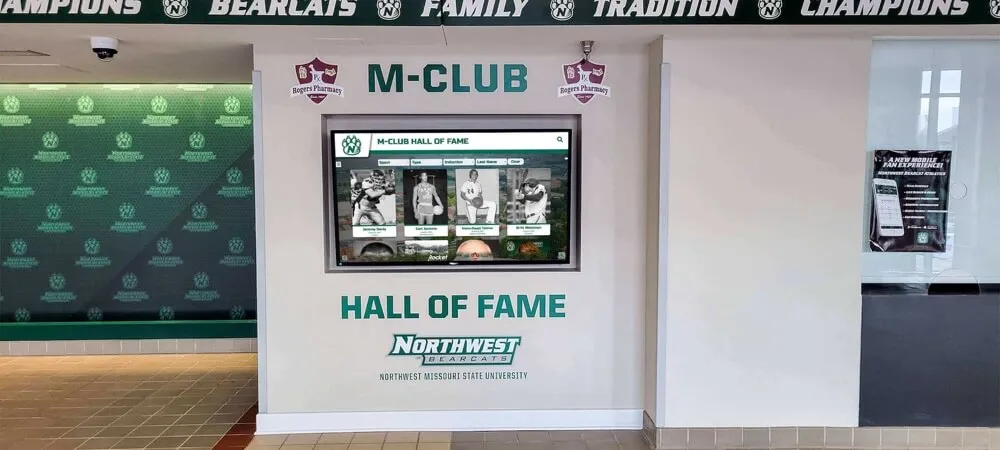
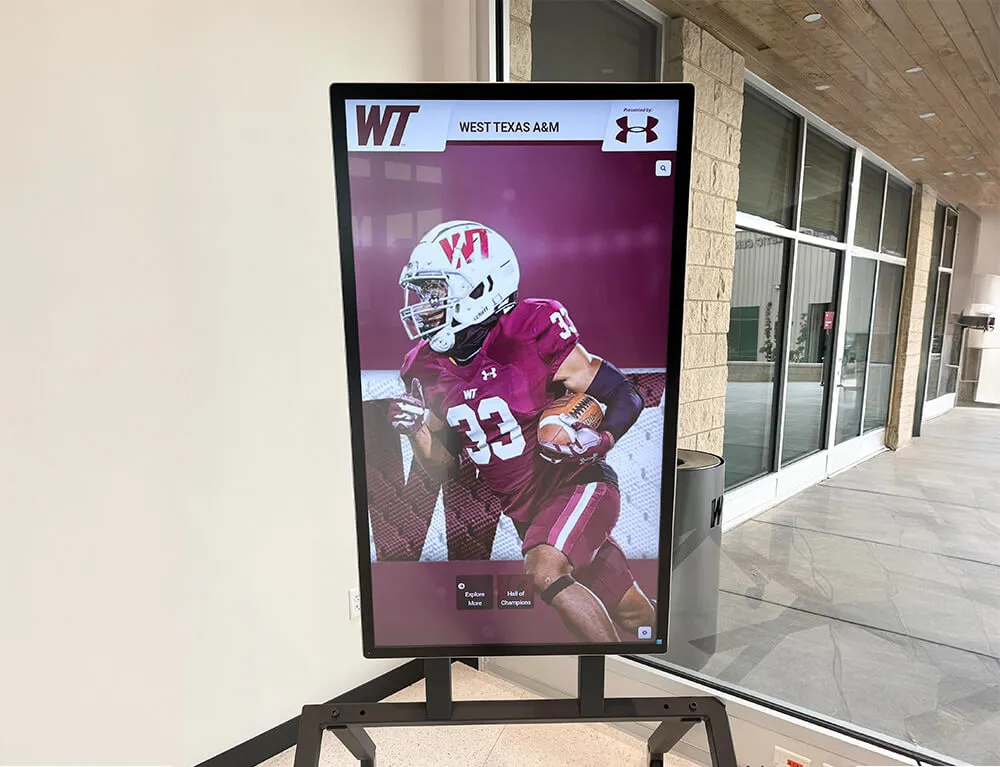
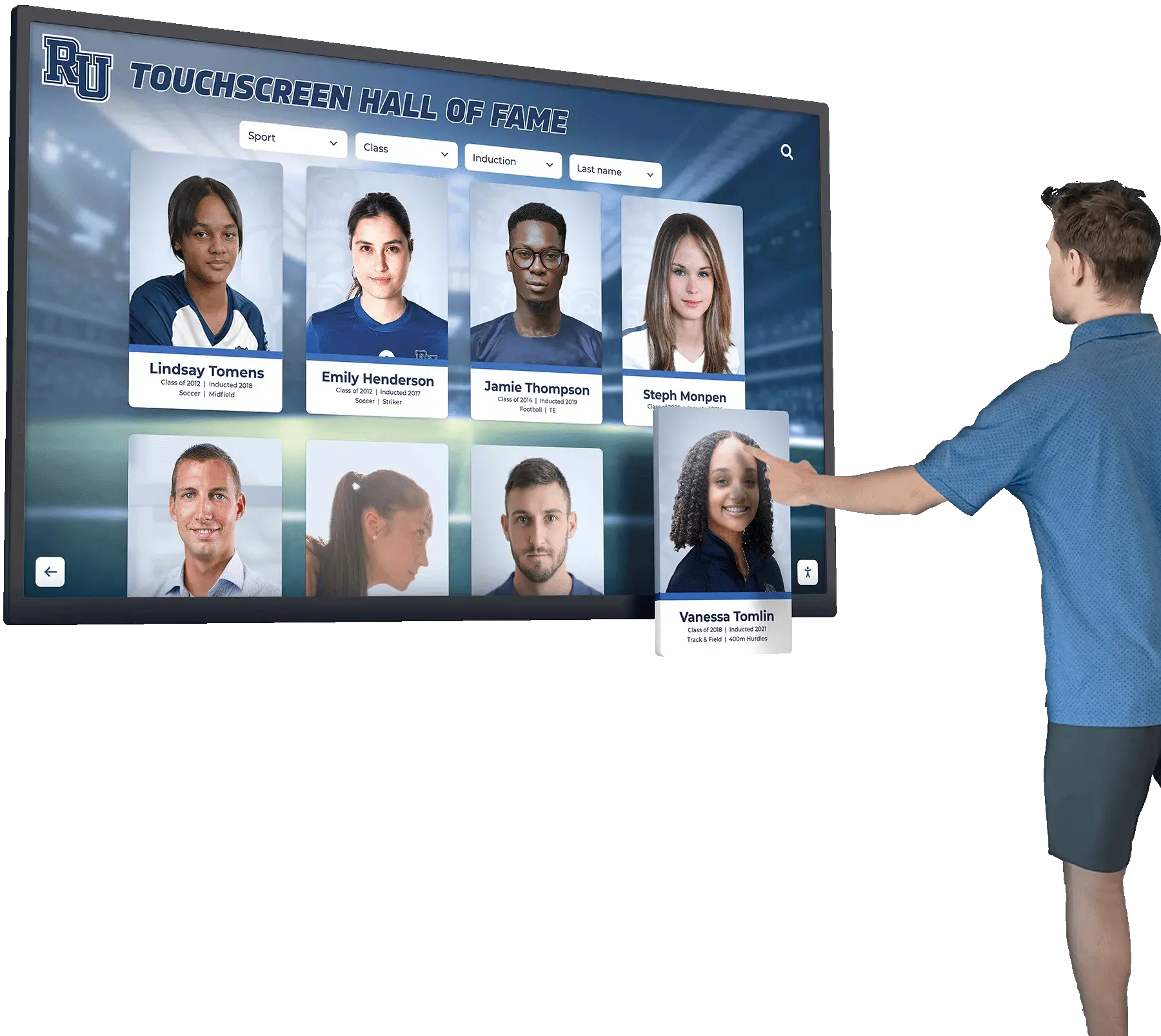
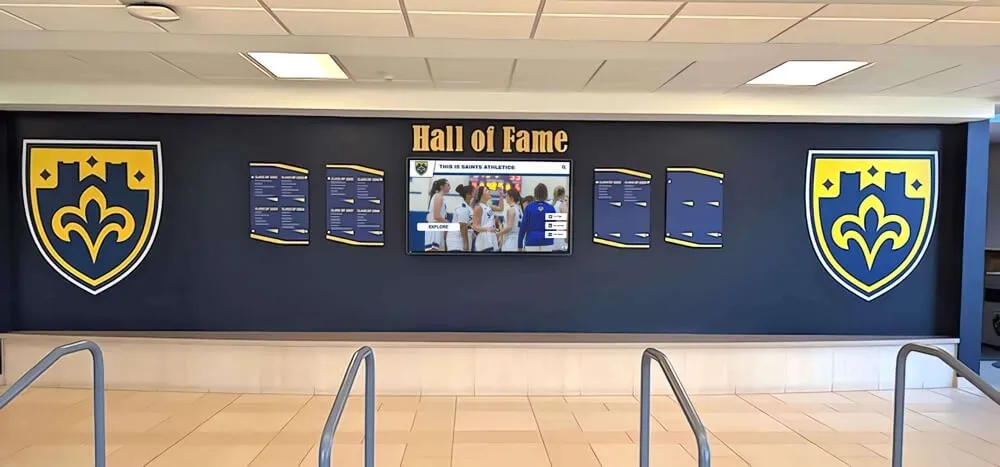
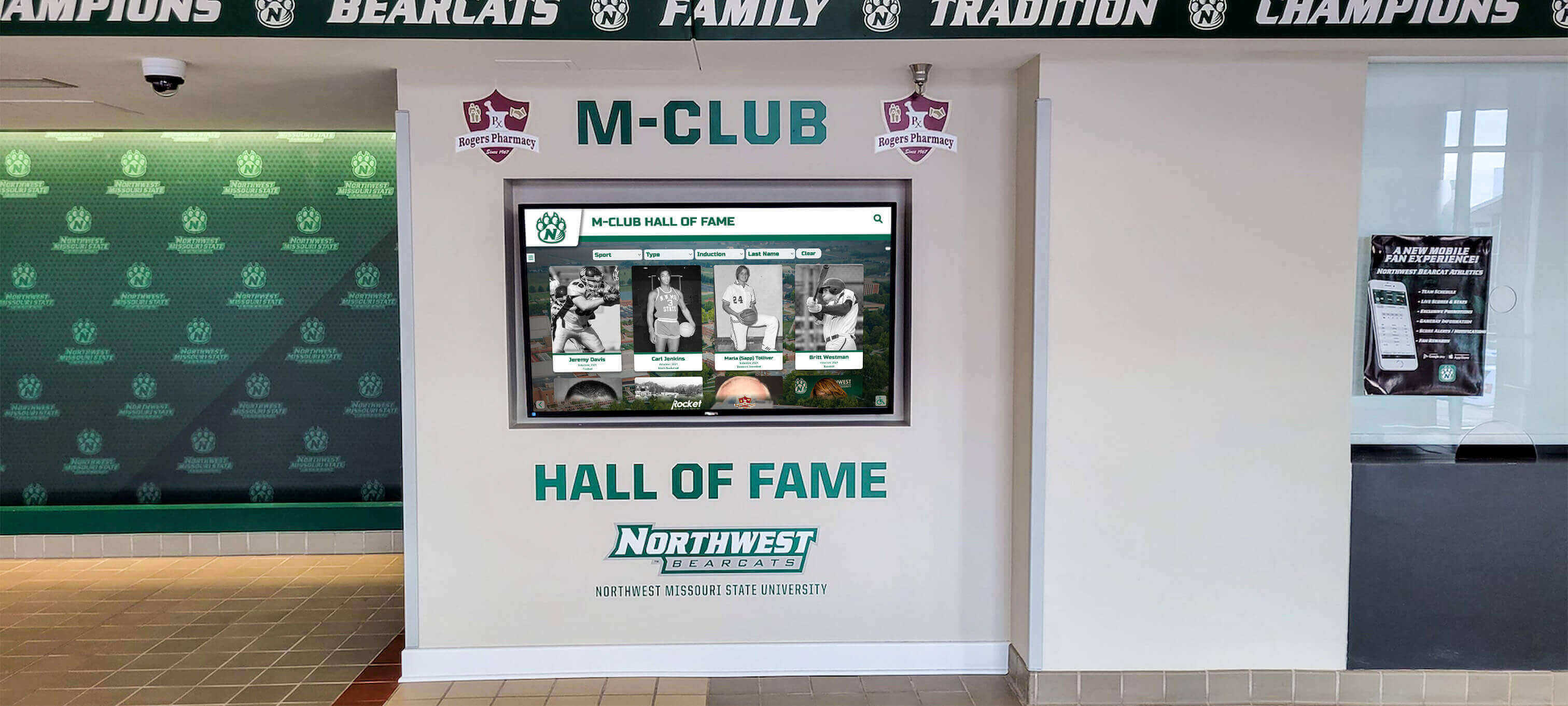
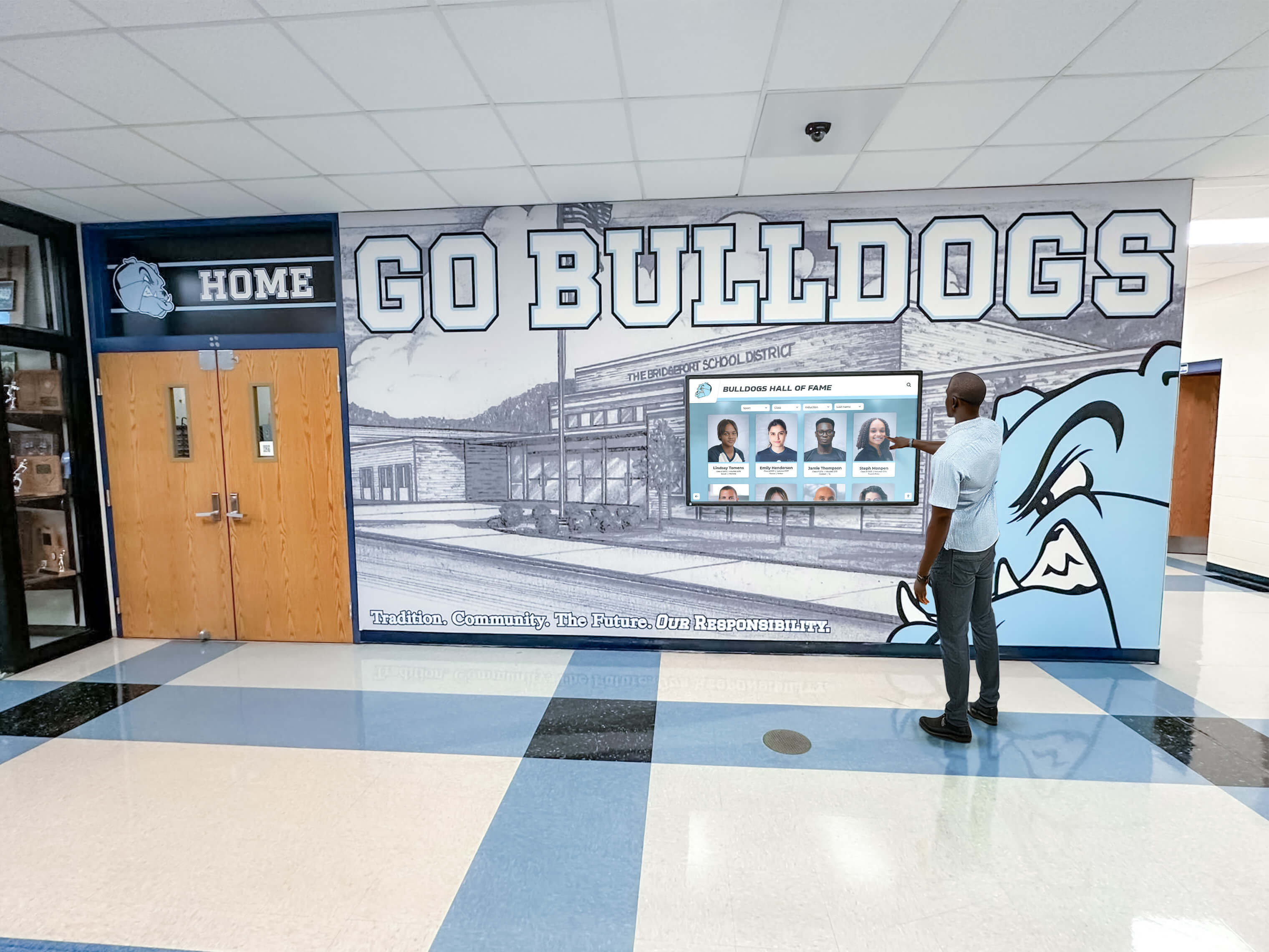
Interactive Touchscreen Displays: Purpose-built interactive touchscreen systems deployed in athletic facilities transform how schools recognize achievement. These platforms enable unlimited inductee profiles without space constraints, rich multimedia storytelling with photos, videos, and detailed narratives, searchable databases allowing visitors to find specific athletes or teams, dynamic content updates adding new inductees instantly without physical modification, and engaging interactive experiences converting passive viewing into active exploration.
Schools implementing digital halls of fame typically position touchscreen displays in main gymnasium lobbies, athletic center entrances, common areas where students congregate, and locations visible during recruiting visits and athletic events. Solutions like Rocket Alumni Solutions specifically serve athletic recognition needs through sport-specific templates, statistical tracking capabilities, team roster management, and intuitive content management that athletic administrators can handle without technical expertise.
Web-Based Recognition Platforms: Digital recognition extends beyond physical campus boundaries through web-based platforms accessible anywhere. Online halls of fame enable alumni to explore achievements remotely, provide searchable databases accessible to media and researchers, create social sharing opportunities extending recognition reach, and support alumni networking by connecting former teammates. Web platforms complement physical displays rather than replacing them—together they create comprehensive recognition ecosystems serving multiple audiences.
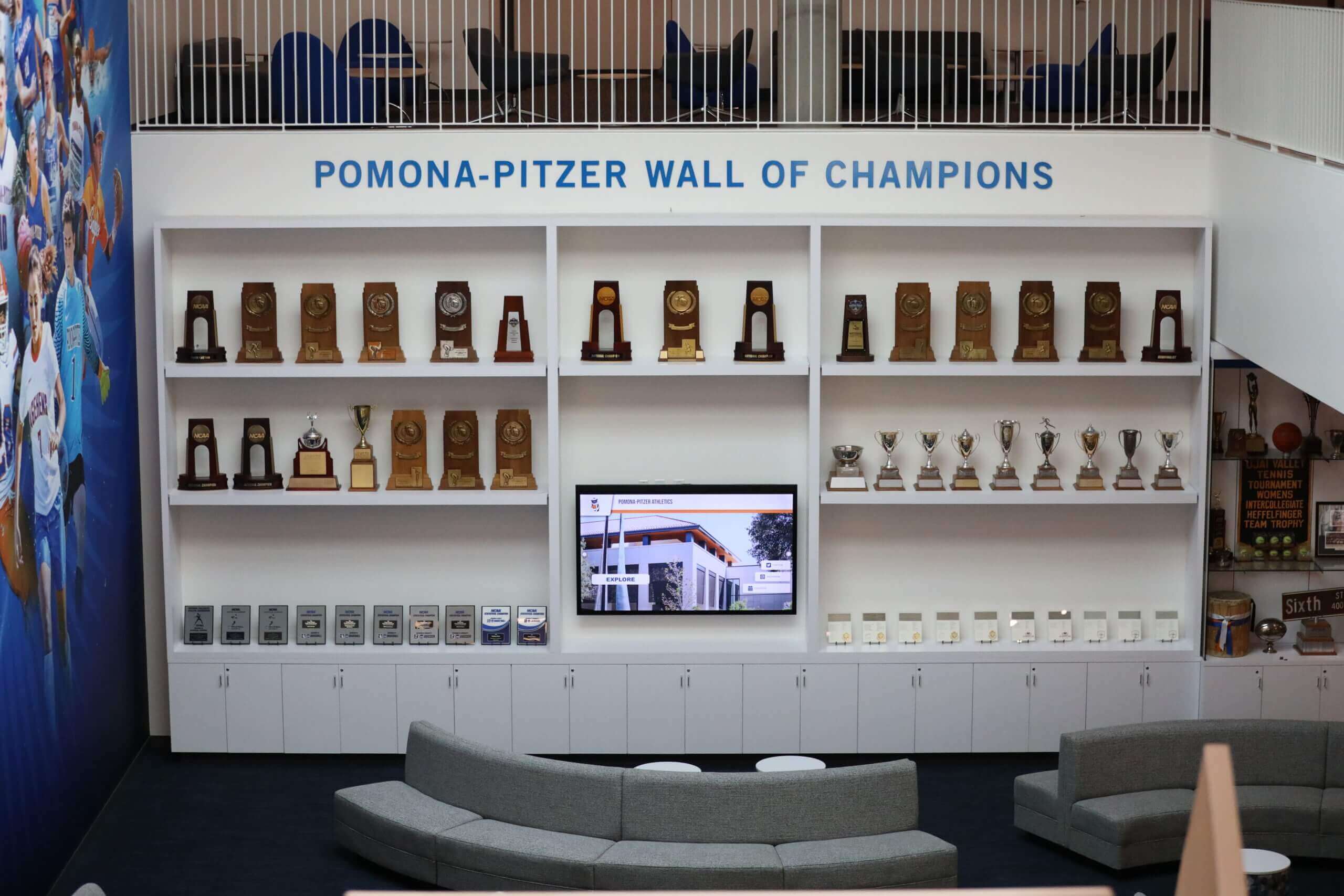
Integration of Physical and Digital: The most sophisticated implementations blend traditional and digital recognition strategically. Physical elements provide the permanence and tradition many stakeholders value, while digital platforms deliver unlimited capacity and rich storytelling. Integrated approaches might include QR codes on physical plaques linking to detailed digital profiles, digital displays placed directly adjacent to trophy cases adding context to artifacts, physical inductee plaques updated annually with digital displays maintaining complete historical records, and blended ceremonies where physical elements are presented but digital archives capture complete documentation.
Understanding basketball hall of fame recognition approaches provides insights into sport-specific recognition considerations applicable across athletic programs.
Implementation Planning and Execution
Moving from planning to reality requires systematic implementation addressing timeline, budget, content development, and stakeholder communication.
Establishing Realistic Timelines
Athletic hall of fame implementation typically requires 12-24 months from initial planning through formal launch.
Phase 1: Planning and Design (3-6 months): Initial phases establish foundational elements including defining institutional objectives and recognition scope, developing selection criteria and committee structure, determining physical/digital recognition approaches, securing budget approval and funding, and appointing selection committee members. This planning phase proves critical—rushing through these decisions creates problems that persist throughout the hall of fame’s existence.
Phase 2: Initial Selection and Content Development (6-9 months): Once frameworks are established, the first induction class must be selected and documented. This phase includes soliciting and reviewing nominations, committee deliberations and selections, research and documentation of selected inductees’ achievements, content creation including writing profiles and collecting multimedia, and physical display design and production or digital platform configuration. Initial classes often include larger numbers recognizing accumulated achievements from earlier years.
Phase 3: Installation and Launch (2-3 months): Final implementation includes physical display installation or digital platform deployment, content loading and system testing, staff training on content management and updates, promotion and marketing building awareness, and formal dedication events celebrating launch. Timing launch ceremonies strategically—perhaps during homecoming, significant athletic milestones, or dedicated athletic hall of fame weekends—maximizes attendance and impact.
Phase 4: Ongoing Management: After initial launch, sustainable management processes include annual nomination and selection cycles, regular content updates and additions, physical maintenance or digital platform management, induction ceremonies celebrating new classes, and continuous engagement maintaining hall of fame visibility. Successful halls of fame treat recognition as ongoing programs rather than one-time projects.
Budgeting and Funding Strategies
Athletic hall of fame implementation requires significant investment, though costs vary tremendously based on approach sophistication.
Initial Investment Components: Traditional physical recognition costs include display cases and installation ($5,000-$25,000), individual plaques or nameplates ($50-$200 each), professional design and fabrication services, and any facility renovation required for display installation. Digital recognition investments include touchscreen hardware ($3,000-$8,000 per display), software platforms and licensing (varies by provider), installation and network infrastructure, and initial content development ($5,000-$20,000 depending on inductee numbers).
Comprehensive implementations blending physical and digital elements typically require initial investments of $25,000-$75,000, though smaller schools can launch more modest programs for $10,000-$20,000 by focusing on core elements and expanding over time.
Annual Operating Costs: Ongoing hall of fame expenses include annual induction ceremony costs, content updates and maintenance, digital platform subscriptions or support contracts ($1,000-$5,000 annually), physical display cleaning and upkeep, and staff time managing selection processes and content. Many schools find that initial investment represents the primary expense, with ongoing costs remaining modest once systems are established.
Funding Approaches: Schools fund halls of fame through various mechanisms including normal capital budgets or athletic facility improvement funds, dedicated fundraising campaigns from boosters and athletic supporters, naming opportunities and recognition sponsorships, class reunion gifts and legacy giving, and alumni-specific fundraising tied to hall of fame establishment. Many schools find that athletic hall of fame projects generate enthusiastic donor support when positioned as permanent recognition celebrating the programs donors care deeply about.

Content Development Strategies
Comprehensive inductee documentation requires systematic content development processes.
Historical Research and Documentation: Schools with long athletic traditions face substantial historical documentation challenges. Limited records, incomplete statistics, and missing photos characterize many earlier eras. Effective historical research includes systematic review of yearbooks, school newspapers, and official records, outreach to alumni requesting photos and memorabilia, consultation with retired coaches and longtime athletic staff, local newspaper archive research for game coverage and achievement documentation, and engagement with athletic booster organizations maintaining informal records.
Rather than delaying launch until historical documentation is complete, many schools implement in phases—starting with well-documented recent achievements before systematically working backward through earlier decades.
Creating Compelling Inductee Profiles: Effective hall of fame content transcends bare statistics to tell achievement stories. Quality profiles include biographical information and athletic background, career highlights and statistical achievements, championship participation and significant victories, post-graduation athletic and professional success, personal reflections on athletic experience when available, and photos showing inductees during competition and careers. Written narratives should capture what made each inductee exceptional rather than simply listing accomplishments.
Multimedia Content Collection: Digital platforms enable rich multimedia that brings recognition to life. Schools should systematically collect game action photos and team pictures, highlight videos from key performances and championships, audio interviews with inductees or coaches, scanned historical documents and newspaper clippings, and video testimonials from teammates and coaches when possible. This multimedia content creates engagement impossible with text-based profiles alone.
Comprehensive approaches to showcasing athletic achievements digitally provide additional content development insights applicable to hall of fame implementation.
Managing Induction Ceremonies and Annual Processes
Beyond initial launch, sustainable halls of fame require annual cycles recognizing new classes while maintaining engagement with existing inductees.
Planning Effective Induction Ceremonies
Annual induction ceremonies serve multiple purposes simultaneously—formally recognizing new inductees, engaging alumni and current community members, generating fundraising and development opportunities, and creating traditions building institutional culture.
Event Format and Program Elements: Successful ceremonies typically include formal recognition of each inductee with brief remarks, video presentations highlighting achievements, opportunities for inductees to speak briefly, participation by current student-athletes and teams, athletic director and school administrator remarks, and social time enabling networking among inductees across generations.
Ceremony length should respect busy schedules—90 minutes to 2 hours typically accommodates meaningful recognition without losing audience attention. Some schools hold ceremonies in conjunction with athletic events creating built-in audiences, while others schedule standalone evening events.
Timing and Scheduling Considerations: Strategic timing maximizes attendance and impact. Common approaches include homecoming weekends creating natural alumni return occasions, dedicated athletic hall of fame weekends with full-day programming, major athletic event days (championship games, rivalry competitions), and spring ceremonies avoiding fall athletic schedule conflicts. Schools should survey alumni preferences and track attendance patterns to improve timing.
Physical Recognition Elements: Ceremonies typically include presentation of physical recognition items to inductees—plaques or framed certificates, commemorative gifts or school merchandise, personalized jerseys or similar athletic memorabilia, and professional photos capturing the moment. These tangible items provide lasting remembrance beyond the ceremony itself.
Live-Streaming and Recording: Recording ceremonies and making them available online extends reach to those unable to attend while creating permanent documentation. Simple live-streaming through school social media or YouTube enables remote viewing, while professional recording creates archive footage. Digital platforms can integrate ceremony videos directly into inductee profiles creating permanent records.
Maintaining Engagement Year-Round
Effective halls of fame remain active presences rather than static displays updated annually.
Featured Inductee Rotations: Digital displays enable regular content rotation keeping recognition fresh. Schools might feature different inductees monthly, highlight seasonal sports from current competition, showcase milestone anniversaries of historic achievements, and rotate between individual athletes, teams, and contributor recognitions. This regular change maintains interest and ensures all inductees receive featured attention periodically.
Alumni Networking and Communication: Hall of fame inductees represent highly engaged alumni populations. Schools can facilitate networking among inductees through online communities or social media groups, periodic reunion events beyond annual ceremonies, participation in mentorship programs connecting them with current student-athletes, and involvement in athletic program fundraising and development efforts. These ongoing relationships strengthen the mutual value of hall of fame recognition.
Integration with Athletic Program Culture: Current student-athletes benefit when hall of fame recognition is woven into program culture. Effective integration includes references during team meetings and practice sessions, featured inductee spotlights in program newsletters and social media, involvement of inductees in current team events when possible, and physical display placement ensuring daily visibility. When current athletes regularly encounter hall of fame recognition, it shapes program culture and provides aspirational models demonstrating achievement possibilities.
Research on software products for athletic administrators includes recognition management platforms that streamline ongoing hall of fame administration.

Addressing Common Challenges and Pitfalls
School administrators establishing halls of fame encounter predictable challenges that preparation can help navigate successfully.
Maintaining Selection Process Fairness
Hall of fame credibility depends on perceptions of fair, consistent selection processes.
Avoiding Recency Bias: Selection committees naturally remember recent athletes and teams more vividly than those from decades past. This recency bias can skew recognition disproportionately toward recent graduates unless actively countered. Strategies include establishing mandatory consideration of nominees from various eras, conducting systematic historical research identifying overlooked achievements, and implementing objective criteria that don’t inherently favor recent nominees.
Managing Political Pressure: School administrators often face pressure from influential alumni, donors, or community members advocating for specific nominees. Maintaining selection integrity requires clear, published criteria applied consistently, confidential deliberation processes preventing external influence, documentation justifying selections based on established standards, and willingness to decline inducting individuals who don’t meet criteria regardless of outside advocacy. Committee composition including members with institutional loyalty but relative independence helps resist inappropriate pressure.
Balancing Sport-Specific Recognition: Comprehensive athletic programs create natural tensions between major sports dominating recognition and smaller programs feeling undervalued. Schools must decide whether to establish equal quotas across sports, apply uniform achievement standards potentially resulting in unequal representation, or create sport-specific criteria acknowledging different competitive landscapes. No approach satisfies everyone, but transparent decision-making and clear rationale help stakeholders understand selection outcomes even when disappointed.
Preventing Stagnation and Maintaining Relevance
Halls of fame risk becoming outdated and ignored without sustained attention and regular updates.
Content Freshness and Regular Updates: Static recognition quickly loses impact as attention spans shorten and audiences expect dynamic content. Schools should establish routines for adding new inductee profiles immediately after selection, updating existing profiles with career developments and achievements, rotating featured content highlighting different achievements seasonally, and incorporating new multimedia as it becomes available. Digital platforms make these updates straightforward through cloud-based management, while physical displays require more substantial effort for additions.
Technology Refresh and Platform Evolution: Digital recognition systems require periodic technology refresh as hardware ages and software platforms evolve. Schools should budget for display replacement every 7-10 years, software platform updates or migrations to improved systems, and network infrastructure improvements supporting evolving technology. Working with providers committed to ongoing platform development ensures recognition systems benefit from technological improvements rather than becoming obsolete.
Responding to Changing Values and Priorities: Institutional values and societal priorities evolve over decades. Hall of fame selection criteria, recognition language, and emphasized achievements may require revision over time to reflect contemporary values while respecting historical context. Schools should periodically review whether current criteria and processes remain appropriate, incorporate stakeholder feedback about recognition priorities, and make thoughtful adjustments when warranted while maintaining core standards.
Managing Controversies and Difficult Decisions
Athletic recognition occasionally generates controversy requiring administrative attention.
Handling Inductee Misconduct: School administrators must establish policies addressing what happens when inductees’ subsequent conduct contradicts institutional values. Some schools remove individuals from halls of fame following serious criminal convictions or ethical violations, while others maintain that recognition honored achievements at specific times regardless of subsequent actions. Clear policies established proactively prevent reactive decision-making during crises.
Addressing Historical Inequities: Many schools recognize that historical halls of fame reflect biases of their eras—underrepresentation of women’s athletics, minority athletes, or certain sports. Administrators should honestly assess whether historical selection reflected genuine achievement differences or systemic bias, conduct targeted research identifying overlooked achievements from underrepresented populations, and potentially establish special recognition categories or expedited processes rectifying historical inequities. This work demonstrates institutional commitment to equity while strengthening hall of fame comprehensiveness.
Posthumous Recognition Considerations: Nearly all schools include provisions for posthumous induction honoring individuals who died before induction or before meeting standard eligibility criteria. Policies should address when posthumous induction is appropriate, whether standard criteria apply or exceptions are warranted, and how families participate in recognition. Thoughtful posthumous recognition honors deserving individuals while maintaining selection process integrity.
Understanding common challenges in implementing digital recognition displays helps administrators avoid predictable pitfalls during planning and execution.
Measuring Success and Demonstrating Value
School administrators must justify hall of fame investments through demonstrated value to multiple stakeholder groups.
Quantitative Success Metrics
Measurable indicators reveal whether halls of fame achieve intended objectives.
Engagement and Utilization Metrics: Digital platforms provide analytics documenting actual usage including visitor interaction frequency and duration, most-viewed profiles and content, search terms revealing visitor interests, and peak usage times. Physical display observation and informal visitor counting provide rougher engagement estimates. Growing engagement over time indicates successful implementation, while declining interest suggests needed adjustments.
Alumni Participation and Connection: Hall of fame effectiveness supporting alumni engagement appears in ceremony attendance trends, inductee response rates to outreach and update requests, hall of fame references in alumni communications and social media, participation in alumni programs and networking, and correlation with broader alumni giving and engagement metrics. Strong alumni participation indicates the hall of fame successfully maintains connections that support institutional advancement.
Institutional Visibility and Recognition: Athletic recognition contributes to broader school reputation through media coverage referencing hall of fame inductees, prospective family feedback during recruitment, social media reach and engagement with recognition content, and awards or recognition from athletic associations and peer institutions. Consistent positive mentions suggest the hall of fame enhances institutional visibility.
Qualitative Impact Assessment
Beyond quantitative metrics, stakeholder perspectives reveal whether halls of fame deliver meaningful value.
Student-Athlete Perspectives: Current student-athletes can articulate whether hall of fame recognition motivates them and influences program culture. Surveys, focus groups, and informal conversations reveal whether athletes see hall of fame inductees as role models, understand achievement pathways to recognition, feel pride in program tradition and excellence, and value opportunities to meet and learn from inductees.
Alumni and Inductee Feedback: Inducted individuals provide crucial perspectives on recognition meaningfulness. Schools should regularly gather feedback about ceremony experience and recognition quality, ongoing engagement and connection maintained through hall of fame, pride in recognition and willingness to participate in school activities, and suggestions for improving processes or recognition elements.
Administrative Assessment: School leaders and athletic administrators should evaluate whether hall of fame implementation aligns with initial objectives, requires sustainable administrative effort, generates positive community response and support, supports broader institutional advancement goals, and justifies ongoing investment compared to alternative resource uses.
Comprehensive approaches to measuring digital hall of fame success provide frameworks applicable to both traditional and contemporary recognition programs.

Future Trends in Athletic Recognition
Athletic halls of fame continue evolving as technology advances and institutional priorities shift.
Emerging Recognition Technologies
Contemporary recognition platforms increasingly incorporate advanced capabilities that enhance engagement and accessibility.
Augmented Reality and Mobile Integration: Some schools are experimenting with augmented reality applications that overlay digital content on physical displays when viewed through mobile devices. Visitors scanning QR codes near physical plaques access rich multimedia profiles, video highlights, and interactive content expanding recognition beyond physical display constraints. This blended approach combines traditional permanence with digital storytelling advantages.
Personalized Recognition Experiences: Advanced digital platforms enable personalized content tailored to individual visitors. Systems might highlight inductees from visitors’ graduation classes, emphasize sports matching visitor interests, or recommend related content based on browsing patterns. This personalization increases engagement by making large recognition databases feel personally relevant rather than overwhelming.
Social and Collaborative Features: Some platforms incorporate social elements allowing visitors to comment on profiles, share favorite athletes or moments, and contribute photos or memories. Alumni can tag themselves or teammates in photos, and inductees can update their own profiles with career developments. These collaborative features transform recognition from one-way institutional communication into dynamic community engagement.
Evolving Recognition Priorities
Contemporary values influence what schools choose to honor through athletic halls of fame.
Holistic Student-Athlete Recognition: Many schools are expanding recognition beyond pure athletic achievement to honor student-athletes demonstrating academic excellence, community service, leadership, and character alongside athletic success. This holistic approach recognizes that schools value multidimensional excellence rather than athletic performance in isolation.
Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Emphasis: Schools increasingly scrutinize whether recognition systems equitably honor achievements across all demographic groups and sports programs. Proactive efforts include conducting equity audits of historical inductees, targeted research identifying underrecognized achievements from women’s athletics and minority populations, establishing criteria ensuring equitable representation, and creating recognition categories celebrating achievements beyond traditional competitive success.
Community and Team Culture Recognition: Some schools are establishing recognition beyond individual and team achievement to honor contributions to athletic community and culture. Categories might include distinguished service to athletics, exemplary team culture building, exceptional sportsmanship, or sustained program support. This expanded scope acknowledges that athletic excellence requires contributions beyond championship performance.
Taking the First Steps Toward Establishing Your Athletic Hall of Fame
For school administrators ready to establish or enhance athletic recognition programs, systematic planning creates foundations for long-term success.
Conducting Needs Assessment
Begin with honest evaluation of current athletic recognition and clear articulation of what improvements should accomplish.
Current State Analysis: Document existing recognition through physical displays in athletic facilities, informal recognition practices, historical archives and documentation quality, stakeholder satisfaction with current recognition, and administrative resources currently dedicated to recognition. This baseline assessment clarifies specific problems that new or enhanced halls of fame should address.
Stakeholder Input: Gather perspectives from multiple stakeholder groups including current student-athletes and coaches, athletic administrators and staff, alumni and former athletes, parents and athletic supporters, and school leadership and board members. Understanding diverse priorities helps ensure hall of fame design satisfies multiple constituencies while avoiding approaches that please no one.
Institutional Objective Alignment: Clarify how athletic hall of fame implementation supports broader institutional goals including student development and school culture, alumni engagement and institutional advancement, community relations and school reputation, and athletic program excellence and competitive success. Explicit connections between recognition programs and strategic institutional objectives help secure necessary support and resources.
Building Implementation Support
Successful implementation requires coalition building and resource commitment.
Identifying Champions: Athletic halls of fame need dedicated advocates driving implementation including athletic directors or senior athletic administrators, engaged alumni willing to lead fundraising, school administrators supporting resource allocation, and board members or community leaders lending credibility. These champions sustain momentum when obstacles arise during extended implementation timelines.
Securing Resources: Early resource commitment prevents stalled projects. Work to identify initial funding through operating budgets, capital campaigns, donations, or phased implementation, allocate adequate staff time for planning and content development, and commit to ongoing support for annual induction processes and maintenance. Underfunded or understaffed halls of fame struggle regardless of how well they’re designed initially.
Choosing Implementation Partners: School administrators should evaluate whether internal resources can handle implementation or external support would prove valuable. Decisions include content development (internal staff, professional services, or hybrid approach), physical display design and installation (internal facilities, contracted vendors), digital platforms (building custom, licensing existing, or turnkey solutions), and ongoing management and support (internal capacity, contracted services). Purpose-built platforms like Rocket Alumni Solutions offer turnkey implementation specifically designed for school athletic recognition needs.
Pilot Testing and Phased Implementation
Rather than attempting comprehensive implementation immediately, consider phased approaches reducing risk.
Starting with Core Recognition: Initial phases might include establishing selection criteria and committee structure, recognizing an inaugural induction class through existing budget and resources, implementing basic physical or digital display in a single high-traffic location, conducting initial induction ceremony creating momentum, and demonstrating value before seeking expanded resources. This incremental approach proves feasibility while building support for future expansion.
Learning and Iterating: Treat initial implementation as learning opportunity—gather feedback from all stakeholder groups, assess what worked well and what requires adjustment, refine processes and systems based on experience, and document lessons guiding future development. Early iterations rarely achieve perfection, but systematic learning enables continuous improvement.
Planning Future Expansion: After successful core implementation, expand systematically including additional display locations and recognition categories, enhanced digital capabilities and web access, historical research adding earlier eras, expanded annual programming and alumni engagement, and integration with broader institutional advancement efforts. Phased expansion allows sustainable growth as resources permit while maintaining quality throughout.
Conclusion: Creating Lasting Legacy Through Athletic Recognition
Athletic halls of fame represent significant institutional investments requiring substantial planning, implementation effort, and ongoing management. When executed thoughtfully, they deliver remarkable value that compounds over years and decades—strengthening school culture, preserving institutional history, engaging alumni, and celebrating the athletes and coaches whose dedication and excellence define athletic programs.
School administrators should approach hall of fame establishment systematically through clear articulation of institutional objectives and recognition scope, thoughtful development of selection criteria and governance structures, strategic choices about physical and digital recognition approaches, realistic implementation planning with adequate resources, and sustained commitment to annual processes and ongoing management.
The most successful athletic halls of fame share common characteristics regardless of institutional size or resources. They honor diverse achievements and populations fairly, maintain consistent selection processes building credibility, evolve continuously rather than remaining static, engage stakeholders actively through ceremonies and ongoing communication, and align with broader institutional values and strategic goals.
Contemporary recognition technologies enable schools to honor athletic achievement more comprehensively than ever before. Digital platforms eliminate space constraints that forced previous generations to make painful choices about which accomplishments warranted recognition. Interactive experiences engage visitors actively rather than passive glancing at plaques. Web accessibility extends recognition reach beyond campus boundaries to alumni worldwide. Yet technology merely enables recognition—the substance lies in the achievements honored and the institutional values athletic halls of fame express.
Whether your school is establishing its first formal recognition program or modernizing traditions spanning decades, the principles remain constant: honor achievement authentically, implement sustainable processes, engage stakeholders meaningfully, and create recognition systems serving your institution’s unique needs and values. The athletes, coaches, and teams who invest themselves in your athletic programs deserve recognition that matches their dedication—thoughtful planning ensures your athletic hall of fame delivers that honor for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long should the waiting period be between graduation and hall of fame eligibility?
Most schools establish waiting periods between 5-25 years, with 10 years representing the most common standard. Shorter waiting periods (5-7 years) work well when schools emphasize high school achievement primarily and want to recognize athletes while memories remain fresh. Longer periods (15-25 years) suit schools heavily weighting post-graduation success and wanting substantial career perspective before recognition. The optimal period depends on your selection criteria emphasis—if you prioritize collegiate or professional achievement, longer periods prove necessary. If high school accomplishments alone suffice, shorter periods maintain connection with inductees while they’re still relatively young. Many schools adopt 10-year standards as reasonable compromises enabling some post-graduation achievement assessment while maintaining manageable contact with potential inductees.
Should our hall of fame prioritize individual athletes or team accomplishments?
Comprehensive halls of fame honor both dimensions through separate categories. Individual recognition celebrates standout athletes who achieved exceptional personal excellence through career statistics, championship performances, and post-graduation success. Team recognition honors squads that achieved collective excellence through championships, historic seasons, or cultural significance. Most effective halls of fame maintain both categories since athletic excellence manifests individually and collectively. The relative emphasis depends on institutional values—some schools celebrate individual achievement prominently, while others emphasize team culture and collective accomplishment. Consider including both categories with clear criteria for each rather than forcing choice between recognition dimensions that both deserve acknowledgment.
How can small schools with limited budgets establish meaningful halls of fame?
Effective recognition requires commitment more than large budgets. Resource-limited schools can implement meaningful programs through phased implementation starting with core elements and expanding over time, simple physical recognition using quality plaques or displays rather than expensive custom installations, cost-effective digital platforms with monthly subscription pricing avoiding large upfront hardware investments, volunteer committee service and alumni contributions reducing professional service costs, and donated administrative time rather than dedicated staff positions. Begin with basic recognition honoring truly exceptional achievements, demonstrate value to stakeholders, then expand as resources grow. Even modest recognition programs authentically celebrating achievement deliver tremendous value compared to no formal recognition. Quality matters more than sophistication—simple programs implemented well surpass elaborate systems executed poorly.
What if our school has limited historical records for potential inductees from early eras?
Incomplete historical documentation challenges many schools with long traditions. Practical approaches include implementing in phases by starting with well-documented recent decades before systematically working backward through history, conducting targeted historical research through yearbook review, newspaper archives, retired coach interviews, and alumni outreach requesting photos and information, accepting that some historical information will remain incomplete and documenting what can be verified rather than waiting for perfect records, establishing criteria acknowledging documentation limitations for early eras while maintaining standards for recent nominees, and engaging alumni volunteers often passionate about historical research and willing to contribute time schools lack. Rather than delaying hall of fame establishment until comprehensive historical documentation exists, launch with available information and continuously expand historical recognition as research uncovers additional achievements.
How do we handle controversial cases where potential inductees’ post-graduation conduct conflicts with school values?
Schools should establish clear policies addressing inductee misconduct before controversies arise. Common approaches include maintaining that recognition honored achievements at specific times regardless of subsequent behavior, removing individuals from active recognition following serious criminal convictions or conduct fundamentally contradicting institutional values, creating emeritus or archived status acknowledging recognition without active display, and case-by-case evaluation by athletic director and school leadership for situations falling between clear thresholds. Document policies clearly to enable consistent application preventing reactive decision-making during crises. Consider whether conduct directly relates to athletic achievement being honored or represents separate post-graduation behavior. Most schools distinguish between serious crimes or profound ethical violations warranting removal versus personal struggles or mistakes warranting compassion while maintaining recognition. Whatever approach you adopt, transparency about policies and decision-making processes maintains community confidence even when specific decisions prove controversial.
Should we include coaching and contributor recognition or focus exclusively on athletes and teams?
Many schools expand halls of fame beyond athletes and teams to honor coaches who shaped programs, administrators who supported athletic excellence, boosters and donors enabling program success, and other contributors who made lasting impacts. This inclusive approach acknowledges that athletic excellence depends on contributions beyond on-field performance. However, it also complicates selection by requiring separate categories with different criteria and potentially diluting focus on athletic achievement. Schools must decide whether their hall of fame should comprehensively honor all athletic program contributors or maintain narrow focus on competitive achievement. If including non-athlete categories, establish clear separate criteria and selection processes ensuring consistent standards. Many schools implement this recognition through dedicated sections or separate categories preventing contributor recognition from overwhelming athlete achievement.
What role should current student-athletes play in hall of fame governance and selection?
Some schools include student-athlete representatives on selection committees to incorporate current athlete perspectives and demonstrate that recognition serves contemporary program culture. Student involvement brings valuable current athlete viewpoints, creates connection between inductees and current teams, and provides leadership development opportunities. However, student participation also raises questions about whether athletes possess sufficient institutional perspective for multi-decade selection decisions, can maintain confidentiality during deliberations, and have time for meaningful participation amid academic and athletic demands. If including students, clearly define their roles—perhaps advisory rather than voting positions, or participation in specific selection aspects rather than full process. Alternative approaches involve student-athletes in ceremonies and programming without formal selection role, ensuring current athletes engage with hall of fame recognition without selection committee membership.
How can we ensure equitable recognition across all sports programs?
Athletic programs with diverse sports must balance equal treatment with genuine achievement differences across sports with varying competitive landscapes. Strategies include applying uniform achievement thresholds equally across sports (conference championships, all-state recognition, etc.) potentially resulting in unequal representation but consistent standards, establishing sport-specific criteria acknowledging different competitive contexts and achievement measures, setting quotas ensuring minimum representation from various sports, creating separate induction classes for major and minor sports, and conducting equity audits reviewing whether historical inductees reflect program diversity. No approach satisfies everyone—equal standards may disadvantage sports with elite competition, while sport-specific criteria can appear as double standards. Transparency about approach and rationale helps stakeholders understand selection outcomes. Regular review ensures recognition patterns reflect genuine achievement rather than inadvertent bias toward certain programs.
Ready to transform how your school celebrates athletic excellence? Book a demo to explore how purpose-built recognition platforms can help your institution establish an athletic hall of fame that serves your unique needs while honoring the athletes and coaches who define your program’s excellence.